Content:
- What is a Filter Capacitor?
- Filter Capacitor Applications
- Filter Capacitor Circuit to Block DC and Pass AC
- DC filter capacitor calculation
- Filter capacitor in rectifier
- Filter capacitor for bridge rectifier
- Filter capacitor value calculation
- Low pass filter capacitor
- Bypass filter capacitor
- High frequency filter capacitor
- 3 terminal filter capacitor
- Harmonic filter capacitor
- Feedthrough filter capacitor
- Line filter capacitor
- Alternator filter capacitor
- Electrolytic filter capacitor
- EMI filter capacitor
- Filter capacitor design
- Filter capacitor amplifier
- Filter capacitor selection
- High voltage filter capacitor
- How to test filter capacitors
- SMD filter capacitor
- FAQ
What is a Filter Capacitor?
The capacitor’s impedance can be defined as a function of frequency as the capacitor is a reactive element, it is suitable for using it as an analog electronics filter.
A filter capacitor is a passive filter that consists of the passive element. Capacitor effects of any signal are frequency-dependent. This capacitor characteristic is used to design filters that can filter out a specific frequency range of signals as required.
Filter Capacitor Image

Working of Filter Capacitor
The capacitor is a reactive circuit element; its impedance and resistance will vary with the frequency signal passing through it.
The working of the filter-capacitor is based on the fundamental principle of capacitive reactance. The value of capacitive reactance changes with the frequency applied to the capacitor for lower frequency signal capacitor offers a higher resistance, and higher frequency signal capacitor provides low resistance. The capacitor is always trying to maintain the capacitance of the capacitor, so the capacitor will try to resist small current flow in the circuit creates capacitor impedance.
Filter Capacitor Replacement
The filter-capacitor can be replaced by Active Capacitor, Inductor filter circuit, FET circuits, etc.
Filter Capacitor Types
The filter-capacitor can be classified as following as basic types:
- Low Pass capacitor-filter
- High pass capacitor-filter
- Bandpass capacitor-filter
- Bandstop / Band Reject capacitor-filter
Filter Capacitor Formula
As we got to know, there is a relationship between the capacitor’s capacitive reactance (Xc) with the capacitor’s input signal frequency and capacitance.
Xc=1/ (2πfC)
So, the capacitive reactance (Xc) of the filter capacitor is inversely proportional to the frequency (f) of the signal.
Filter Capacitor Circuit
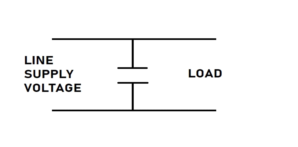
Filter Capacitor Applications
The filter-capacitor is used in various applications such as:
- Block the DC or AC component of the signal.
- Bypass DC or AC part of the signal.
- High voltage filter applications.
- To limit the frequency band.
- To remove unwanted noise from the circuit.
- To remove interference in circuitry.
- It is used to remove radio noise.
Filter Capacitor Circuit to Block DC and Pass AC
When a capacitor is connected to a series with the DC source in a completely discharged state, the current will flow until the capacitor is fully charged. At that stage, the capacitor voltage is equal to the applied voltage, and at that point, the capacitor is saturated now no current can flow through it, so the capacitor will behave as an open circuit. As we know, DC usually e is a constant value that is it has 0Hz frequency. As the capacitor offers high resistance towards low frequency, when the capacitor is connected in series with the DC source, it will block all the DC components from the signal and let AC pass through it.
DC filter capacitor calculation
As we know, the DC signal is usually a constant value, I.e. it has 0 Hz frequency.
Now Xc=1/ (2πcf) as f=0
Xc= ∞
So for the DC input, the capacitor provides infinite resistance, so I = V/Xc
As for the value of Xc= ∞, the value of I=0.
Filter Capacitor in Rectifier
The output of the rectifier is pulsating in nature which makes it suitable for DC supply in the electronic circuit, so the capacitor is connected across the load. The filter-capacitor helps to reduce the pulsating behaviour of the rectifier output.
