Negative acceleration, also known as deceleration or retardation, occurs when an object slows down its speed over time. It is the opposite of positive acceleration, which causes an object to speed up. Negative acceleration can be observed in various real-life scenarios, such as a car coming to a stop, a ball thrown upwards and then falling back down, or a rocket slowing down as it re-enters the Earth’s atmosphere. In these examples, the object’s velocity decreases, resulting in a negative acceleration. Understanding negative acceleration is crucial in physics and engineering, as it helps us analyze and predict the motion of objects in different situations. In this article, we will explore several examples of negative acceleration and delve into the concepts behind them. So, let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of negative acceleration!
Key Takeaways

- Negative acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time.
- Examples of negative acceleration include a car slowing down, a ball thrown upward and coming back down, and a rocket descending after reaching its peak altitude.
- Negative acceleration is represented by a negative value in equations and can be calculated using the formula: acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity) / time.
Negative Acceleration Examples
Negative acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. This can happen due to various factors such as the application of brakes, friction, or interaction with a denser medium. Let’s explore some examples of negative acceleration in different scenarios.
Car Slowing Down
When a car slows down, it experiences negative acceleration. This is caused by the application of brakes, which generate a force that opposes the car’s motion. The brakes convert the car’s kinetic energy into heat energy, resulting in a decrease in velocity.
To understand how brakes cause negative acceleration, consider the difference between the car’s initial and final velocity. Initially, the car is moving at a certain speed, but as the brakes are applied, the car’s velocity gradually decreases. This decrease in velocity is an example of negative acceleration.
Switching Off the Grinder
In the context of rotational motion, negative acceleration can be observed when a grinder is switched off. When the grinder is running, it has a certain angular velocity. However, when it is switched off, the rotational motion gradually decelerates.
The grinder’s negative acceleration is due to the depletion of energy. As the grinder loses energy, the rotational speed decreases, resulting in negative acceleration.
Roller Coaster Coming to Rest

During a roller coaster ride, the speed gradually decreases as the coaster approaches the end of the ride. This decrease in speed is an example of negative acceleration.
As the roller coaster nears the end of the ride, various mechanisms, such as friction and brakes, are employed to slow it down. These mechanisms generate forces that oppose the roller coaster‘s motion, causing it to decelerate. The negative acceleration experienced by the roller coaster during the deceleration phase leads to a decrease in speed.
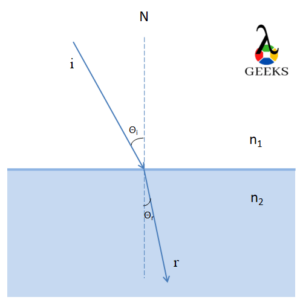
Light Traveling from Rarer to Denser Medium

When light passes from a rarer medium, such as air, to a denser medium, such as water or glass, its speed decreases. This change in speed is an example of negative acceleration.
The decrease in light speed is caused by the interaction of light with particles in the denser medium. These particles absorb and re-emit the light, resulting in a slower propagation speed. The negative acceleration of light in this scenario is a consequence of its interaction with the denser medium.
Flowing Tunnel Meeting the Pond Water
When flowing water meets stationary water in a pond, the force of the flowing water gradually reduces. This reduction in force leads to a decrease in velocity, which is an example of negative acceleration.
As the flowing water enters the pond, it experiences resistance from the stationary water. This resistance opposes the flow of water, causing it to slow down. The negative acceleration in this case is a result of the force of flowing water gradually decreasing as it meets the stationary water.
Object Slowing due to Friction

Frictional force can cause an object to slow down, resulting in negative acceleration. When an object is in motion, the opposing force of friction acts against its motion, gradually reducing its velocity.
Friction occurs when two surfaces come into contact and experience resistance to relative motion. As the object moves, the frictional force opposes its motion, causing it to slow down. The negative acceleration experienced by the object is a consequence of the opposing force of friction.
Kingfisher Diving in the River
When a kingfisher dives into a river, it experiences negative acceleration due to water resistance. As the bird enters the water, the resistance of the water opposes its motion, causing it to slow down.
During the dive, the kingfisher’s speed and acceleration gradually decrease. The negative velocity and acceleration experienced by the bird are a result of the opposing force of water resistance.
Applying Brakes on Bicycle
When brakes are applied to a moving bicycle, it undergoes negative acceleration. The friction between the brake pads and the bicycle wheel generates a force that opposes the bicycle’s motion, causing it to slow down.
As the brakes are engaged, the bicycle’s speed decreases gradually. This decrease in speed is an example of negative acceleration caused by the friction between the brake pads and the bicycle wheel.
In conclusion, negative acceleration can be observed in various scenarios, such as when a car slows down, a grinder is switched off, or a roller coaster comes to rest. It can also occur when light passes from a rarer to a denser medium, flowing water meets stationary water, objects slow down due to friction, a kingfisher dives in a river, or brakes are applied to a bicycle. These examples highlight the diverse ways in which negative acceleration manifests in our everyday experiences.
Ball Sliding Down from Slider
When a ball slides down from a slider, it experiences negative acceleration as its velocity decreases. This phenomenon can be explained by considering the forces opposing the ball’s motion, such as friction and air resistance.
Explanation of how negative acceleration occurs as the ball’s velocity decreases

As the ball slides down from the slider, its initial velocity is high. However, as it moves along the slider, various factors come into play that cause its velocity to decrease. One of these factors is negative acceleration.
Negative acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. In the case of the ball sliding down from the slider, negative acceleration is experienced as the ball’s velocity gradually slows down. This negative acceleration can be attributed to the forces acting against the ball’s motion.
Description of the forces opposing the ball’s motion, such as friction and air resistance
Friction is one of the forces that opposes the ball’s motion as it slides down from the slider. When the ball comes into contact with the surface of the slider, friction acts in the opposite direction to the ball’s motion. This frictional force causes the ball’s velocity to decrease gradually.
Air resistance is another force that opposes the ball’s motion. As the ball moves through the air, it experiences resistance due to the air molecules colliding with its surface. This resistance slows down the ball’s velocity, leading to negative acceleration.
Both friction and air resistance contribute to the ball’s negative acceleration as it slides down from the slider. These forces act in the opposite direction to the ball’s motion, gradually reducing its speed.
In summary, when a ball slides down from a slider, it experiences negative acceleration as its velocity decreases. This negative acceleration is caused by the opposing forces of friction and air resistance. These forces act against the ball’s motion, gradually slowing it down. Understanding these concepts helps us comprehend the physics behind the motion of objects and how forces can affect their velocity.
Calculation of Negative Acceleration
Negative acceleration refers to the decrease in velocity over time. It occurs when an object slows down or decelerates. In this section, we will explore the formula for calculating negative acceleration using initial and final velocity and time. We will also provide an example calculation to demonstrate the process.
Formula for calculating negative acceleration using initial and final velocity and time
To calculate negative acceleration, we can use the formula:
Acceleration = (Final Velocity - Initial Velocity) / Time
Where:
– Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of an object changes over time.
– Final Velocity is the velocity of the object at the end of the given time period.
– Initial Velocity is the velocity of the object at the beginning of the given time period.
– Time is the duration over which the change in velocity occurs.
By plugging in the appropriate values into this formula, we can determine the negative acceleration of an object.
Example calculation to demonstrate the process
Let’s consider an example to better understand how to calculate negative acceleration. Imagine a car braking to slow down from a speed of 60 meters per second (m/s) to a complete stop in 10 seconds.
Given:
– Initial Velocity (Vi) = 60 m/s
– Final Velocity (Vf) = 0 m/s
– Time (t) = 10 seconds
Using the formula mentioned earlier, we can calculate the negative acceleration:
Acceleration = (Final Velocity - Initial Velocity) / Time
Acceleration = (0 m/s - 60 m/s) / 10 s
Acceleration = -60 m/s / 10 s
Acceleration = -6 m/s²
Therefore, the car experiences a negative acceleration of -6 meters per second squared (m/s²) as it slows down to a stop.
It’s important to note that negative acceleration does not necessarily mean that the object is moving in the opposite direction. It simply indicates a decrease in velocity over time. In this example, the car is still moving forward, but its speed is decreasing.
Understanding how to calculate negative acceleration is essential in various fields, including physics, motion analysis, and engineering. It allows us to analyze the behavior of objects in motion and make predictions about their future positions and velocities.
In the next section, we will explore more examples of negative acceleration in different scenarios to further illustrate its significance in the study of motion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answers to common questions about negative acceleration, including its calculation, significance, and examples
Negative acceleration is a concept that often raises questions among those studying physics and motion. In this section, we will address some frequently asked questions about negative acceleration, including how it is calculated, its significance, and provide examples to help you better understand this concept.
How is negative acceleration calculated?
Negative acceleration, also known as deceleration or retardation, occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. To calculate negative acceleration, you need to determine the change in velocity and divide it by the change in time. The formula for calculating acceleration is:
Acceleration = (Final Velocity - Initial Velocity) / Time
If the final velocity is smaller than the initial velocity, the resulting value will be negative, indicating negative acceleration.
What is the significance of negative acceleration?
Negative acceleration is significant because it represents a decrease in velocity, or in other words, a slowing down of an object’s motion. It occurs when an object experiences a force that opposes its motion, causing it to decelerate. Negative acceleration is commonly observed in everyday situations, such as when a car brakes to slow down or when a ball is thrown upwards and experiences the force of gravity pulling it back down.
Can you provide some examples of negative acceleration?
Certainly! Here are a few examples of negative acceleration:
-
Car Braking: When a car applies its brakes, it experiences negative acceleration as it slows down. The force applied by the brakes opposes the car’s forward motion, causing it to decelerate.
-
Free Fall: When an object is dropped from a height, it accelerates downwards due to gravity. However, as it approaches the ground, the force of gravity gradually decreases its speed, resulting in negative acceleration.
-
Thrown Ball: When a ball is thrown upwards, it experiences negative acceleration as it moves against the force of gravity. As it reaches its highest point and starts to descend, the force of gravity causes it to decelerate.
-
Water Flow: When water flows through a narrow pipe or a faucet, it experiences negative acceleration as it slows down due to friction with the pipe walls or air resistance.
These examples illustrate how negative acceleration occurs in various scenarios and helps us understand the concept better.
In conclusion, negative acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. It is calculated by determining the change in velocity and dividing it by the change in time. Negative acceleration is significant as it represents a decrease in velocity or a slowing down of an object’s motion. Examples of negative acceleration include car braking, free fall, thrown ball, and water flow. Understanding negative acceleration is essential in comprehending the principles of motion and physics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, negative acceleration is a phenomenon that occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. It is commonly referred to as deceleration or slowing down. Negative acceleration can be observed in various real-life examples, such as a car coming to a stop, a ball thrown upwards and then falling back down, or a rocket slowing down as it returns to Earth. Understanding negative acceleration is crucial in fields like physics and engineering, as it helps in analyzing the motion of objects and designing systems that require controlled deceleration. By studying these examples and the principles behind negative acceleration, we can gain a deeper understanding of how objects move and interact with their surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is acceleration negative in free fall?
Acceleration is negative in free fall because the force of gravity acts in the opposite direction to the motion of the object. This causes the object to accelerate downwards, resulting in a negative acceleration.
What is an example of negative acceleration in physics?
An example of negative acceleration in physics is when a car is braking. As the driver applies the brakes, the car slows down, and its velocity decreases. This decrease in velocity over time results in a negative acceleration.
What is negative acceleration and how does it relate to negative velocity?
Negative acceleration refers to a decrease in velocity over time. It occurs when an object is slowing down or moving in the opposite direction to its initial motion. Negative velocity, on the other hand, simply refers to the object moving in the opposite direction to the chosen positive direction. Negative acceleration can cause negative velocity, but they are not the same thing.
What causes negative acceleration?
Negative acceleration is caused by forces that oppose the motion of an object. For example, when a car is braking, the friction between the tires and the road creates a force that acts in the opposite direction to the car’s motion. This force results in a negative acceleration, causing the car to slow down.
Can acceleration be negative?
Yes, acceleration can be negative. Negative acceleration occurs when an object is slowing down or moving in the opposite direction to its initial motion. It is important to note that negative acceleration is not the same as deceleration. Deceleration refers specifically to a decrease in speed, while negative acceleration refers to a decrease in velocity.
What is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time?
The rate of change of velocity with respect to time is known as acceleration. It measures how quickly an object’s velocity is changing over time. Acceleration can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on whether the object is speeding up, slowing down, or maintaining a constant velocity.
How can acceleration be defined?
Acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. In simpler terms, acceleration measures how quickly an object’s velocity is changing over time.
What are some examples of positive acceleration?
Some examples of positive acceleration include a car accelerating from rest, a ball falling freely under the influence of gravity, or a rocket taking off into space. In all of these cases, the velocity of the object is increasing over time, resulting in positive acceleration.
What are some examples of negative acceleration?
Some examples of negative acceleration include a car braking to a stop, a ball thrown upwards against gravity, or a rocket descending back to Earth. In these cases, the velocity of the object is decreasing over time, resulting in negative acceleration.
How does acceleration relate to motion and velocity?
Acceleration is closely related to motion and velocity. It describes how an object’s velocity changes over time. If an object’s acceleration is positive, it means the object is speeding up. If the acceleration is negative, it means the object is slowing down or moving in the opposite direction to its initial motion. Velocity, on the other hand, is the rate at which an object’s position changes with respect to time. It is the combination of speed and direction.
Also Read:
- Acceleration due to gravity on moon
- Centripetal acceleration and mass
- Gravitational acceleration formula
- How to find acceleration from distance
- How to find max acceleration in simple harmonic motion
- How to find acceleration of electron
- How to find tangential acceleration
- Centripetal acceleration and centrifugal acceleration
- Constant acceleration examples
- How to find angular acceleration without time
Hi, I’m Akshita Mapari. I have done M.Sc. in Physics. I have worked on projects like Numerical modeling of winds and waves during cyclone, Physics of toys and mechanized thrill machines in amusement park based on Classical Mechanics. I have pursued a course on Arduino and have accomplished some mini projects on Arduino UNO. I always like to explore new zones in the field of science. I personally believe that learning is more enthusiastic when learnt with creativity. Apart from this, I like to read, travel, strumming on guitar, identifying rocks and strata, photography and playing chess.