This Article on kingdom fungi examples illustrates the all-around information about the 20+different kingdom fungi, their Characteristics, and classification with examples in detail.
The word “Kingdom Fungi” refers to any organisms which are mostly eukaryotes, saprophytes, unique multicellular and heterotrophic.
Now take a look at the Kingdom Fungi and their classifications with examples in a detailed way :
List of Classifications
List of kingdom fungi examples:
- Rhizopus stolonifer
- Basidilobolus ranarum
- Claviceps purpurea
- Neurospora crassa
- Auricularia auricular
- Mucor indicus
- Blackslea trispora
- Clavaria
- Cyathus
- Xylaria hypoxylon
- Calocera viscosa
- Agaricus bisporus
- Candida valida
- Mucor racemosus
- Lichtheimia corymbifera
- Ustilago avenae
- Puccinia graminis
- Alternaria solani
- Penicillium chrysogenum
- Trichoderma viridae
Classifications of Kingdom Fungi:
Phycomycetes
It is a one type of fungi which sub classified in to,
1.Oomycetes
It contains non flagellate gametes, formation of spore via sacs in asexual reproduction, white rust, and late blight and it possesses the coenocytic type of mycelium. Examples of Oomycetes are Albugo, Phytophthora,Plasmopara, Aphanomyces, and Water molds
Basidomycetes
This group of fungi is very familiar that also known as the club fungi. It produces basidiospore and basidium-spore-producing club-shaped structures. Examples include Puccinia( Rust fungi), Auricularia auricular (jelly fungi), Puffball (Morgenella fuliginea), Mushroom (Agaricus), smut (Ustilago).
Ascomycetes
This group of fungi also known as Sac fungi, which have Four to eight ascospores, one saclike structure known as an ascus. Examples include Claviceps purpurea, Truffles, Cladonia, Powdery mildews, Neurospora crassa.
Zygomycetes
These groups of fungi produce sporangiophores via asexual reproduction and by the process of mitosis. It contains sporangia borne on the hyphae produce via asexual reproduction. It exhibits a yeast form of growth like a unicellular. It contains the thallus of coenocytic hyphae. It also has sexual reproduction by which it produces heterokaryotic zygosporangium which releases haploid spores. Examples are Rhizopus stolonifer, Bread mold, Rhizopus oryzae, Mortierella vinacea, Mucor indicus, Blackslea transport, Rhizopus sporangium, Kickxella sporangium, Basidilobolus conidium, conidiobolus conidia.
Detaromycetes
Some fungi do not display a sexual phase, such fungi belong to the phylum of Deuteromycota, in which sexual reproduction is missing. such kind of fungi is also known as an Imperfect Fungi. Examples are Metarhizium Roberts, Beauveria bassiana, Lecanicillum lecanii, and Coleomycetes.
Kingdom fungi examples in a brief:
Rhizopus stolonifer
These fungi belong to the family Rhizopidaceae or Mucoraceae. These species are heterophilic and reproduce both sexually and asexually. It is the most common and important species of rhizopus and it is a member of Zygomycota. It produces a mycelium which has an aerial structure for its growth that is provided by stolons. The size of spores mainly depends on the availability of nutrients. This fungus is very useful in fermented industries.

Basidilobolus ranarum
These fungi belong to the family Basidobolaceae. It is one kind of filamentous fungi having yellowish gray to whitish-gray in color, waxy, round, folded, and glabrous-like structure. Hyphae of these fungi are wide and have a few septa. They bloom like whitish spores termed sporangiospores or mycelia.
Claviceps purpurea
These fungi belong to the family Clavicipitaceae and it is a member of Ascomycota. The most common name for this fungi is termed as an “Ergot”. The fungi release some sticky and thick liquid termed a honeydew and it can spread rapidly on the parts of the plant or spread by insects just because the asexual spore of this species produce externally in an abundance manner. These fungi have various applications for used in therapeutic purposes.
Neurospora crassa
These fungi belong to the family Sordariaceae and it is a members of Ascomycota. It is one filamentous heterothallic fungi containing ascospores. There are two processes responsible for the haploid mycelium reproduction. one is the proliferation of existing mycelium and the other is macro and microconidia formation. The most common characteristic of these fungi is their spores resemble the axons.
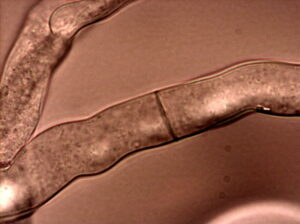
Auricularia auricular
These fungi belong to the family Auriculariaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycota The fruiting bodies of these fungi has brown with ear-shaped. The most common name of these fungi is a black wood ear, jelly ear, or tree ear. The spores have a whitish mass inside of the fruitbody which is hyaline, smooth yellowish.
Mucor indicus
These fungi belong to the family Mucoraceae and it is a members of Zygomycetes fungi. It produces hyphal sporangiophores via asexual reproduction. Mucor indicus is mainly useful for industrial purposes. It can produce oil and its biomass has a rich source of linolenic acid. It can also use for the production of ethanol same as Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Blackslea trispora
These fungi belong to the family Choanephoraceae and it is a member of Zygomycetes. It undergoes both asexual and sexual reproduction. It can produce sporangia asexually in which the hyphae of the black slea are highly branched, aseptate, and very dense form. It also produces Zygospores via sexual reproduction which is slightly flattened and spherical. It can act as an antioxidant for the health and is useful in industrial production.
Clavaria
These fungi belong to the family Clavariaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycetes. The species of this fungi are saprotrophic, they produce some fruit bodies which are coral-like, branched, cylindrical to club-shaped termed basidiocarps. The species of this fungi have different colors namely brown, yellow, black, or violet but that depends on the species.The most common species are Clavaria acuta,Clavaria flavipes,Clavaria fumosa and many more.
Cyathus
These fungi belong to the family Nidularaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycetes. These fungi look like nests of tiny birds filled with eggs termed a “bird’s nest fungi” The mycelia of this fungus are collectively known as a Funiculus. The lifecycle of this fungi is to reproduce both sexually and asexually through the process of mitosis. This fungus useful agriculture and the bioremediation process.
Xylaria hypoxylon
These fungi belong to the family Xylariaceae and it is a members of Ascomycota.The most common name of this fungus is collectively known as carbon antlers or stag’s horn fungus. The ascocarp of this fungi is flattened, sparsely branched, and twisted. The reproduction of these fungi is asexually from ascospores which are smooth, black, and kidney-shaped. These fungi act as an antitumor in nature.
Calocera viscosa
These fungi belong to the family Dacrymycetaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycota. The most common name of this fungi is yellow staghorn. These fungi contain basidiocarps which have white branches, yellow and bright orange. These fungi mostly grow on conifer wood. This fungus is an antitumor.
Agaricus bisporus
These fungi belong to the family Agaricaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycota. it is one type of mushroom. It reproduces via spore asexually which is a form on a basidium. The lifecycle of these fungi develops secondary mycelium that is formed from the primary after the fusion of hyphae. It is widely used for health purposes.
Candida valida
These fungi belong to the family Saccharomycetaceae and it is a members of Ascomycota. This fungal species is a type of yeast widely used for the industrial and fermentation industry.
Mucor racemosus
These fungi belong to the family Mucoraceae. It exhibits dimorphism which means, yeast-like morphologies they possess and filamentous. Reproduction occurs both sexually and asexually. This fungus is widely used for manufacturing enzymes at the industrial level and dairy food production.
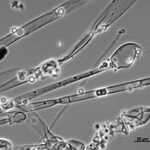
Lichtheimia corymbifera
These fungi belong to the family Lichtheimiaceae and it is a member of Zygomycota. It acts as a saprotrophic mold that contains pear-shaped sporangia having dark and small spores. It possesses sporangiophores that are slightly branched and pigmented.
Ustilago avenae
These fungi belong to the family Ustilaginaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycota. This fungus is commonly known as a “Semiloose smut of oats”.The spore of this fungi contains a black mass covered on the surface of the grain and it can easily spread to other plants or enter into the ovaries of flowers and affect them.
Puccinia graminis
These fungi belong to the family Pucciniaceae and it is a member of Basidiomycota. This fungus is also known as cereal rust, stem rust, or black rust. This kind of fungus easily spread on the parts of the plant absorbs the nutrients, interferes with the vascular tissue of the plant, weakens the steam, and reduces the age and fitness of the plants.
Alternaria solani
The species of this fungi belong to the Pleosporaceae family. The main characteristic of this fungi is that it has a pattern like a spot on a leaf termed a “Bullseye”, It reproduces asexually via mitosis and these fungi do have not any useful applications for any process and development.
Penicillium chrysogenum
The species of this fungi belong to the Trichocomaceae family. The conidia of these fungi produce by dry-shaped conidiophores for reproduction, which are blue to blue-green. This fungus can be found in indoor environments or salted food products.

Trichoderma viridae
These imperfect fungi belong to the family of Hypceraceae. It reproduces asexually via the process of mitosis. This fungus can produce varieties of enzymes namely, chitinases and cellulase that is useful for industrial purpose.
Also Read:
- Is dna replication semiconservative
- Do eukaryotic cells have lysosomes
- Active transport examples
- Are ribosomes found in nucleus
- Cytoskeleton
- Competitive inhibition examples
- Is adenine used in dna replication
- Unsaturated fatty acid examples
- Endonuclease enzyme example
- Molecules active transport examples

Hello, I am Bhairavi Rathod, I have completed my Master’s in Biotechnology and qualified ICAR NET 2021 in Agricultural Biotechnology. My area of specialization is Integrated Biotechnology. I have the experience to teach and write very complex things in a simple way for learners.