In a half rectifier circuit, one ideal diode in the voltage source is an AC source with a sinusoidal signal in the positive half of the signal. The diode is in forward bias, so the diode is forward biased, and the capacitor got charged. In the negative half of the signal, the diode is in reverse bias, so no current flow through the diode, and the charged capacitor will discharge through the load resistor, that’s how the filter capacitor reduces the pulsating nature of the output of the rectifier.
To keep the output voltage from reducing too much during capacitor discharge, select a capacitor with a value so that time constant is much higher than the discharge interval. The filter-capacitor is connected in parallel with the load, so this filter circuit is also known as a shunt capacitor-filter. A capacitor is of the larger value connected across the load impedance.
Filter Capacitor for Bridge Rectifier
A bridge rectifier converts AC to DC by using four diodes same as the half-bridge rectifier. The output is pulsating in nature, so a capacitor is connected across the load to make a more pure DC form. The working is the same as the half rectifier filter circuit. The main advantage of a full-wave bridge rectifier is that its output is less pulsating behaviour than that of the half-wave rectifier, so the capacitor size in bridge filter circuit can be smaller than that of the half-wave filter-capacitor.
Filter Capacitor Value Calculation
How to calculate the filter capacitor value in power supply ?
The relation between the capacitance of Capacitor (C) with change (Q) and voltage (V) across the capacitor is defined as C=QV
The relation between the charge and the current is Q= IT
As we know that time is inversely proportional to the time T=1/f
For the above equations, we get C=I/(FV)
Low Pass Filter Capacitor
Low pass filter only passes the frequency signal, which is lower than that of the filter’s cutoff frequency. For this low pass filter, the relationship between capacitor resistance and the cutoff frequency is
fc = 1/(2πRC)
The resistor in the circuit is independent of the variation of the applied frequency, but the capacitor is sensitive to the changes in the input signal frequency.
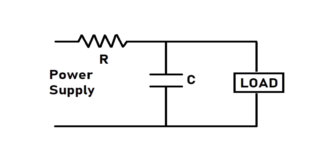
When the input signal frequency is low, the capacitor’s impedance is higher than the impedance of the resistor to the input voltage drop across the capacitor. Still, when the input signal frequency is high, then the capacitor’s impedance is lower than that of the resistor does more voltage drop across the resistor. Low frequency gets passed through, and high frequency gets blocked.
In a low pass filter, the frequencies below the cutoff frequency are known as passband, and the frequency above the cutoff frequency is known as stopband.
Low pass filters are used for
- To reduce electrical noise
- To limit the bandwidth of the signal
- To reduce interference
The gain of the low-pass filter in magnitude can be calculated by
Gain of filter = 20log (Vout/Vin)
Vout-> output voltage of the filter
Vin-> input voltage of the filter
Low Pass Filter Capacitor Type
It can be of two type:
- First Order Filter-Capacitor
- Second Order Filter-Capacitor
The low pass filter circuit above has only one reactive component capacitor, called one poll filter or first-order filter.
In the second-order of the low pass filter, it has to the reactive element that is capacitor in its circuit does design is helpful when the signal does not provide a wideband range between desired and undesired frequency components.
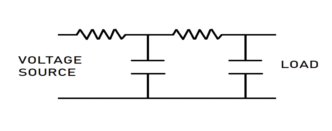
Bypass Filter Capacitor
Here one end of the capacitor is linked to the power supply, and the other is linked directly to the ground. This capacitor helps to reduce the effect of voltage spikes or any AC component from the power supply; it shorts the AC signal to the ground and reduces AC noise to produce a much clear DC signal.
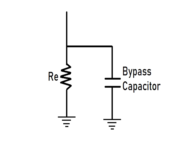
The capacitor in this circuit must have at least one-tenth of resistance as that of the resister Re. As we know, electric current chooses the path with a low resistance to following if it has multiple paths to choose from is; the capacitor offers great resistance to low frequency, so only the AC component of the signal passes through it. The DC component of the input signal will pass through the resistor Re.
High Frequency Filter Capacitor
A high pass filter is a filter that blocks low frequency and let pass through the higher frequency signal here. The frequency lower than the cutoff frequency is blocked, and the frequency higher than the cutoff frequency allowed to pass through this filter is also called a low cut filter. A capacitor is linked in series with the input supply; the resistor is linked in parallel.
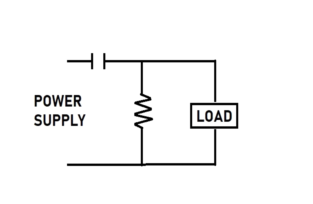
As we know, when the frequency of the input signal is low, the capacitor’s impedance is higher as the capacitor is in series with the power supply through which only a high-frequency signal can pass it.
The above circuit is a first-order high pass capacitor filter as there is only one reactive element in that circuit.
The second-order high pass capacitor-filter and the first order high pass capacitor filter are cascaded together to form a second-order high pass capacitor-filter.
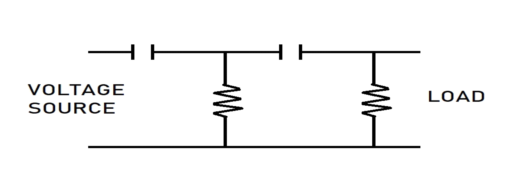
3 Terminal Filter Capacitor
Three terminal capacitor-filters consist of a three-terminal capacitor, which features a more negligible impedance than two terminal capacitors. Which allows it to reduce the impedance in the higher frequency band with lesser number of the reactive element it has great noise suppression effect these are used in power lines of circuit, smartphones, LED TV etc.
Harmonic Filter Capacitor
The harmonic filter can be designed of series or parallel reactive elements to block or shunt the harmonic currents. They can be available in several shapes and sizes. Still, when this capacitor is connected in parallel with the power supply, it helps reduce harmonic current and voltage in the circuitry.
The capacitor required in the harmonic filter must accept the given magnitude of various orders of harmonic current. A harmonic current can be a non-sine wave since the capacitor is very sensitive towards the high tension value. The capacitor is used in the harmonic filter in specific ranges depending upon the capacitor in use. A harmonic filter is formed by a capacitor bank, mainly a group of capacitors of the same rating. This filter converts the harmonic current into heat to protect the load from it.
Feedthrough Filter Capacitor
The feedthrough filter-capacitor is a three-terminal capacitor whose grounding impedance is a small and low effect on the lead impedance. It is specially designed for more efficient performance in filtering circuit.
The ordinary capacitor is not very good for filter application as they have a high impedance which is undesirable and can affect the efficiency of the filtering circuit feedthrough filter capacitor has a small value of shunt capacitance. This capacitor is used in AC and DC supply lines to reduce harmful interference.
The feedthrough filter-capacitor has a filtering effect close to that of an ideal capacitor. The capacitor was initially designed for DC power lines in the RF system, blocking RF energy and letting DC signals pass through it.
Line Filter Capacitor
The line filter capacitor is a capacitor used to suppress electrical noise generated from the power supply.
The power supply can have various disturbances that include transient surges and fluctuations in its supply voltage. To reduce the effect of such noise, line filter capacitors use line filter capacitors that can endure fluctuations or transients for a more extended period without falling into it.
Line filter capacitor is used to
- keep potentially damaging line transients
- To reduce line disturbance produced by the source
- To reduce the circuit generated noise
There are two topologies used in the line filter: one is an X capacitor, and the other is a Y capacitor.
In X Capacitor, here capacitor is connected across the line supply X capacitor is used where cellular could not lead to an electric shock. It eliminated the electrical noise coming from the power supply and made it used in high-frequency applications. The capacitance of X capacitor can range from 1microF to 10MicroF.
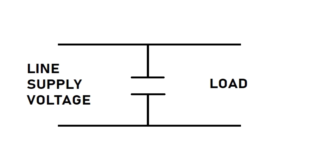
Y capacitor, in this topology, capacitors are connected between the line voltage supply and the chassis of the appliances list of colleges used for an application that could lead to electrical shock. The range of this capacitor can be from 0.001 micro F to 1micro F.
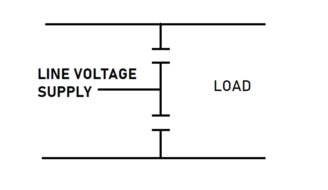
Filter Capacitor in a Power Supply Circuit
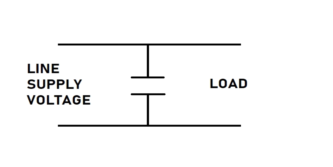
Alternator Filter Capacitor
Alternator stator windings generate the current 3 phase AC. There is not much ripple voltage to produce radio noise. A diode converts the AC to DC, and if any alternator diode fails, the ripple voltage will increase, or noise can be caused by those who have electrical connections. Still, a filter-capacitor can be used to minimize the noise in the circuit. The filter-capacitor can either block the unwanted AC voltage or bypass the unwanted AC voltage back to the source.
Electrolytic Filter Capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a capacitor whose positive plate is made of metal and covered by an insulating oxide layer over the metal. This capacitor uses an electrolyte to have a massive capacitance than other capacitors. The capacitor is used in a filter circuit that combines AC power DC voltage electrolytic capacitor filter to eliminate 60 Hz to 120 Hz AC ripple in DC power supply.
EMI Filter Capacitor
Capacitors used in filtering electromagnetic interference in AC and DC power lines are known as EMI filter capacitors. This capacitor can fail due to over-voltage and transients. There are two different types of topology used in filter capacitor X, and Y. X capacitor topology is used for differential mode EMI filtering. In contrast, Y capacitor topology is used in standard mode EMI filtering.
Theoretically, several capacitor technologies design X or Y capacitors, but the most commercially available are film capacitors or ceramic capacitors.
Filter Capacitor Design
Filter capacitors can be designed in different ways as per requirement.
When a low pass filter is created, the capacitor is then connected across the load. When a high pass filter is designed, the filter-capacitor is in series with a power supply. The capacitor-filter is used as a bypass filter when the capacitor is connected between the ground and power supply. Different filter capacitors can be designed based on the different ranges of operations, costs, decisions, operating temperatures and sizes.
Filter Capacitor Amplifier
The filter capacitor has a great disadvantage: the amplitude of the output signal is lower than that of the input signal due to an attenuation of the signal. This means the overall gain of the filter-capacitor is less than one, so there may be a need to amplify the output signal.
Different amplifiers can be used to restore or control the attenuated signal, such as OpAmp, transistors or FETs. After the capacitor-filter amplifier can draw power from an external source to boost or amplifier the output signal through the capacitor-filter, the output signal of the capacitor-filter can be altered or reshaped as required by the amplifier circuit.
Filter Capacitor Selection
How to select filter capacitor value ?
Select the capacitor-filter based on:
- Cost
- Precision
- Range of operation
- Stability
- Leakage current
- Size
- Operating temperature
High Voltage Filter Capacitor
High Voltage capacitor passive circuit component that can store charge and energy for use in High Voltage application, ordinary capacitor cannot be used in high voltage applications so high voltage capacitor used in higher voltage range application such as high voltage power line filtering, high voltage AC or DC filtering, high voltage AC or DC bypass, etc. These capacitors are designed where the two metal plates of the capacitor are separated by dielectric metal in between for efficient operation in high voltage application.
How to Test Filter Capacitor
There are two ways to check the filter-capacitor:
- Before checking the capacitor, make sure the capacitor is fully discharged. If it is not fully discharged, then discharge the capacitor by connecting it through a load. If you are using a multimeter, then set the metre to read high ohm range. Correctly connect the positive and negative end of the capacitor with the multimeter. The meter should begin from 0 and then move towards infinity, that shows the capacitor is in working condition; if the meter stays at 0, then the capacitor is not charging through the meter, that shows it is not working properly.
- Another way to test the filter capacitor, charge the capacitor with the DC voltage supply and then observe the voltage across the anode and cathode of the capacitor. In this test, the capacitor’s polarity is essential just before applying the voltage. Check the capacitor after charging, disconnect the voltage source from the capacitor, and use a multimeter to observe the voltage on the capacitor. Upon checking, the charged capacitor must hold the voltage applied. The voltage will rapidly drop to zero when the multimeter is connected because the capacitor will be discharging through the multimeter. If the capacitor is not holding any value near the applied voltage, then the capacitor is not working correctly.
