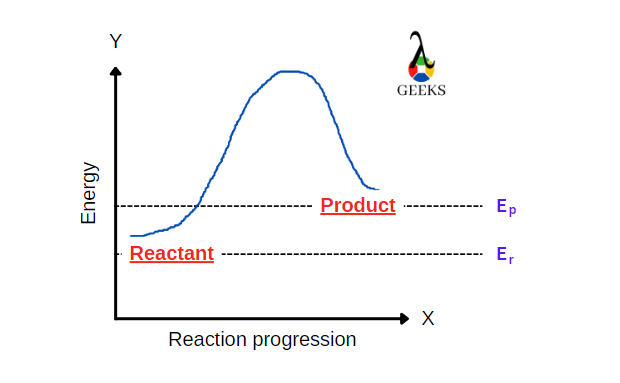
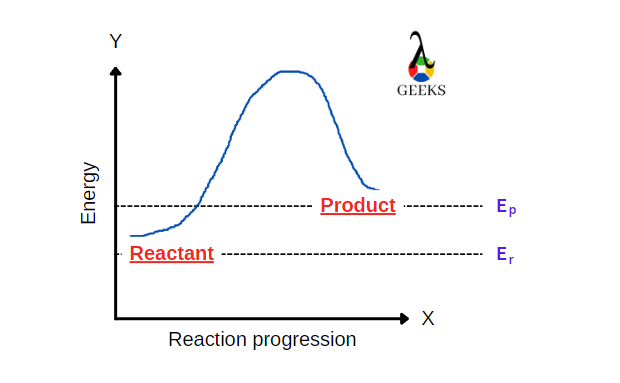
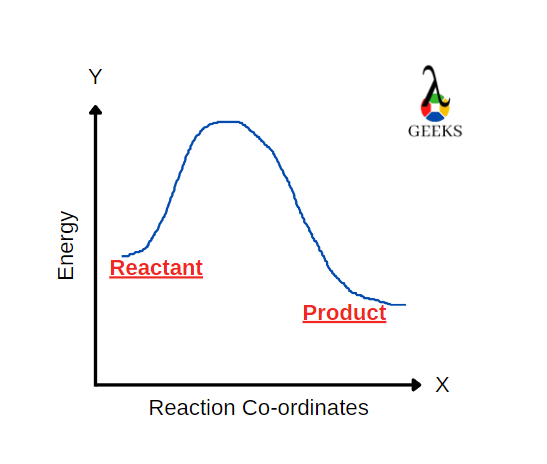
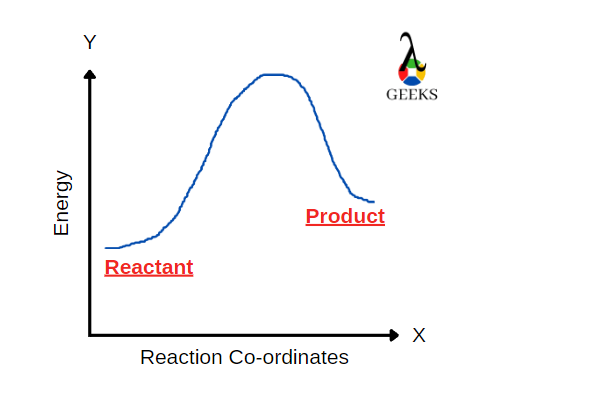
15 Facts on HBr + FeCl3: What, How To Balance & FAQs
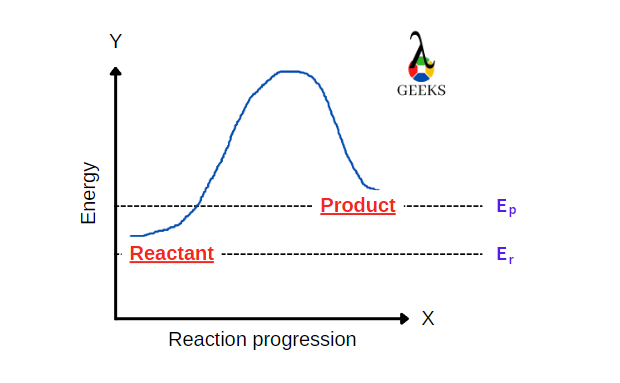
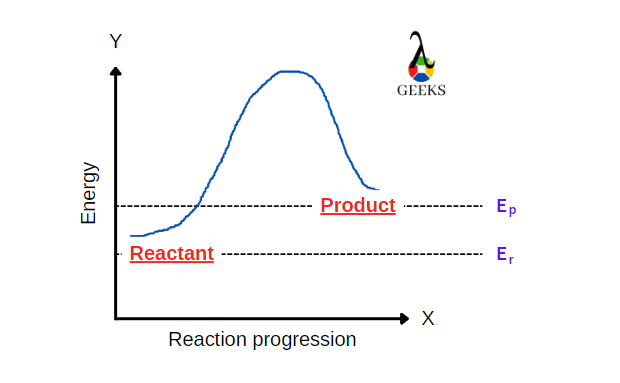
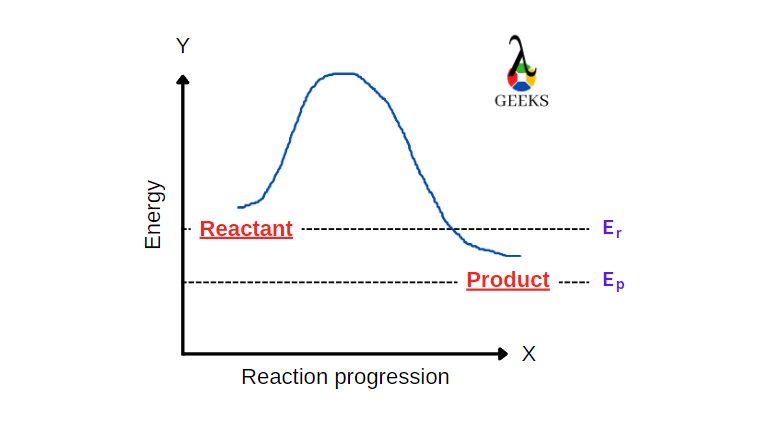
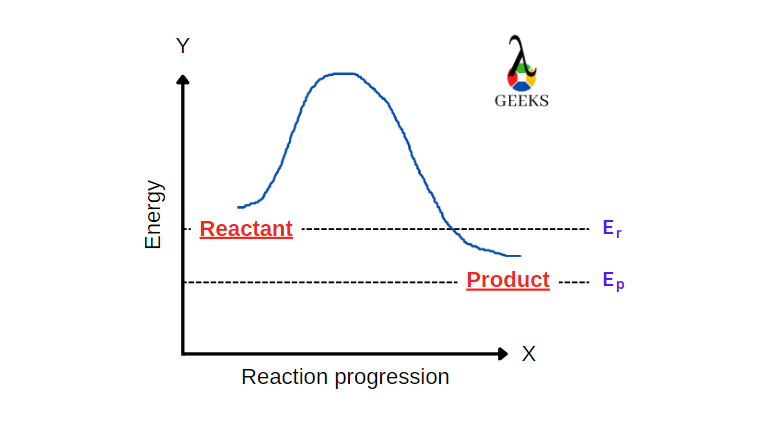
FeCl3 is an inorganic compound having a +3-oxidation state. HBr is a strong acid. Let us see how these two react with each other through this article. Ferric chloride (FeCl3), also called iron (III) chloride, is an anhydrous compound. Its colour changes as the viewing angle is changed. HBr is a strong acidic compound generally … Read more