Incomplete dominance is a concept in which the produced offspring show partial expression of both the parents like red flower and white flower plant is cross bred and the resultant flowering plant show pink flowers.
Here are the list of Incomplete Dominance Example
- Incomplete Dominance Example in Plants- Four o’clock flowering plant
- Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans-Shape and texture of hair
- Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans-Pitch of the voice
- Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans- Color of the skin
- Incomplete Dominance Example in Animals- Fur texture
- Incomplete dominance examples in humans-Eye
Incomplete dominance can be easily understood as it is a blend of both the parental characteristics/ features/ traits.
Incomplete Dominance Example in Plants- Four o’clock flowering plant
- Four o’clock plant is one of the best examples for incomplete dominance.
- The scientific name of the Four o’clock flowering plant is Mirabilis jalapa.
- The Four o’clock flowering plant produces flowers in two colors.
- One is red and the other is white color.
- When these 2 color flowering plants are cross bred, it does not produce white or red color instead it produces pink color.
- The offspring showed a blend of both the parental characteristics.

Image credits- Wikimedia
Read More on Sequence Of Nitrogenous Bases In DNA: What, Why, Purpose, Detailed Facts
Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans-Shape and texture of hair
- Another best and lively example for incomplete dominance is the shape and texture of hair in humans.
- We know that incomplete dominance is the blend of both the parental features.
- Lets see a example here, Bob and Mary have a beautiful daughter called Alice
- Bob has curly thick hair and Mary has straight hair which is thin
- Alice has beautiful wavy hair that is straight from the roots and moderately curly from the mid to the ends.
- So this is called the incomplete dominance in case of the shape and texture of hair in humans.
- Alice has got the straight hair from her mom, Mary and the mid till end which is curly from her father.
- So both the parental traits are blended here and this is why it is called the incomplete dominance.
Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans-Pitch of the voice
- The pitch of the voice also matters here a lot, the same as hair shape and texture.
- There can be a blend of one parent’s shrill voice and one parent’s soft voice and the resultant child may have a perfect tone in the pitch of his/ her voice.
Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans- Color of the skin
- The Incomplete Dominance Example in Humans on the basis of the skin can be easily explained.
- Father is dark skinned and mother is fair skinned, when the child born is in lighter shade of brown or sandy color, this is one of the best examples of incomplete dominance based on skin color.
Incomplete Dominance Example in Animals- Fur texture
- The texture and color of the fur in cats dogs and horses specifically shows incomplete dominance frequently when compared to other animals.
- Incase of chicken and other birds, the shape and feathery features also exhibit incomplete dominance.
- In rabbits, when a long fur and short fur rabbit is bred the offspring will be a medium fur rabbit.
- In certain birds, when a black male organism and white female organism is bred the resultant offspring will be in blue tinted color feather, this is because of the dilution gene that dilutes the melanin pigment production and blends both the gene.
Incomplete dominance examples in humans-Eye
- A good example of incomplete dominance is color of eye
- Brown eye color is considered the most dominant eye color gene
- Blue eye color is considered the recessive eye color gene
- The presence of golden brown iris is considered to be incomplete dominance as it is a blend of two colors.
- The manufacturing of both eumelanin and pheomelanin results in this color here.
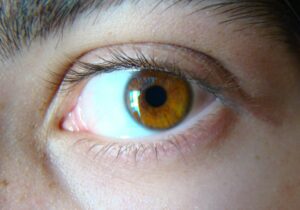
Image Credits- Wikimedia
Incomplete dominance example punnett square
- Punnett square is a diagram which is square in shape and it is used to predict the possible traits of the offspring of different characteristic parents.
- Please have a look at this square diagram of Punnett square
- When a red flower is cross bred with white flowers, the resultant offspring plant has a blended characteristic of both parents.
- Red + White = White
- Red color flower is denoted as R R
- White color flower is denoted as r r
- R R + r r = Rr
- Where Rr is White color flower
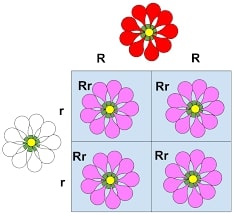
Image credits- Wikimedia
Incomplete dominance example blood group:
- Blood group shows codominance and not incomplete dominance.
- We know that incomplete dominance is the blend of characteristics that result in a unique trait or feature.
- In codominance is when the expression of both the alleles in a gene happen completely
- Eg: father is A positive, mother is B positive the result child may be (probability bases) AB positive.
- Here there is blending of AB but A is individually expressed B is individually expressed. There is no new group in which both have blended and formed a group. A and B are individually expressed
- This is why blood group fall under codominance and not in incomplete dominance
Read More on Difference between animal and plant cell chromosomes: Comparative analysis on structure, function and facts
Incomplete dominance ratio
- The ratio of incomplete dominance is 1:2:1
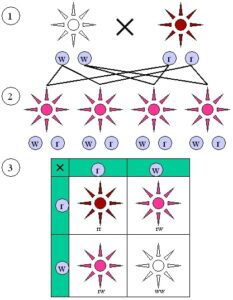
Image credits- Wikimedia
- In F2 generation the red, pink, white flowers ratio is 1:2:1
Also Read:
- Are algae eukaryotic
- Protein denaturation temperature
- Is helicase an enzyme
- Scorpion examples
- Fungi cell walls and protists cell walls
- Do plant cells have lysosomes
- Protein synthesis in endoplasmic reticulum
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids examples
- Do prokaryotic cells have cilia
- Do bacteria ferment

Hello, I am Sugaprabha Prasath, a Postgraduate in the field of Microbiology. I am an active member of the Indian association of applied microbiology (IAAM). I have research experience in preclinical (Zebrafish), bacterial enzymology, and nanotechnology. I have published 2 research articles in an International journal and a few more are yet to be published, 2 sequences were submitted to NCBI-GENBANK. I am good at clearly explaining the concepts in biology at both basic and advanced levels. My area of specialization is biotechnology, microbiology, enzymology, molecular biology, and pharmacovigilance. Apart from academics, I love gardening and being with plants and animals.
My LinkedIn profile-