The Otto Cycle, fundamental to gasoline engines, consists of four strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. It achieves thermal efficiency up to 25-30%. The compression ratio, typically between 8:1 and 12:1, directly influences efficiency and power output.
Otto Cycle Definition
The Otto cycle engine | Valve timing diagram
- Inlet valve opens at 5-100 before the Top Dead Center. This is to ensure that the inlet should open fully when piston reaches at TDC and fresh charge start entering to cylinder as early as possible after TDC.
- Suction valve close at 20 – 300 after Bottom dead center BDC to take the advantage of momentum of moving gases.
- The spark takes place 30 – 400 before TDC. This is to allow time delay between spark and completion of combustion.
- Pressure at the end of power stroke is above atmospheric which increases the work to expel the exhaust gases. So exhaust valve opens at 20 – 300 before BDC so that at BDC pressure reduces to atmospheric pressure and useful work can be saved.
- The exhaust valve closes at 15 – 200 after TDC so that inertia of exhaust gas has a tendency to to scavenge the cylinder which will increase volumetric efficiency.
Otto cycle efficiency | thermal efficiency of Otto Cycle Formula
The efficiency of Otto cycle is specified by
![]()
Where r = compression ratio.
Otto Cycle diagram
Otto cycle P-V diagram | Otto cycle T-S diagram


Otto, Diesel and Dual cycle | Comparison
Case 1: For similar compression ratio and similar heat i/p this relationship will be
[Qin]otto = [Qin]Diesel.
[QR]otto< [QR]Diesel.

In this case of same compression ratio and equal heat input it will be
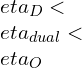
Case 2: In this case of, same compression ratio and same heat-rejection, this relationship will be
[Qin]otto> [Qin]Diesel.
[QR]otto= [QR]Diesel.

In this case of, same compression ratio and same heat-rejection.
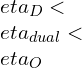
Case 3: In this case of, same Maximum Temperature and same heat-rejection.
[QR]otto= [QR]Diesel
[Qin]Diesel>[Qin]otto

For same Maximum Temperature and same heat rejection
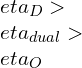
Compression ratio of Otto cycle
Compression ratio of Otto cycle is defined as the ratio of volume before expansion to volume after expansion
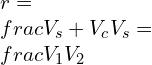
Where Vs = Swept volume of cylinder
Vc = Clearance volume of the cylinder
In this cycle Compression ratio is generally 6 – 10. It is limited to 10 because of knocking in the engine.
Mean effective pressure formula for Otto cycle
Usually Pressure inside the cylinder on an IC engine is continuously changing; mean effective pressure is an imaginary pressure which is assumed to be constant throughout the process.
![]()
Where rp = Pressure ratio = P3/P2 = P4/P1
Otto cycle analysis | Otto cycle calculations | Otto cycle efficiency derivation
Consider an air standard Otto cycle with initial Pressure, Volume and temperature as P1, V1, T1 respectively.


Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression.
![]()
Where,
r is the compression ratio.
Process 2 -3: Heat addition at constant Volume is calculated as,
Qin = m Cv [T3-T2].
Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic expansion is calculated as
![]()
Process 4 -1: Heat-rejection at constant Volume will be
QR = m Cv [T4-T1]
Work done = Qin – QR.
Efficiency of the Otto cycle is represented as.
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \\\\\\eta=1-\\frac{[T_4-T_1]}{[T_3-T_2]}\\\\\\\\ \\frac{T_2}{T_1}=\\frac{T_3}{T_4}\\\\\\\\ \\frac{T_4}{T_1}=\\frac{T_3}{T_2}\\\\\\\\ \\eta=1-\\frac{1}{r^{\\gamma-1}}](https://lambdageeks.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f49c7bd3e52c0f607a4e2c504e1ab46b_l3.png)
Where r = compression ratio.
Working of Two stroke Engine
Two strokes’ engines work on both Otto cycle as well as diesel cycle.
Atkinson cycle vs Otto cycle
| Atkinson Cycle | Otto cycle |
| Atkinson cycle uses slightly different valve timing diagram. The Inlet valve remains open till the start of compression stroke | Inlet valve opens at 5-100 before the Top Dead Center. This is to ensure that the inlet should open fully when piston reaches at TDC and fresh charge start entering to cylinder as early as possible after TDC. |
| Provides higher fuel economy as compared to Otto cycle. | Provides Lower fuel economy as compared to Atkinson cycle. |
| Provides Lower peak power as compared to Otto cycle. | Provides higherPeak power as compared to Atkinson cycle. |
| Mostly used in Hybrid vehicles where electric motor compensates the power deficiency. | Mostly used in 4-stroke and 2 – stroke SI engine where higher power is required |

Brayton cycle vs Otto cycle
| Brayton Cycle | Otto cycle |
| Constant Pressure Heat addition and heat rejection takes place in Brayton cycle. | Constant volume Heat addition and heat rejection takes place in Otto cycle. |
| It has capabilities to handle large volume of low-pressure gas. | Not capable of handling large volume of low-pressure gas due to restriction in reciprocating engine space. |
| High temperature is experienced throughout the steady state flow process. | High temperature is experienced by the engine only during Power stroke. |
| Suitable for gas turbine | Suitable for IC and SI engine. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Otto cycle engine
Advantages:
- This cycle has more thermal efficiency in comparison to diesel and dual cycle for identical compression ratio and equal heat input rate and same compression ratio and same heat rejection.
- This cycle engine required less maintenance and are simple and light-weight in design.
- For complete combustion pollutant emissions are low for Otto engines.
Disadvantages:
- Has lower compression ratio thus it is Poor at moving heavy loads at low speed.
- Will not be able to withstand higher stresses and strains as compared with diesel engine
Example of Otto cycle | Otto cycle problems
Q.1] A spark Ignition engine designed to have a compression ratio of 10. This is operating at low temperature and pressure at value 2000C and 200 kilopascals respectively. If Work O/P is 1000 kilo-Joule/kg, compute maximum possible efficiency and mean effective pressure.
Efficiency of this cycle is given by
![]()
Where r = compression ratio = 10
![]()
For compression process
![]()
![]()
![]()
For expansion process, we can assume that
![]()
![]()
![]()
Net work done can be computed by the formula
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \\\\1000=0.717*[473-1188+T_3-T_4]\\\\\\\\ 1000=0.717*[473-1188+2.512 T_4-T_4]\\\\\\\\ T_4=1395 K](https://lambdageeks.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7b3a245ad98e31383d6f4d9583e34a18_l3.png)
![]()
According to ideal gas theory, we know
P1v1 = RT1
v1=(RT1)/(P1)=(0.287*473)/200=0.6788 m3/kg
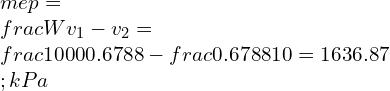
Q.2] what will be the effect on the efficiency of an Otto cycle having a compression ratio 6, if Cv increases by 20%. For the purpose of calculation Assume, that Cv is 0.718 kJ/kg.K.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \\\\\\frac{\\mathrm{d} C_v}{C_v}=0.02\\\\\\\\ \\eta=1-\\frac{1}{r^{\\gamma -1}}=1-\\frac{1}{6^{1.4 -1}}=0.511\\\\\\\\ \\gamma -1=\\frac{R}{C_v}\\\\\\\\ \\eta=1-[\\frac{1}{r}]^\\frac{R}{C_v}](https://lambdageeks.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-757291f702fb1983830f344901562518_l3.png)
Taking log on both sides
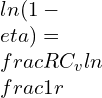
Differentiating both sides
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \\\\\\frac{d\\eta}{1-\\eta}=\\frac{-R}{C_v^2}*dC_v*ln[1/r]\\\\\\\\ \\frac{d\\eta}{1-\\eta}=\\frac{-R}{C_v}*\\frac{dC_v}{C_v}*ln[1/r]\\\\\\\\ \\frac{d\\eta}{\\eta}=\\frac{1-\\eta}{\\eta}*\\frac{-R}{C_v}*\\frac{dC_v}{C_v}*ln[1/r]\\\\\\\\ \\frac{d\\eta}{\\eta}=\\frac{1-0.511}{0.511}*\\frac{-0.287}{0.718}*0.02*ln[1/6]\\\\\\\\ \\frac{d\\eta}{\\eta}=-0.0136\\\\\\\\ \\frac{d\\eta}{\\eta}*100=-0.0136*100=-1.36\\%](https://lambdageeks.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ef306304ee4e226f05089530564c7534_l3.png)
I.e. If Cv increases by 2% then η decrease by 1.36%.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Otto and Diesel cycle?
In Otto cycle heat addition takes place at constant volume while in diesel cycle, heat addition at constant pressure takes place and Otto-cycle has lower compression ratio below 12 while, diesel cycle has higher compression ratio up to 22. Otto-cycle uses spark plug for ignition while diesel cycle needs no assistance for ignition. Otto-cycle has lower efficiency as compared to diesel cycle.
Which fuel is used in Otto cycle ? | What is 4-stroke fuel?
Generally Petrol or gasoline mixed with 3-5% ethanol is used in Otto engine. In air standard Otto-cycle, air is assumed to be as a fuel.
Which is more efficient Otto or Diesel cycle?
The normal range of compression ratio for diesel cycle is 16-20 while in Otto-cycle compression ratio is 6 – 10 and due to higher compression ratio used in diesel cycle, the efficiency of diesel cycle is greater than Otto-cycle.
How does Otto cycle works?
- Inlet valve opens at 5-100 before the Top Dead Center. This is to ensure that the inlet should open fully when piston reaches at TDC and fresh charge start entering to cylinder as early as possible after TDC.
- Suction valve close at 20 – 300 after Bottom dead center BDC to take the advantage of momentum of moving gases.
- The spark takes place 30 – 400 before TDC. This is to allow time delay between spark and completion of combustion.
- Pressure at the end of power stroke is above atmospheric which increases the work to expel the exhaust gases. So exhaust valve opens at 20 – 300 before BDC so that at BDC pressure reduces to atmospheric pressure and useful work can be saved.
- The exhaust valve closes at 15 – 200 after TDC so that inertia of exhaust gases tends to scavenge the cylinder which will increase volumetric efficiency.
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression
![]()
Where r = compression ratio
Process 2 -3: Heat additions at constant Volume
Qin = m Cv [T3-T2]
Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic expansion
![]()
Process 4 -1: Heat-rejection at constant Volume will be
QR = m Cv [T4-T1]
Work done = Qin – QR.
Efficiency of the Otto-cycle is represented as.
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \\\\\\eta=1-\\frac{[T_4-T_1]}{[T_3-T_2]}\\\\\\\\ \\frac{T_2}{T_1}=\\frac{T_3}{T_4}\\\\\\\\ \\frac{T_4}{T_1}=\\frac{T_3}{T_2}\\\\\\\\ \\eta=1-\\frac{1}{r^{\\gamma-1}}](https://lambdageeks.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f49c7bd3e52c0f607a4e2c504e1ab46b_l3.png)
Where r = compression ratio.
Difference between Otto cycle Diesel cycle and Dual cycle
Otto cycle vs Dual cycle

Otto cycle vs Carnot cycle
| Carnot CycleOtto cycleIt consists of two reversible isothermal process and two reversible adiabatic processes. | Ideal air standard Otto-cycle consists of two Isochoric process and two reversible adiabatic processes. |
| It is a hypothetical cycle and is not practically possible to construct. | It is a real cycle and is the basis of working of modern Spark ignition engine. |
| It serves as a yardstick to measure the performance of other engine cycles. | It does not serve as a yardstick to measure the performance of other engine cycles. |
| It has 100% efficiency. | It has overall thermal efficiency in the range of 50 – 70 %. |
| It can be reversed to obtain Carnot refrigeration / heat pump with maximum coefficient of performance. | It is a non-reversible cycle. |
Otto cycle vs Atkinson cycle
| Atkinson Cycle | Otto cycle |
| Atkinson cycle uses slightly different valve timing diagram. The Inlet valve remains open till the start of compression stroke | Inlet valve opens at 5-100 before the Top Dead Center. This is to ensure that the inlet should open fully when piston reaches at TDC and fresh charge start entering to cylinder as early as possible after TDC. |
| Provides higher fuel economy as compared to Otto-cycle. | Provides Lower fuel economy as compared to Atkinson cycle. |
| Provides Lower peak power as compared to Otto- cycle. | Provides higher Peak power as compared to Atkinson cycle. |
| Mostly used in Hybrid vehicles where electric motor compensates the power deficiency. | Mostly used in 4-stroke and 2 – stroke SI engine where higher power is required |
Otto cycle formula
The efficiency of Otto-cycle is given by the equation
![]()
Where r = compression ratio = 10
Otto cycle with polytropic process example
An SI engine has a compression ratio 8 while operating with low temperature of 3000C and a low pressure of 250 kPa. If Work o/p is 1000 kilo-Joule/kg, then compute highest efficiency. The compression and expansion takes place polytropically with polytropic index (n = 1.33).
Solution: The efficiency of Otto- cycle is given by the equation
![]()
Here γ = n
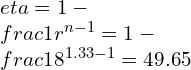
Why the Otto cycle is known as a constant volume cycle?
For this cycle, heat-addition and rejection happens at the fixed volume and the amount of work done is proportionate on heat addition and heat rejection rate, because of this reason Otto-cycle is termed as constant volume cycle.
What are the limitations of the Otto cycle?
- It has lower compression ratio thus it is Poor at moving heavy loads at low speed.
- Cannot withstand higher stresses and strains as compared with diesel engine.
- Overall fuel efficiency is lower than diesel cycle.
Are two stroke engines considered to be Otto cycle engines?
Two strokes engines work on both Otto-cycle as well as diesel cycle. The working of 2-stroke engine is given below:
- Piston moves down and useful power is obtained. The downward motion of piston compresses the fresh charge stored in crankcase.
- Near the end of expansion stroke, the piston will reveal the exhaust-port at first. Then the cylinder pressure will drop to atmospheric pressure as during that time combustion materialwill leave from the cylinder.
- Further motion of piston reveals the transfer port allowing the slightly compressed charge in crank case to be entered the engine’s cylinder.
- Projection in piston prevents the fresh charge from passdirectly to the exhaust port and scavenging the combustion materials.
- When piston move up from bottom dead centre to top dead center and the transfer port closes at first then exhausts port will close and compression will happen. At the same time vacuum is created in crankcase and fresh charge enter into crankcase for next cycle.
Why is the Atkinson cycle more efficient even though it produces lower compression and pressure than the Otto cycle?
In Atkinson cycle, for isentropic expansion process in Otto cycle is further allowed to proceed and extend to lower cycle pressure in order to increase the work output and we know that efficiency increases for increase in work produced. That is, why the Atkinson cycle is more efficient even though it produces lower compression and pressure than the Otto cycle.
What is the compression ratio of the Otto cycle
Compression ratio of this cycle is elaborated as
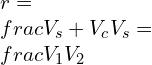
Where,
Vs = Swept volume of cylinder.
Vc = Clearance volume of the cylinder.
Generally in Otto cycle compression ratio is 6 – 10. It is limited to 10 because of knocking in the engine.
Otto cycle vs diesel cycle efficiency
The normal range of compression ratio for diesel cycle is 16-20 while in Otto cycle compression ratio is 6 – 10 and for more compression ratio used in diesel cycle, the efficiency of diesel cycle is greater than Otto cycle.
Case 1: For same compression ratio and exactly identical heat input, the relationship will be
[Qin]otto = [Qin]Diesel.
[QR]otto< [QR]Diesel.

In this case of same compression ratio and equal heat input it will be
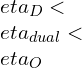
Case 2: In this case of, same compression ratio and same heat-rejection, this relationship will be
[Qin]otto> [Qin]Diesel.
[QR]otto= [QR]Diesel.

In this case of, same compression ratio and same heat-rejection.
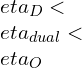
Case 3: In this case of, same Maximum Temperature and same heat-rejection.
[QR]otto= [QR]Diesel
[Qin]Diesel>[Qin]otto

For same Maximum Temperature and same heat rejection
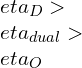
Under which condition the efficiency of Brayton cycle and Otto cycle are going to be equal.
The efficiency of Otto cycle is given by the equation
Solution: The efficiency of Otto cycle is given by the equation
![]()
r = compression ratio = V1/V2
The efficiency of Brayton cycle is given by the equation
![]()
r = compression ratio = V1/V2
For same compression ratio of the Brayton and Otto cycle, their efficiency will be equal.
To know about Polytropic Process (click here)and Prandtl Number (Click here)

I am Hakimuddin Bawangaonwala , A Mechanical Design Engineer with Expertise in Mechanical Design and Development. I have Completed M. Tech in Design Engineering and has 2.5 years of Research Experience. Till now Published Two research papers on Hard Turning and Finite Element Analysis of Heat Treatment Fixtures. My Area of Interest is Machine Design, Strength of Material, Heat Transfer, Thermal Engineering etc. Proficient in CATIA and ANSYS Software for CAD and CAE. Apart from Research.