Spliceosome is a multi megadalton ribonucleoprotein complex in eukaryotes, which stimulates RNA splicing mechanisms. Let’s discuss each and every Spliceosome function respectively.
The assembly of Ribonucleic acids and protein elements stimulates the spliceosome function. There are five major Uridine rich snRNAs known as U-RNAs, such as U1, U2, U4, U5 ,U6 and around 100 protein components are assembled to form spliceosome complexes. Some major functions of spliceosome are mentioned below-
Recognise number of substrates and binds
The first function of a spliceosome complex is to recognise the substrate. Here the U1 unit plays a major role and recognises the 5′ splice site of the intron and binds with that. The U2 snRNP recognises the branch point sequence near the 3′ splice site and binds with that, forming A complex. The U4, U5, U6 snRNPs join together and form a B complex.
Stimulates transesterification
After binding the spliceosome causes two steps transesterification process. In the first transesterification step the 3’ hydroxyl group of adenine nucleotides in the branch point attacks the 5’ splice site of the intron. At second esterification step 3′-hydroxyl of the releasing 5′ exon attacks 3′ splice site and cut the intron between the exons.
Creates a loop
After the first nucleophilic attack the spliceosome folds the intron structure and causes a loop in the pre-mRNA. This loop-like structure reassembles as the lariat which eliminates after the second nucleophilic attack .
Remove introns
After the nucleophilic attacks the spliceosome causes the intron excision. The two attacks cut each of the splice sites of an intron (non coding sequences of pre-mRNA) and remove it from the structure.
Ligase exons
After the intron excision process the spliceosome facilities exon ligation. The exon or the coding sequences of pre-mRNA joins together and forms a mature RNA structure.
Involves in different interactive activities within cell
The spliceosome complex is also involved in different kinds of protein -protein interactions, RNA- Protein interactions and RNA-RNA interactions.
Work as a editor
The spliceosome functions as an editor, thus it edits or removes all the unnecessary area or sequences of precursor RNA and produces a mature RNA.
Finally form a mature RNA from precursor RNA
The main spliceosome function is to produce a mature RNA from the pre-mRNA or hnRNA. It removes all the non-coding regions or introns and joins the exons together. This way the spliceosome produces a mature functional RNA.
Each spliceosome function is facilitated by interactions between the subunits of it. In alternative splicing the exon can be seen. In that case different RNA isoforms are produced through creating exon combinations, from a single transcript.
The spliceosome mediated RNA splicing is only present in eukaryotic cells. In prokaryotes splicing mechanism is not needed. Only tRNA splicing occurs in prokaryotes.
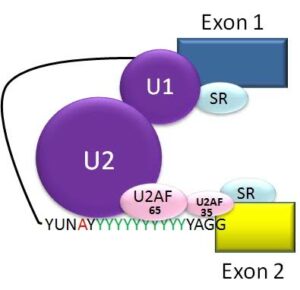
Spliceosomal A Complex formation from Wikimedia Commons
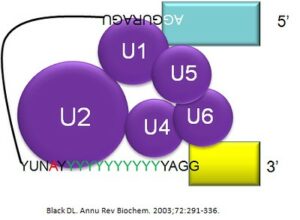
Splicesomal B complex formation from Flickr.com
Minor spliceosome function
Minor spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein complex found in some rare classes of pre-mRNA introns, having U5, U11, U12, U4atac, U6atac and several protein elements as their functional subunits.
The minor spliceosome function is the same as the major spliceosome Function. It forms a mature RNA from a precursor RNA or hnRNA. Here U11 and U12 snRNPs play crucial roles in recognition of substrates. After that association of U4atac, U6atac and U5 facilitates two step nucleophilic attacks and causes intron excision. After the removal of introns, exons are joined with each other and form a mature RNA.
The minor spliceosome mediated splicing is generally found in some rare classes of eukaryotes such as insects, fungi and plants, etc.
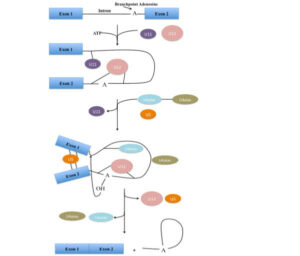
Minor spliceosome function from Wikimedia Commons
Spliceosome assembly function
The spliceosome is made up of five major snRNPs such as U1, U2, U4, U5 ,U6 units and around 100 protein subunits. These all subunits assemble to facilitate splicing mechanism and produce a mature RNA structure.
The function of spliceosome assembly is to stimulate splicing and form a mature RNA from a precursor RNA.
The interaction and binding of snRNP U1 to the GU rich 5′ splice site and binding of snRNP U2 to the Branch Point Sequence (BPS) near 3′ splice site, begins the spliceosome assembly functions. It folds the RNA structure and form A complex.
After that U4, U5 and U6 snRNPs interact and bind with the intron structure in close proximity to the Adenine of the branch point, forming B complex. This causes a nucleophilic attack of -OH of the adenine (branch point sequence) to the 5′ splice site and cut off the end. It gives a loop-like structure called lariat to the intron. After that the newly exposed -OH of 5′ exon attacks on the 3′ splice site. The U5 then removes the intron structure and joins the exons to form a mature RNA.
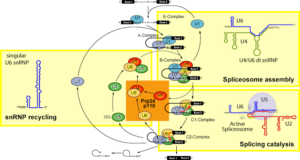
Spliceosome Function from Wikimedia Commons
Spliceosome components function
Spliceosome contains five major snRNP (U1, U2, U4, U5 ,U6 units)and around 100 protein subunits in its structure. The whole structure is involved actively in the splicing mechanism.
The function of spliceosomal components like U1 and U2 is to recognise the substrate or the number of substrates in which they have to work. After recognising they bind with the introns at some conserved sequences. The U4, U5, U6 and all other proteins are majorly involved in the intron excision process and exon ligation process.
To know more about RNA splicing steps read our article on RNA Splicing Steps: Detailed Analysis And Facts
Function of spliceosomes in protein synthesis
The spliceosome function in protein synthesis is very crucial. If the non coding sequences or introns are not cut out by spliceosome before the translation, the protein synthesis process is hampered.
After transcription the precursor RNA has several non coding unnecessary sequences between them. The spliceosome removes all the introns or unessential sequences and joins the exon or the coding sequences together to form a mature mRNA. These mature mRNAs are then ready to decode specific functional protein elements. This way the spliceosome function is very essential in the protein synthesis process.
To know more about RNAs read our article on Is RNA Antiparallel: What, Why, Detailed Facts
Small RNAs in spliceosome function
The small RNAs are non coding poly ribonucleotides, having less than 200 nucleotides in their structure. Among several small RNAs, specifically the small nuclear RNAs or snRNAs are used in spliceosome function.
The snRNAs or U-RNAs used in the spliceosomal complex are U1, U2, U4, U5, U6, etc. These snRNAs actively participate and stimulate the whole splicing mechanism. U1 and U2 first recognizes and binds with them. The U4, U5 and U6 stimulate the next splicing mechanism. The U5 is very crucial in the intron removal and exon ligation process.
As a whole we can say that spliceosome function is very important in the RNA translation and protein synthesis process. It produces a mature RNA from precursor RNA. The spliceosome function completely depends on its snRNPs components. Hope this article on spliceosome function will be helpful to you.
Also Read:
- Cytosol function
- Rna splicing function
- Function of plasmid in bacteria
- Parenchyma cells function
- Uracil function in rna
- Golgi apparatus function
- Cytoplasm function
- Function of cytoplasm in bacteria
- Cytoplasm function in animal cell
- Chromosome functions in animal cell

Hello, I am Piyali Das, pursuing my Post Graduation in Zoology from Calcutta University. I am very passionate on Academic Article writing. My aim is to explain complex things in simple way through my writings for the readers.