Plasmids can be found in some fungi and higher plants.
Plasmids are small circular DNA fragments that can replicate themselves independent of the nuclear DNA. Across the century, it was believed to be a characteristic of prokaryotic or bacterial cells.
Later scientific studies showed that some eukaryotic cells also contain these self-replicating DNA fragments. Naturally found to be in fungi and some higher plants- the presence of plasmids in animals cells is still unknown.
As to the question “do eukaryotes have plasmids” the most commonly studied ones are those found in unicellular fungi or yeast.
All about plasmids:
- Plasmids are the small circular DNA fragments found outside of nuclear DNA i.e extra-chromosomal.
- They can replicate independently of nuclear DNA in a suitable host.
- They do not contain any form of genetic information.
- Plasmids can range in length from one thousand to a hundred thousand DNA base pairs.
- Till a certain time in scientific exploration, it was considered a feature solely unique to prokaryotic or bacterial cells.
- Later studies showed that plasmids were also found in eukaryotic cells- like in fungi and some higher animals.
- Plasmids carry a minimum of one gene that is beneficial to the host but do not carry any genetic information about the organism as such.
- Though most of them are made of double-stranded DNA, some plasmids can be made of single-stranded DNA or even RNA but the cases are very rare.

Image: Wikipedia
Why do eukaryotes have plasmids?
The main function of plasmids in eukaryotes is to clone genes.
Eukaryotic cells are way more complex in structure and composition compared to prokaryotes and so plasmids are strictly restricted to single-celled eukaryotes like yeast.
Yeast cells are more simple due to being unicellular. Scientists know that these plasmids have some functions but, what they are is still unknown. However, scientists have studied and developed these plasmids to clone specific genes that they want to express.
Do all eukaryotes have plasmids?
The appearance of plasmids in eukaryotes is very seldom or rare.
Plasmids were considered to be a feature unique to bacteria but were later discovered in archaea, some single-celled fungi and less than a handful of plant cells.
Eukaryotic DNA organization is very organized and complex. This diminishes the necessity of extrachromosomal DNA. In eukaryotes, extrachromosomal DNA is restricted to mitochondrial DNA and it is not common to see it floating about in the cytoplasm.
Hence eukaryotic cells having cytoplasm is a rarity in nature.
Which plasmid is found in eukaryotes?
Plasmids are found in eukaryotes are the same that is found in prokaryotes.
Plasmids refer to extrachromosomal free circular DNA found in the cytoplasm. Irrespective of the organism the structure or the typical nature of the plasmid does not undergo any major change.
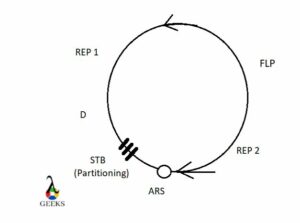
A plasmid of scientific importance found in yeasts is called a 2µ plasmid found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is a 6.3-kilobase plasmid that is extrachromosomal in nature but still occurs in the nucleus. Like chromosomal DNA it is covered by nucleosomes and can initiate replication by itself.
Does eukaryotic DNA have plasmids?
Plasmids are DNA fragments themselves and so DNA cannot contain plasmids.
Eukaryotic chromosomal DNA is conserved and organized. Plasmid DNA in eukaryotes occurs inside the nucleus, though it is extrachromosomal in nature.
Plasmids are DNA fragments themselves are a separate entity from the chromosomal DNA even if they both occur inside the nucleus. In short they are not related or connected to each other in terms of uses or functions.
Do eukaryotic cells have plasmid DNA in the cytoplasm?
It seems that unlike prokaryotes eukaryotic DNA occurs inside the nucleus.
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. But all the organelles and genetic material in eukaryotes are membrane-bound.
In eukaryotes, the genetic material is practically restricted to the nucleus except for that present in mitochondria. The mitochondria are also membrane-bound, so for extrachromosomal DNA to exist out of the nucleus it must be inside a membrane as well.
Seeing how the cell would consider it a wastage of resources, hence the plasmid DNA is contained in the nucleus as well.
Which eukaryotes have plasmids?
Plasmids in eukaryotic cells are restricted to some single-celled fungi and some plant cells.
Eukaryotic genetics and proteomics is a complex matter and is regulated by a large number of enzymes and mechanisms. Hence the presence of plastids in eukaryotic cells is quite a rarity.
Unlike bacteria, eukaryotes like single-celled yeast and a few plant cells are the only ones discovered to possess plasmids. Before it was considered a feature that differentiated prokaryotes from eukaryotes.

Image: Wikipedia
But later it was discovered in archaea and eukaryotes a swell. However, it is a feature more commonly found in parasitic or organisms solely dependant on a host for survival.
Can plasmids replicate in eukaryotic cells?
Plasmids in eukaryotes have the ability to replicate autonomously.
The 2µ plasmid in yeast is covered by nucleosomes just like the chromosomal DNA. The plasmid replication is initiated by the replication enzymes in the nucleus.
The fact that they replicate independently is a truth, but that replication is initiated by the enzymes that initiate replication in the chromosomal DNA. This occurs once every cycle that the cell propagates and host replication enzymes are ample inside the nucleus.
Normal DNA replication is unidirectional but plasmid replication is bi-directional. The site for bi-directional DNA replication is called “autonomous replication sequence” or ARS.
Also Read:
- Venus flower basket types
- Dispersive dna replication
- Do bacteria have peptidoglycan
- Hand anatomy
- Plant cell parts and functions
- Is adenine a pyrimidine
- Endoplasmic reticulum in cytoplasm
- Coenzyme and holoenzyme
- Plant enzyme example
- Fermentation in cytoplasm

I am Trisha Dey, a postgraduate in Bioinformatics. I pursued my graduate degree in Biochemistry. I love reading .I also have a passion for learning new languages.
Let’s connect through linked in: