hexanol structure and all its details were explained in this article.
Hexanol is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H14O or CH3(CH2)4CH2OH . It is formed by the replacement of one of the hydrogen atom in hexane with an OH group. It’s vapours are heavier than air and it is less denser than water.
It is a clear liquid with no color. It has a pleasant or fruity smell. It’s taste can be fruity or fatty like taste. It’s boiling point and melting point is 1570C and -44.60C respectively. In additional to 1- hexanol there is two extra isomers like 2- hexanol and 3- hexanol.
The difference seen here is the attachment of OH group. In 2- hexanol OH is in second carbon while in 3- hexanol it is in third carbon. Hexanol is mostly used in perfume industry.
Lewis Structure of Hexanol
The Lewis structure of all molecules can be drawn easily by knowing some basic rules. We all know that Lewis structure is the most important and simple representation of electrons and bonds in between atoms.
- Hexanol is long chain molecule with six carbon atoms, one oxygen and fourteen hydrogen atoms. So we need to find it’s total valence electrons. The total valence electrons in hexanol is (4×6) +(1 x 14) + 6= 44.
- Draw the symbol of six carbon atoms joined with single bonds and draw symbol of hydrogen atoms for all the carbon atoms. The first carbon should be attached with three hydrogen and rest with two.
- Now there is six carbons and thirteen hydrogen are present in the structure. Now we need to add OH group over there. In this step draw OH symbol on the sixth carbon to complete the structure. Lone pairs of oxygen also depicted over there.
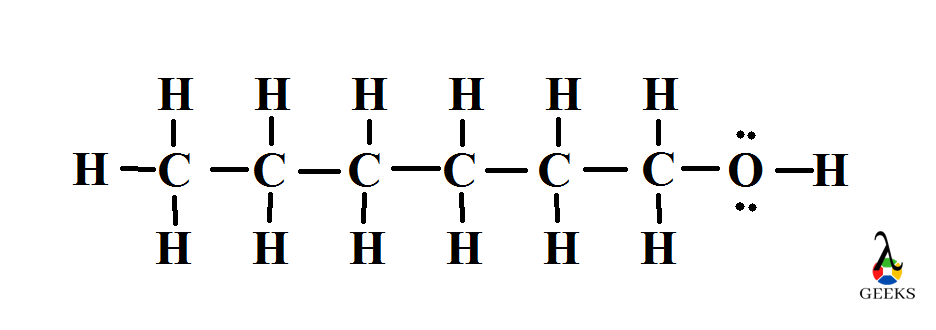
- On looking our structure there is six carbon atoms, fourteen hydrogen and one oxygen atoms over there as per the formula. The formal charge of all the atoms present in here is zero. So this will be stable Lewis structure of hexanol.
Resonance Structure of Hexanol
There is no resonance structure observed for resonance. Even though the lone pairs in oxygen can involve but that will unstabilise carbon. So resonance can’t be observed in hexanol.
Shape and Angle of Hexanol
Hexanol is a straight chain molecule with six carbon , 14 hydrogen and one oxygen. Due to sp3 hybridization of carbon and oxygen atom it can have bond angle of 1090.
Formal Charge of Hexanol
Formal charge of hexanol is found by calculating the formal charge of each atom present here. The formal charge of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is zero in hexanol. So hexanol has a formal charge value 0.
Octet Rule in Hexanol
According to octet rule after bond making all atoms should have eight electrons in its valence shell. Here is both oxygen and carbon all its valence shells are filled with eight electrons. We know that hydrogen need only two electrons for stable existence. Hydrogen also gets two electrons and are stable.
Lone Pairs in Hexanol
In hexanol lone pairs is associated with oxygen only. One oxygen atom has two lone pairs in it. So the lone pairs in hexanol is two.
Valence Electrons in Hexanol
The total number of electrons seen in the valence shell or the valence electrons in hexanol is 44.
Hybridisation in Hexanol
The hybridisation observed in hexanol is sp3.
Solubility of Hexanol
Solubility of can be defined as the ability of one substance to get dissolved in another substance. Hexanol is soluble in ethanol, acetone, chloroform, ether, benzene and is slightly soluble with carbon tetra chloride.
Is Hexanol Soluble in Water ?
Hexanol is slightly soluble in water. It is not able to get dissolved in water easily. 5900 mg/L of hexanol dissolve in water at 25 . This is due to the presence of long carbon chains in hexanol. Since OH group is polar it has the ability to dissolve in water.
But the long carbon chains present here is hydrophobic in nature. So it won’t allow the OH group to dissolve in water. So it’s solubility is low. Also the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in between hexanol molecules is strong. So there needs more energy to break this bond and makes bond with water. This is also a reason for its low solubility.
Is Hexanol is more Soluble than Butanol ?
Solubility of hexanol is lower than butanol. As the length of carbon chain increases its solubility decreases. This is due to the hydrophobic action of long carbon chains. In butanol there is only four carbon atoms but in hexanol there is six. That difference cause this effect. The solubility of butanol and hexanol is 0.11 and 0.0058 respectively.
Does Hexanol Dissolve in Hexane?
Hexanol being non polar will get dissolved in non polar solvent like hexane.
Is hexanol Polar or Non polar ?
Hexanol contains a large hydrophobic part attached with a small OH group. Due to the largeness of the hydrophobic part it is non polar molecule.
Is Hexanol a weak Acid?
Hexanol is a neutral molecule but sometimes it can be a weak acid.
Is Hexanol an electrolyte?
Hexanol doesn’t contains any ions or they won’t get dissociate to produce ions in solution. So they won’t conducts electricity. So it is not an electrolyte.
Is Hexanol a Hydrocarbon ?
Hexanol is a hydrocarbon with six carbons, fourteen hydrogens and one oxygen atom.
Is Hexanol a Ketone or Aldehyde?
Hexanol is neither a ketone nor an aldehyde. But on oxidation of hexanol can yield ketone and aldehyde.
Is Hexanol Corrosive or not ?
Hexanol is stable under proper storage and under handling temperature and pressure. It is not corrosive or irritant to skin but can sometimes cause eye irritation.
Is Hexane Conductive?
Hexane is a non polar molecule. It can’t dissociate to give ions which are prime for electricity conduction. So hexane is a non conductive substance.
Is Hexane Compatible with Acetone ?
Hexane is compatible with acetone. Acetone can acts as both polar and non polar solvent. It acts in accordance with the substance which is to be dissolved in it. Since hexane being a non polar molecule acetone acts a non polar. So hexane is compatible with acetone.
Hexane Covalent or Ionic?
Hexane is a covalent compound. Hexane is an unbranched alkane with six carbon atoms. All its bonds are made by mutual sharing of electrons. So it is a covalently bonded molecule.
Does Hexanol makes Hydrogen Bonding?
Yes, hexanol makes hydrogen bonds with each other. The electronegative oxygen of one hexanol molecule attracts and makes bond with the hydrogen of another hexanol molecule. So they makes intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Molar Mass of Hexanol
The molar mass of hexanol is 102.17
Hexanol Hydrophobic or not ?
Hexanol is a hydrophobic molecule. Hexanol contains a long carbon chains which is hydrophobic and a OH group which is hydrophilic in nature. Due to the bulkiness of long hydrophobic part the effect of OH group is nullified. So it acts a hydrophobic molecule.
Conclusion
Hexanol is a molecule with long hydrophobic chain. Its Lewis structure is drawn above with indicating its lone pairs. It is covalent molecule with inter molecular hydrogen bonding. Its solubility in water is low but founds good in ethanol. It is a non conductive substance with non polar behavior. Hexanol is a non electrolyte with fruity smell.

Hi… I am Aparna Dev, a chemistry Postgraduate with a good understanding of chemistry concepts. I am working in Kerala Minerals and Metals Limited Kollam with experience in the development of electrocatalysts as a part of post graduate thesis.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aparna-dev-76a8751b9