SMD filter capacitor
SMD stands for surface mounted device which means SMD capacitor is the surface-mounted capacitor nowadays SMD capacitor is widely in use as a filter because they are smaller in size and can be placed easily on the circuit board surface mounted technology allows faster and reliable construction of Electronic element, so it is capacitor are readily available and having cheaper and higher performance.
FAQ
What does a filter capacitor do ?
Filter-capacitors can be used for different purposes with different arrangements in the circuit.
The filter-capacitor can be used to restrict the DC component of the input signal. It can also reject or bypass the AC component of the input signal. Filter-capacitors can limit the signal’s bandwidth or remove a specific range of frequency from the signal. It can also be used to remove unwanted components or noise from the circuitry.
How to select filter capacitors?
Select the capacitor-filter based on:
- Cost
- Precision
- Range of operation
- Stability
- Leakage current
- Size
- Operating temperature
What is the effect of a capacitor as a filter?
The capacitor is used as a filter. It can filter out AC or DC components from the signal or eliminate a specific frequency range.
Capacitor offers high resistance towards the low-frequency input signal. In contrast, it offers low resistance to the high-frequency signal, so when the capacitor is connected in series with the power signal, only the AC component can pass through that. Only the DC component can passes through the load when the capacitor is linked in parallel to the load.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of capacitor filter?
There are several advantages and disadvantages of capacitor filters.
The advantages of capacitor-filters are cheaper, smaller in size, readily available. The disadvantages of the filter-capacitor are that it is sensitive to temperature change, its capacitance reduces with time.
What happens when filter capacitor value is larger?
The larger the filter-capacitor value, the size of the capacitor also increases with it.
With a larger filter capacitor, the voltage will be minimal. The time constant will be large. The charge will be maintained for a longer period, but it will draw a large amount of current and take a long time to complete the charge and be expensive.
Which one is best either capacitor filter or inductor filter?
The filter can be designed with either a Capacitor or Inductor or by using both.
Capacitor-filters are cheaper than inductor fitters. The size of the filter-capacitor is always less than the size of the inductor filter. The capacitor-filter is better at a smoothening voltage, whereas the inductor filter is better at smoothing current.
Which type of capacitor is used in a low-pass filter?
In a low pass filter, the capacitor is connected across the load.
The type of capacitor used in low pass filter depends on the operating range, temperature, sensitivity, stability, cost, size, etc. The capacitor, which fulfils the requirements, can be used.
What is the difference between a rail and a filter capacitor in a circuit?
A rail capacitor is used in power rail, and the filter capacitor is used for different purposes.
A rail capacitor is used to filter out the noise or ripple in the rail power line. This capacitor is mainly used to maintain the voltage in its rated value and to stabilize it. Where is the filter capacitor used for different purposes such as to eliminate the AC component of the signal, block DC component signal, as bypass filter, EMI filter, limit the bandwidth of the signal, eliminate a specific range of the signal, etc.
Why do we use capacitors as filters in rectification when capacitors are used to block DC and allow AC?
When we use a filter-capacitor in the rectification circuit, it only reduces the AC component of the signal.
In the rectifier circuit, the filter-capacitor is linked in parallel to the load appliances circuit. The DC component of the input signal can pass through the load, and the AC component of the input signal will pass through the filter capacitor. The capacitor shows low resistance towards the high-frequency signal.
What is the effect of filter capacitance magnitudes on the ripple voltage in DC power supplies?
When the filter-capacitor is connected in series with the DC power supply, it reduces the power supply’s AC component.
A filter-capacitor is used in circuitry to minimize the ripple voltage of the power supply.
The ripple voltage output from the filter can be calculated by
Vr= Vp/(2fCR)
Where Vr =ripple voltage
Vp = peak voltage
f= frequency of the signal (supply)
C= Capacitance of the Capacitator
R= the value of the resistance
I have graduated in Applied Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering. I’m a curious-minded person. I have an interest and expertise in subjects like Transducer, Industrial Instrumentation, Electronics, etc. I love to learn about scientific researches and inventions, and I believe that my knowledge in this field will contribute to my future endeavors.