Cellular respiration cycle is combination of various metabolic processes to derive energy from nutrients or food molecules. All living organisms including bacteria, plants, animals all use cellular respiration process to produce energy. Here we describe all possible aspects regarding cellular respiration cycle.
Cellular respiration cycle is a combination of some metabolic processes that occurs in living cells, which converts food or nutrients into energy units (ATP) and releases different by-products from it.
Predominantly the respiration process occurs in oxygen rich environment and this kind of cellular respiration is known as aerobic respiration process.
In absence of oxygen lower organisms also derive energy by breaking sugar molecules. This process is known as anaerobic respiration process or fermentation process.
The cellular respiration process is amphibolic in nature means during this process complex breaks into smaller molecules as well as the by-products are involved later in constructing other complex molecules. Therefore the respiration process consists of both catabolic and anabolic characteristics, thus the reaction is amphibolic.
Cellular respiration formula
The basic formula of cellular respiration cycle (typical aerobic respiration) is-
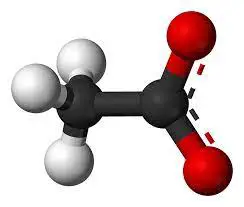
Glucose +6 water → 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water + 36-38 ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 –> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 or 38 ATP
The equation specifies that during cellular respiration (in presence of Oxygen molecule) one Glucose molecule burns with 6 oxygen molecules to produce 36-38 ATP molecules as energy units. The reaction also releases 6 carbon dioxide molecules and 6 water molecules as by- products.
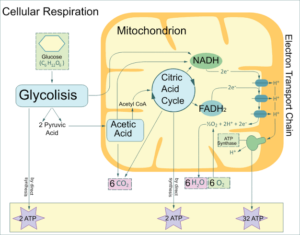
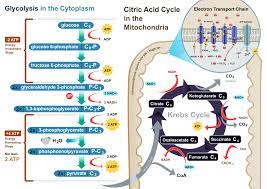
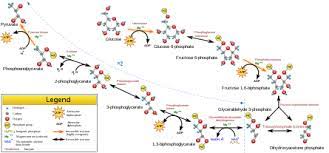
Cellular respiration diagram
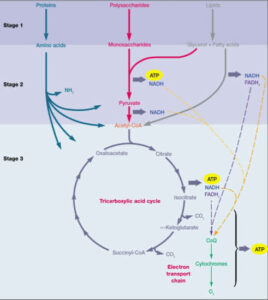
From the diagram of cellular respiration we can see that there are 4 major steps through which the required energy of cell is produced cyclically. The first step Glycolysis takes place in cytoplasm of cell and the other steps take place in mitochondrial matrix of cell.

Cellular Respiration Cycle from Wikimedia Commons
Cellular respiration reactants
The main reactant in cellular respiration cycle is Glucose and Oxygen molecules.
In cellular respiration process basically the nutrient or food molecule like carbohydrate, proteins participates in respiration process to produce energy. The main reactant is the oxygen molecule in this process. The oxygen serves as the last electron acceptor molecule during the oxidative phosphorylation process.
Cellular respiration cycle process
Cellular respiration process is combination of various metabolic reactions through which Glucose molecules breaks down.
The cellular respiration process (aerobic) generally undergoes four major steps to generate most of the energy. The steps are including-
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in the cellular respiration process. In this process 1 Glucose molecule breaks into 2 pyruvic acid or pyruvate molecules. The Glycolysis process occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell. Ten different reactions are involved to facilitate the process. Enzymes involved in Glycolysis pathway are hexokinase, phosphoglucomutase, phosphofructokinase, aldolase, Triose-phosphate isomerase, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerokinase, phosphoglyceromutase, enolase, pyruvate kinase, etc.
During this process 1 Glucose (6-carbon) molecule breaks into 2 pyruvate molecules (3- carbon), releases 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules as by-products.
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) → Pyruvate (CH₃COCOOH) + 2 NADH + 2 ATP
Throughout the process oxygen molecules are not necessary, that’s why Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration processes. This process was discovered by German biochemist Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas and after their names the whole process is known as Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway or EMP pathway.
Acetyl-CoA formation
After the end of the glycolysis pathway the pyruvate converts into acetyl-CoA which later participates in Krebs cycle process. In this process the pyruvate oxidised to form a 2-carbon acetyl group. After the 2-carbon acetyl group bonds with coenzyme -A and produces Acetyl-CoA.
After Glycolysis the pyruvate enters mitochondria and the acetyl-CoA formation reaction occurs in the matrix of mitochondria.
This acetyl-CoA formation process is very significant in cellular respiration process. As only though this process the pyruvate converts into acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA is the only component which can undergoes Krebs cycle procedure. It is also very significant because due to this process the pyruvate cross the plamsa membrane and travels into the mitochondrial matrix from the cytoplasm of cell.
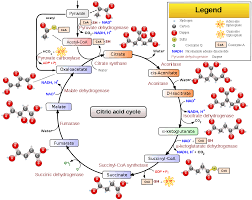
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle is the third and most important step in cellular respiration process. It only occurs in an aerobic environment. In case of anaerobic respiration after Glycolysis the pyruvate directly breaks and produces organic by-products to release energy.
In Krebs cycle process the acetyl-CoA breaks and after several reactions produces 2 carbon dioxide molecules, 1 GTP (or ATP), 1 FADH2 and 3 NADH molecules. At around 8 different enzymes are involved in this process such as, Citrate synthase, Aconitase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate, Succinyl-CoA synthetase, Succinate dehydrogenase, Fumarase, Malate dehydrogenase, etc.
In this process Citric Acid or citrate is produced as the first reaction product. That’s why the cycle is also called the Citric Acid Cycle. As the citrate has three carboxylic groups (- COOH), the reaction is also known as TCA cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.
Electron transport chain
It is the last step of cellular respiration cycle where finally most of the energy releases after electron transfer via membrane proteins in the mitochondrial matrix. The NADH, FADH2 molecules transfer electrons and release energy.
In the aerobic respiration process oxygen molecules act as the last electron acceptor molecule. It produces 36-38 ATP per glucose molecule. It is also known as oxydetive phosphorylation process. In anaerobic respiration process sulphate, nitrate groups act as electron acceptor molecules and produce less amount of energy.
Cellular respiration cycle types
According to the presence of the Oxygen molecule in the environment we can differentiate cellular respiration types.
There are two types of cellular respiration are found in nature. First one is aerobic respiration process, respiration process in presence of Oxygen molecule. Another one is the anaerobic respiration process, in which oxygen molecules are not necessary.
Aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration process is the most common cellular respiration process that occurs in all multicellular living organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, plants, animals, etc.
In this process in the presence of Oxygen molecule the sugar content burns and produces energy for the cell. The whole process consists of four different steps, such as Glycolysis, Acetyl-CoA formation, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. After completing the whole process along with 36-38 molecules of ATP, 6 carbon dioxide molecules and 6water molecules are produced as end products.
Aerobic respiration process from Wikimedia Commons
Glucose +6 water → 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water + 36-38 ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 –> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 or 38 ATP
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration process is mostly occurs in lower groups of organisms body mostly in prokaryotic cells. Anaerobic respiration process is also known as Farmentation process.
In this process in absence of oxygen molecule carbohydrate or glucose molecule breaks down and produce small amount of energy (2ATP) along with some organic by-products. As it lacks oxygen molecule, inorganic groups like sulphate, nitrate groups serve as electron acceptor and release some energy. In anaerobic respiration only Glycolysis and electron transport chain process is found.
There is usually two types of anaerobic respiration process is found –
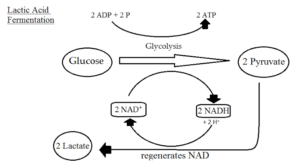
Lactic acid production
In the first one Glucose molecule breaks and produce pyruvate during Glycolysis step and after that the pyruvate converts into lactic acid and produce energy.
C6H12O6 → C3H6O3 + energy (2ATP)
Lactic Acid Fermentation from Wikimedia Commons
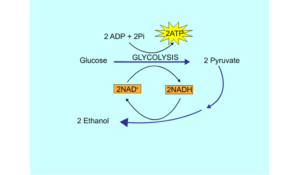
Alcohol farmentation
In the second type of anaerobic respiration process one Glucose molecule breaks and produce pyruvate during Glycolysis step and after that the pyruvate converts into ethanol and produce energy along with a carbon dioxide molecule.
C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2 + energy (2ATP)
Alcohol fermentation from Wikimedia Commons
To know more about anaerobic respiration process read our article on 4+ Anaerobic Respiration Examples : Detailed Explanations
How does cellular respiration work?
The cellular respiration cycle is a very complicated mechanism through which our body gets required energy from the food we take.
The process is started when a living organism take some food. The nutrients from that food are breaks into smaller units like Glucose and through blood flow that reaches each and every cell of the body. After that when the organism breath and takes oxygen, the oxygenated blood also reach each and every cell of the body and the cellular respiration process starts.
At the starting in presence of Oxygen the cell breaks the Glucose and try to produce energy with the help of several enzymes involved in the process. The Glucose molecule undergoes Glycolysis pathway release little amount of energy and converts into pyruvate in the cytoplasm of cell. The pyruvate then transfer into the mitochondrial matrix and oxydised to form acetyl-CoA. Next it undergoes Krebs cycle and after oxydetive phosphorylation process large amount of energy releases. This energy will use for every function of body and that’s gow the cellular respiration process work.
How long does cellular respiration take in plants?
As cellular respiration is a very quick process but every kind of cell completes respiration in different times.
A plant cell respires 24 hours a day because the organism needs energy constantly. According to the cell type a basic cell typically completes a cellular respiration cycle within a milliseconds.
How long does cellular respiration take in humans?
As cellular respiration cycle is a very quick process but every kind of cell completes respiration in different times.
A cell respire 24 hours a day. According to the cell type a cell produces 10 million ATP units per second.
The respiration process depends strictly on the cell type. For example , a muscle cell completes the cellular respiration process more rapidly than a liver cell.
How long does one cycle of cellular respiration take?
How long one cycle of cellular respiration takes completely depends on the type of that particular cell.
Typically a cell completes one cycle of cellular respiration within a millisecond and produces energy.
Cellular respiration cycle product
The main function of the cellular respiration cycle is to produce energy from nutrients. So in both of the cellular respiration processes energy molecules are released.
In the aerobic respiration process along with energy molecules 6 carbon dioxide molecules and 6 water molecules are produced as end products.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 –> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (36 or 38 ATP)
In anaerobic respiration lactic acid production process along with energy lactic acid molecules are produced as the end products of the reaction.
C6H12O6 → C3H6O3 + energy (2ATP)
In the alcohol fermentation process in absence of oxygen molecules along with energy ethanol and carbon dioxide molecules are produced as end products of reaction.
C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2 + energy (2ATP)
To know more about fermentation read our article on Is Fermentation Anaerobic Respiration:What,Why,Detailed Facts
As a whole we can say that cellular respiration process is an most important metabolic process for the energy of living organisms. Only through this process a cell breaks nutrients and converts it into energy units ATP. Here we discuss all possible aspects regarding cellular respiration process including steps, types and many more. The role of cellular respiration process in generating energy is immense.
Also Read: