Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) are organic aromatic nitrogenous compound known as nucleobases, present in nucleic acids of cells. Here we are going for comparative analysis of Adenine vs thymine.
Adenine vs Thymine
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T), both the nitrogenous chemical compounds exhibit some similarities as well as differences between them. Let’s have a closer look at adenine vs thymine comparison.
| Characteristics | Adenine (A) | Thymine (T) |
| Definition | Adenine is one of the five nitrogenous bases of cells mostly used as a nucleic acid synthetic unit and energy source of cells. | Thymine is one of the five nitrogenous bases of cells, mostly used as DNA synthetic unit and also have some activities as signal transduction molecule |
| Type of nitrogenous base | Purine base | Pyrimidine base |
| Functional groups of nucleobases | It has an amine group (-NH2) on C-6 position in its aromatic ring. | It has two keto groups at C2 and C4 positions and CH3 group at C5 position in its ring |
| Base pairing | Thymine and uracil | Adenine |
| Formula | C5H5N5 | C5H6N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 135.13 g/mol | 126.115 g·mol−1 |
| Solubility | 0.103 g/100 mL | 3.82 g/L |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 | 1.223 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 360 to 365 °C | 316 to 317 °C |
| Nucleoside formation | Adenosine | Thymidine |
| Nucleotides formation | AMP, ADP, ATP, cATP, NAD, FAD,. Etc. | TMP, TDP, TTP, etc. |
| Presence in nucleic acids | DNA and RNA | DNA |
| Hydrogen bond formation | Hydrogenous double bonds | Hydrogenous double bonds |
| Functions in nucleic acids | As Nucleotide monomers construct whole polymeric nucleic acids strands | As monomeric units construct polymeric DNA strands. |
| Other functions | Plays a major role in cellular respiration, serves as an energy source and transfers chemical energy to cells. | Involved In cellular energy transfer activities. |
| Synonyms | 6-Aminopurine | 5-Methyluracil |
By demonstrating comparative analysis of adenine Vs thymine we get some following statements mentioned below.

Adenine (A) structure from Wikimedia Commons
Definition
- Adenine: Adenine is a nitrogenous compound, preferably known as a nucleobase. As a nucleotide subunit it helps in the nucleic acid construction as well as being used as an energy source of cells.
- Thymine: Thymine is also a nitrogenous compound preferably known as nucleobase. As nucleotides it influences DNA synthesis process as well as helps in signal transduction procedure of cell.
Types of nitrogenous base
- Adenine: Adenine is a purine base, meaning it has a pyrimidine ring and an imidazole ring in its structure. Consisting of two two hydrogen-carbon rings and four nitrogen atoms in it.
- Thymine: Thymine is a pyrimidine base, meaning it consists of one hydrogen-carbon ring and two nitrogen atoms in its structure.
Functional groups
- Adenine: It has an amine group (-NH2) on C-6 position in its ring.
- Thymine: Two keto groups at C2 and C4 positions and CH3 group at C5 position is present in the aromaticits ring of Thymine base.
Base pairing
- Adenine: Adenine makes a complementary base pair with pyrimidine base uracil and Thymine.
- Thymine: Thymine makes complementary base pairs with purine base adenine only.
Chemical Formula
- Adenine: The chemical formula of adenine is C5H5N5
- Thymine: The chemical formula of Thymine is C5H6N2O2
Molar mass
- Adenine: The molar mass or molecular weight of adenine is 135.13 g/mol.
- Thymine: The molar mass of Thymine is 126.115 g·mol−1.
Solubility
- Adenine: The solubility of adenine in water is 0.103 g/100 mL.
- Thymine: The solubility of Thymine in water is 3.82 g/L.
Density
- Adenine: Adenine composed of a molecular density of 1.6 g/cm3.
- Thymine: Thymine composed of a molecular density of 1.223 g cm−3.
Melting point
- Adenine: The melting point of adenine is 360 to 365 °C
- Thymine: The Thymine has melting point of 316 to 317 °C
Nucleoside formation
- Adenine: Nucleoside formed by adenine is called Adenosine.
- Thymine: Nucleoside formed by Thymine is called Thymidine.
Nucleotide formation
- Adenine: Adenine forms Nucleotides like AMP (Adenosine monophosphate), ADP (Adenosine diphosphate), ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), FAD, etc.
- Thymine: Thymine forms Nucleotides like TTP (Thymidine triphosphate), TDP (Thymidine diphosphate), TMP (Thymidine monophosphate), etc.
Presence in nucleic acids
- Adenine : Adenine is present in both DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic acid) strands.
- Thymine: Thymine is only present in DNA. In RNA Thymine is replaced by Uracil (methylated version of thymine).
Hydrogen bond formation
- Adenine: Adenine forms hydrogenous double bonds with Thymine during complementary base pairing process.
- Thymine: Thymine forms hydrogenous double bonds with adenine during complementary base pairing process.
Functions in nucleic acids
- Adenine: The main function of adenine as AMP is to participate in both the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) synthesis process. As another nucleotide, adenine serves as an energy source of the cell and takes part in chemical energy transfer activities within the cell.
- Thymine: The main function of thymine is to participate in the DNA synthesis process only.
Other functions
- Adenine: The role of adenine as nucleotides in cellular respiration process is immense. It releases chemical energy by breaking its own bonds and stimulates various cellular Metabolic activities.
- Thymine: Most of the activities of Thymine within the cell remain unknown till now. But there is some data, state the role of thymine as nucleotides in cellular signal transduction pathways.
Synonyms
- Adenine: Adenine is also known as 6-Aminopurine.
- Thymine: Thymine is also known as 5-Methyluracil.
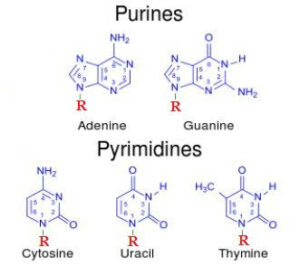
Nucleobases from Wikimedia Commons
Are adenine and thymine equal?
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) both are nucleobases, having some similarities and differences between them.
Adenine (A) and thymine (T) are not equal. There are several aspects by which they differ from each other. They are different kinds of nitrogenous base, adenine is a purine base whereas Thymine (T) is a pyrimidine base. The only similarities is they both are nucleobases (DNA), form complementary hydrogen double bonds between them.
Thymine (T) Structure from Wikimedia Commons
Are adenine and thymine complementary?
In DNA double helix the purine base adenine makes hydrogenous double bonds with pyrimidine base thymine.
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) are complementary to each other, They make hydrogenous double bonds between them in double helical structure of DNA.
As thymine is only present in DNA, adenine makes a complementary base pair with Thymine. In RNA Thymine (T) is not present, there is another nucleobase called uracil ( methylated version of thymine) present. That’s why adenine makes complementary basepair with uracil instead of Thymine in RNA structure.
To know more about Adenosine read our article on Adenosine nucleoside and nucleoside phosphoramidite | Overview of important aspects
As a whole we can say that adenine and Thymine both play a very crucial role in the cells of every living being. Here we compare Adenine vs Thymine, regarding every possible aspect between them. We also discuss some frequently asked questions regarding adenine vs thymine here.
Also Read:
- Is cell membrane an organelle
- Foliose lichen
- Ectoparasite examples
- Is fungi multicellular or unicellular
- Do proteins contain nitrogen
- Are bacteria microorganisms
- Abiotic component
- Nectar flower example
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum function
- Chloroplast growth

Hello, I am Piyali Das, pursuing my Post Graduation in Zoology from Calcutta University. I am very passionate on Academic Article writing. My aim is to explain complex things in simple way through my writings for the readers.