Artificial ecosystems are manmade habitats consisting of biotic and abiotic components that have been put together.
When humans put together a system that has both biotic and abiotic components but required human intervention to function normally.
Artificial Ecosystem examples include:
- Crop fields
- Aquariums
- Gardens
- Dams
- Zoos
- Terrariums
- Greenhouse
- Fish farms
- Artificial wetlands
- Managed forestry
- Parks
- Hydroponics
Next, we will discuss these examples in detail.
Discussion about the Artificial Ecosystem Examples:
Crop fields
Made for the purpose of agriculture for growing food crops, vegetables and edible plants crops fields are probably the most important among the artificial ecosystem examples listed. Earlier most fields grew only one type of crop, but recently due to an increase in soil erosion farmers have been practising crop rotation.

Image: Wikipedia
Aquariums
The most commonly seen in homes among aqua culturists or ornamentally aquariums are also artificial ecosystem examples created by humans. They can be saltwater, freshwater, or brackish water ecosystems created inside glass tanks of various sizes. They are provided with filters and host everything from plants, fishes, corals and anemones to even crustaceans and mollusks.

Image: Wikipedia
Gardens
A Garden is an artificial environment because it was produced by humans rather than occurring naturally. It has biotic and abiotic components, both of which are controlled by people. They are one of the artificial ecosystem examples that are made by people simply in their balcony, terrace or backyard. Gardens can also be for touring purposes solely exhibiting rare flowers or plants. A home garden can feature ornamentals to herbal and edible plants.
Dams
Dams are another of man’s creations among the artificial ecosystem examples. Built over rivers, they are used to store water during the drier seasons and also aid in the production of hydroelectricity. To keep the stagnant water clean, plenty of fish and organisms are kept in these dams that live under the care of humans.
Zoos
Zoos or zoological parks are another commonly known artificial ecosystem examples that are listed above. They are made and maintained by humans to keep animals and birds in captive conditions that are similar to their habitats.
Terrariums
A terrarium is a glass container that contains soil and plants and may be opened to access the plants within for upkeep. Among the artificial ecosystem examples mentioned in the list, terrariums are on a rise in popularity courtesy of plant enthusiasts and botanists.
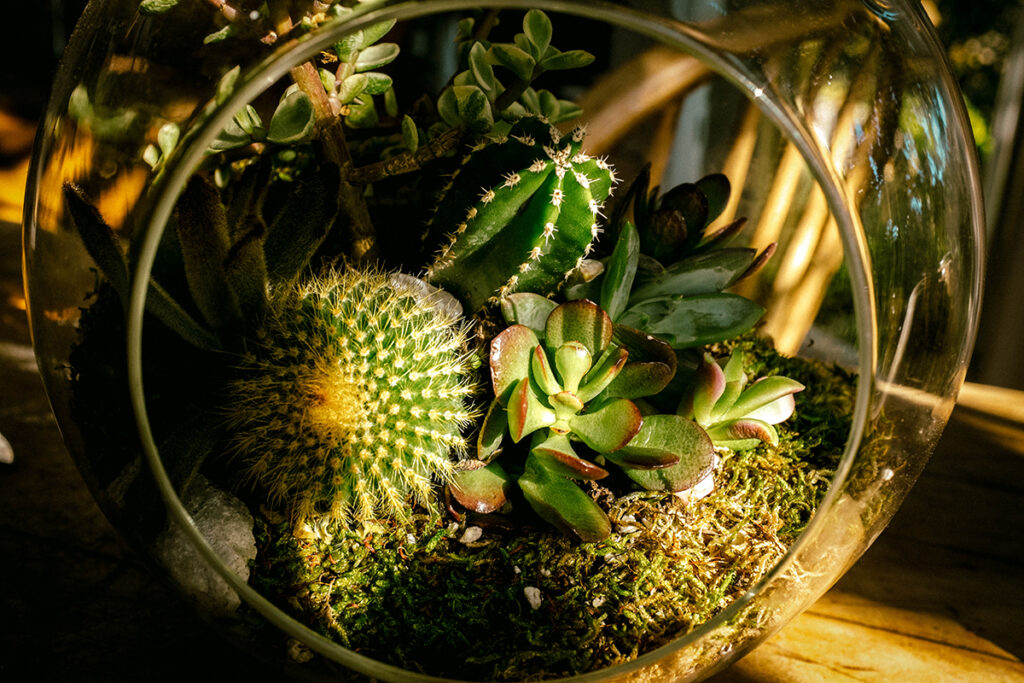

