Unicellular organisms are single-celled organisms, meaning that their body consists of only one cell. All life processes of the organism, such as metabolism, excretion, and reproduction occur in one cell only. Unicellular organisms can either be prokaryotes or eukaryotes.
unicellular plants examples are as follows-
- Chlamydomonas
- Closterium
- Micrasterias
- Cosmarium
- Synechococcus
- Cymbella
- Staurastrum
- Cyanidioschyzon
- Dinoflagellates
- Clostridium
- Vibrio
- Bacillus
- Coccus
- Cyanobacterium
- Amoeba
- Euglena
- Paramecium
- Yeast
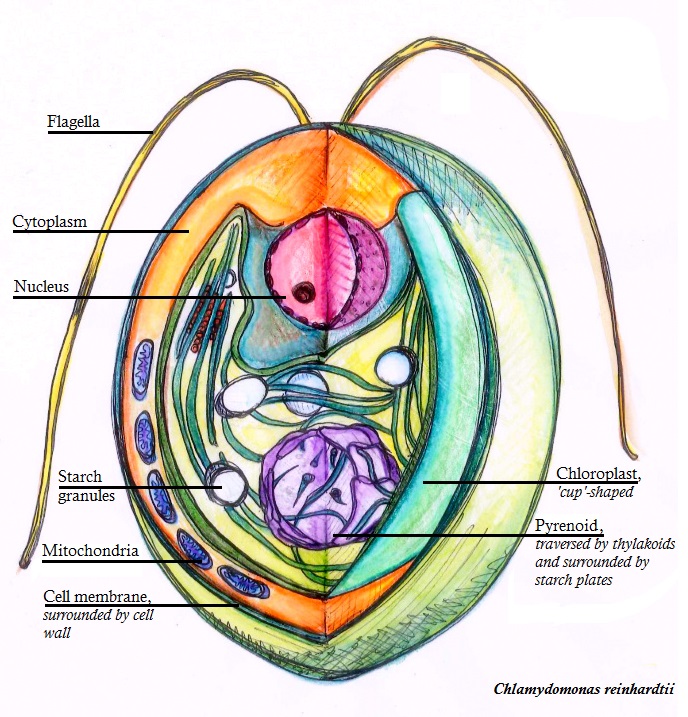
Chlamydomonas–
Chlamydomonas is a single celled, motile green alga found in damp and wet places. It is generally oval in shape and contains a cup shaped chloroplast.
Closterium–
Closterium is an elongated, single celled green alga, abundantly found in water bodies. It is generally crescent shaped and contains two chloroplasts.
Micrasterias–
Micrasterias is a unicellular green alga that exhibits bilateral symmetry. They occur in freshwaters all around the world.
Cosmarium–
Cosmarium is a non motile, unicellular green alga, commonly found in freshwaters. The cells are constricted in the middle giving it a bi-lobed appearance.
Synechococcus–
Synechococcus is a unicellular cyanobacterium. It is elongated in shape. It is found in aquatic habitats.
Cymbella–
Cymbella is a unicellular alga having a silica shell covering consisting of two halves or thecae. It is a typical benthic organism.
Staurastrum–
Staurastrum is a single celled, radially symmetrical green alga. It has a large chloroplast with one pyrenoid in the centre. They are most commonly found in oligotrophic water bodies.
Cyanidioschyzon–
Cyanidioschyzon is a small, unicellular red alga that is club shaped. Cyanidioschyzon merolae contain one chloroplast and one mitochondrion but lack a cell wall. This organism is used to research photosynthesis.
Dinoflagellates–
Most commonly found in freshwater habitats, Dinoflagellates are a group of single celled, eukaryotic protists. Mostly they are found in marine habitats but sometimes also found in freshwater. They possess two flagella that are dissimilar in size. Most dinoflagellates are bioluminescent in nature.
Clostridium–
Clostridium is a unicellular, rod shaped, gram positive bacteria that grow best in moderate temperatures. Some species of Clostridium are pathogenic and grow in anaerobic conditions.
Vibrio–
Vibrio is a comma shaped, unicellular, Gram negative bacteria. They are mostly found in aquatic habitats. They are highly motile in nature. Many species of Vibrio are pathogens. For example, Vibrio cholerae causes cholera in humans.
Bacillus–
Bacillus is a unicellular, rod shaped, gram positive bacteria. They are ubiquitous in nature and produce spores. Bt Toxin in Bacillus thuringiensis is used in developing genetically modified crops.
Coccus–
Cocci are single celled, round shaped bacteria. They vary in size but remain spherical or ovoid in shape. They occur in single cells and sometimes remain attached after cell division.
One pair of cocci are called diplococci. When they are arranged in chains, they are called streptococcus. When they are in an irregular grape-like clusters, they are called staphylococci. Group of 4 cocci is called a tetrad and group of 8 cocci are called sarcina.
Cyanobacterium–
Cyanobacteria are unicellular, prokaryotic, gram negative bacteria. They can photosynthesize and are found in aquatic habitats. Cyanobacterim is also known as blue green alga. They can be found in colonies or as filaments.
Amoeba–
Amoeba is a unicellular, eukaryotic organism that has no particular body shape. They have the ability to alter their shape. They lack cell wall and move using pseudopodia which means ‘false feet’ in Latin. Some amoeba are pathogenic, such as Entamoeba histolytica which causes amoebic dysentry.
Euglena–
Euglena are elongated, single celled protists. They contain one nucleus. Some species of Euglena can photosynthesize and they also feed on other organisms.
They are found in freshwaters as well as marine waters. Euglena reproduces asexually by longitudinal division.
Paramecium–
Paramecium is a eukaryotic, unicellular protist having cilia all over their body. They are oblong in shape and found in aquatic habitats. Paramecium contains two nuclei and numerous contractile vacuoles inside their body. The cilia present all over their bodies help them to move and gather food.
Yeast–
Yeast is a unicellular, eukaryotic organism called Saccharomyces cerevisiae. They belong to the fungus kingdom. They reproduce asexually by budding. Yeast is used in fermentation and baking.
In Conclusion we can say, Unicellular plants simply do not exist. All true plants are multicellular. However, there are some organisms that exhibit some characteristics of plants, which is why they are sometimes categorised as ‘unicellular plants’. Prokaryotic organisms lack a true nucleus and other typical cell organelles. Most prokaryotes are single-celled. Eukaryotic organisms contain a true nucleus and other cell organelles as well. Some eukaryotes are single-celled.
Also Read:
- Chloroplast structure
- Adenine function in rna
- Heterotrophs examples
- Are bacteria photosynthetic
- Dna replication vs polymerase
- Atp synthesis in aerobic respiration
- Adenine structure in rna
- Do prokaryotes have exons
- Dna splicing types
- Are bacteria consumers
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.