Image: Wikipedia
Greenhouse
A greenhouse is usually referred to a glass house used for growing plants in consistent conditions where temperature and humidity and maintained. Similar to that in the atmosphere, the glass walls of the greenhouse allow heat to enter but prevent it from escaping. This maintains a constant temperature, along with added humidity making greenhouses perfect for growing tropical plants and crops in temperate or colder climates.

Fish farms
Fish farms are a rising industry among the artificial ecosystem examples. These farms are similar to any farm that grows fish specifically. They can be aquarium fish, those for consumption or bait or feeders. These are usually done in small ponds dug out by the farmers and maintained to grow various fish species.
Artificial wetlands
Artificial wetlands were created for various purposes. Raw sewage, stormwater, agricultural, and industrial discharges can all be chemically cleaned in constructed wetlands. Constructed wetlands catch runoff, reduce nutrient levels, and provide diverse wildlife habitats, much like natural wetlands.
Managed forestry
Manages forests are of great importance among the artificial ecosystem examples in the field of conservation. These are forest areas created by humans, to imitate the natural forest cover that would grow in that area. These trees and vegetation and grown and transplanted, thereby helping to conserve plant species that are nearly on the brink of extinction due to deforestation and logging.
Parks
Parks are considered artificial ecosystems as they don’t sustain themselves. These can include anything from tourist parks to various national parks. Most of them contain organisms that are brought from their native habitat. They need to be fed and cared for to assure their survival. Tourist parks must be cared for by humans as well. Hence they are among the artificial ecosystem examples
Hydroponics
Hydroponics or aquaculture is probably the least known among the artificial ecosystem examples mentioned in the list. This method become more convenient as the amount of tillable land was not enough to grow crops. In this method farmers grow crops in water that is supplied with nutrients and inert gases, thereby reducing the need for pesticides or fertilizers and also decreasing carbon footprint.
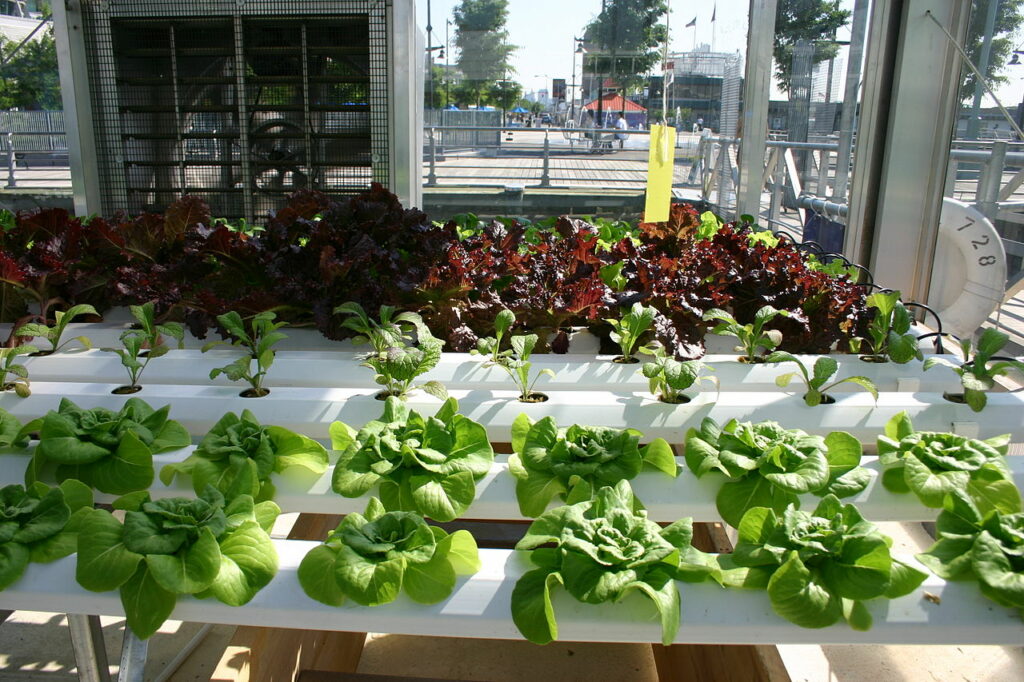

Image: Wikipedia
What is an artificial ecosystem?
Artificial ecosystems are man-made ecosystems that cannot sustain themselves.
Thes ecosystems including biotic and abiotic factors are created by humans for specific purposes. Without them, these ecosystems can not survive.
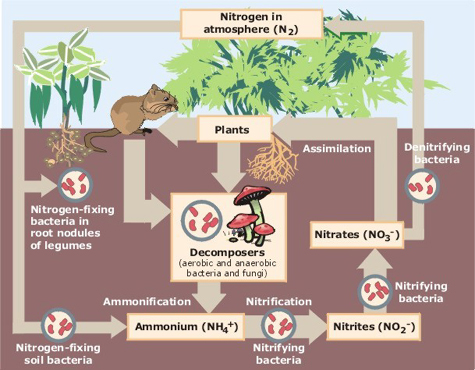
Image: Wikipedia
In these ecosystems, the setup, organisms and energy flow are all regulated by humans. These include aquariums, crop fields, terrariums and many more.
Artificial ecosystem characteristics:
Characteristics of an artificial ecosystem include:
- Artificial ecosystems are entirely man-made and require humans to take care of them.
- Most of them have very little genetic diversity in terms of the organisms-both flora and fauna.
- Artificial ecosystems cannot sustain the evolution of the organism residing in them.
- Both food chains and nutrient cycles are very short and usually incomplete to boot.
Components of an artificial ecosystem:
Like natural ecosystems, artificial ones are also composed of two main parts- biotic and abiotic components.
Biotic components: Biotic components include the flora and fauna that are part of the ecosystem. But unlike natural ecosystems, humans are always [art of the biotic components of the artificial ecosystems.
Abiotic components: These include the non-living factors including the soil, rocks, physical terrain, sunlight, gases and nutrients. Though these seem minimal they are responsible for the flow of energy, nutrients and food in the ecosystem.
Artificial ecosystem structure:
The artificial ecosystem example structures are made up of 3 parts-the biotic factors, the abiotic factors and humans.
Biotic factors include 3 main components-producers, consumers and decomposers. This is also the direction of energy flow in the ecosystem.
The abiotic factors include the soil, sunlight, nutrients, gases and everything that is non-living. These form the base ground or habitat of the ecosystem sustaining the organisms living in them.
Lastly, come the humans that actually construct these ecosystems for their own use. They are necessarily involved in the care of sustenance of these ecosystems otherwise, they will be unable to survive.
Features of an artificial ecosystem:
Features of artificial ecosystems include:
- Artificial ecosystems are made by humans for productivity, conservation or entertainment.
- Since humans create these ecosystems the organism count and variety are regulated, Hence the genetic diversity of these ecosystems is extremely low.
- This also means there is no evolution due to the absence of the natural inducing factors.
- Most times due to the absence of appropriate decomposers and bacteria the nutrient cycles and food chains are cut short. Hence they must be done manually.
Functions of an artificial ecosystem:
- Artificial ecosystems are goal oriented. They are planned and built for specific purposes.
- Some are made for aesthetic or entertainment purposes like gardens and aquariums.
- Artificial ecosystem examples like crop fields and dams are made for the production of food and irrigation. Dams also allow us to supply water to arid regions when required and also to produce hydroelectricity.
- Zoos and forests allow us to conserve flora and fauna species that are endangered, thereby helping more people to know and understand them.
- Lastly, wetlands were created to make sure that wastes could be chemically cleaned before they are released, thereby keeping the environment cleaner.
Also Read:
- Desert biome examples 2
- Do animal cells have a central vacuole
- Box jellyfish types characteristics
- Does the krebs cycle produce water
- Are ribosomes found in nucleus
- Dispersive dna replication
- Animal cell structure
- Do plant cells have cytoskeleton
- Photoautotrophs examples
- Cell membrane structure in animal cell

I am Trisha Dey, a postgraduate in Bioinformatics. I pursued my graduate degree in Biochemistry. I love reading .I also have a passion for learning new languages.
Let’s connect through linked in: