Discrete Random Variable and Mathematical Expectation
Usually we are not interested in all the possible outcome of any random or non-random experiment instead we are interested in some probability or numerical value for the favorable events, for example suppose we are throwing two dice for the sum as 8 then we are not interested in the outcome as first dice having 2 second dice as 6 or (3,5), (5,3), (4,4), (6,2),etc. likewise for the random of experiment of reservoir in daily life we are not interested in the daily increase or decrease of water level but only interested in the rainy season water level after completion.
So such numerical quantities in which we are interested are considered as random variable of the respective random experiment. For this purpose we assign the possible real values to the outcomes of the random experiment numerically. For illustration of assigning numerical value to the outcome consider the experiment of tossing a coin, we assign numerical value 0 and 1 for head and trail respectively in sample space of the random experiment.
Discrete Random Variable
Discrete random variable can be define as the random variable which are finite or countably infinite in number and those who are not finite or countably infinite are Non-discrete random variables. For every element of sample space we are assigning a real number, this can be interpreted in terms of real valued function denoted by X i.e. X:S→R. We call this function as a random variable or stochastic function, which has some physical, geometric or any other importance.
Example: Consider an experiment of throwing two dice then suppose random variable or stochastic function represent sum of the points appeared on the dice then the possible values for the sample space
S={(1,1), (1, 2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5) , (1,6) ,
(2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (2,6),
(3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4), (3,5), (3,6),
(4,1), (4,2), (4,3), (4,4), (4,5), (4,6),
(5,1), (5,2), (5,3), (5,4), (5,5), (5,6),
(6,1), (6,2), (6,3), (6,4), (6,5), (6,6)}
will be X=2, for (1,1)
X=3 for (1,2), (2,1) etc from the following we can understand easily
| X=2 | (1,1) | (1,2) | (1,3) | (1,4) | (1,5) | (1,6) |
| X=3 | (2,1) | (2,2) | (2,3) | (2,4) | (2,5) | (2,6) |
| X=4 | (3,1) | (3,2) | (3,3) | (3,4) | (3,5) | (3,6) |
| (4,1) | (4,2) | (4,3) | (4,4) | (4,5) | (4,6) | |
| X=5 | (5,1) | (5,2) | (5,3) | (5,4) | (5,5) | (5,6) |
| X=6 | (6,1) | (6,2) | (6,3) | (6,4) | (6,5) | (6,6) |
| X=7 | X=8 | X=9 | X=10 | X=11 | X=12 |
In the above table the diagonal elements from right to left will give the sum expressed by the random variable or stochastic function.
The probability for the respective random variable can be expressed as follows
Discrete Probability Distribution
Discrete probability distribution is the probabilities of the random variables which are discrete in nature, in particular if x1, x2, x3, x4, ………., xk are the values of discrete random variable X then P(x1), P(x2), P(x3), P(x4), ……… .P(xk) are the corresponding probabilities.
Probability function/probability distribution we can denote as
P(X=x)=f(x)
and following the definition of the probability this function satisfies following conditions.
- f(x)≥0
- Σ f(x)=1, where this summation is total summation for x.
Example: If a coin tossed two times, then if we express the number of trails come up as random variable X, then it would be
| Outcomes | TT | TH | HT | HH |
| X | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
If we take the fair coin then the above will be the outcome for tossing twice and the probability for such random variable will be
P (X=0) = P (H,H) =1/4
P (X=1) = P (TH or HT) = P (TH ∪ HT) = P ( TH) + P ( HT)=1/4+1/4=1/2
and P ( X=2) = P (TT) =1/4
This probability distribution we can tabulate as follows
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(X=x)=f(x) | ¼ | ½ | 1/4 |
Cumulative Distribution Function (c.d.f)/Distribution Function
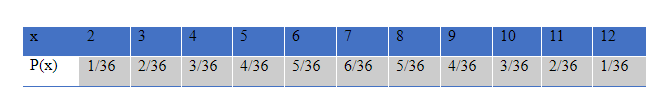
We will define Distribution function or Cumulative Distribution Function (c.d.f) for the discrete random variable X denoted by F(x), for-∞≤x≤∞ as
F(x)=P(X≤x)
Provided it follows
- For any x,y , x≤y, F(x) ≤ F(y) i.e. cumulative distribution function F(x) is non-decreasing.
- F(x) =0 and F(x)=1
- F(x+h)=F(x), ∀ x i.e. . cumulative distribution function F(x) is right continuous.
Since for the discrete random variable probability for X=x is P(X=x), for x1<X<x2 will be P(x1<X<x2) and for X≤x is P(X≤x).
We can write the Distribution function for discrete distribution function as follows
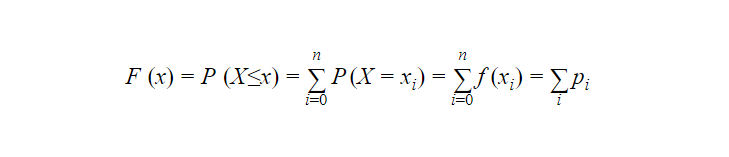
we can obtain the probability function from the distribution function as
P (X=x) = f(x) =F(x)-F(u)
Example: The probability for the discrete random variable is given as follows
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | 0 | 1/10 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 3/10 | 1/100 | 1/50 | 17/100 |
Find F2, F5, F(7)?
Solution:
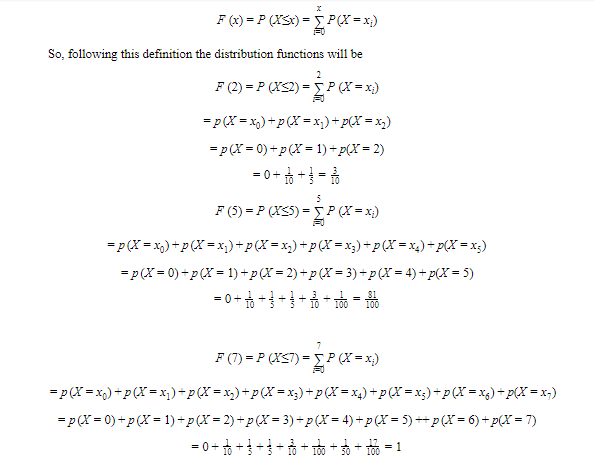
Mathematical Expectation
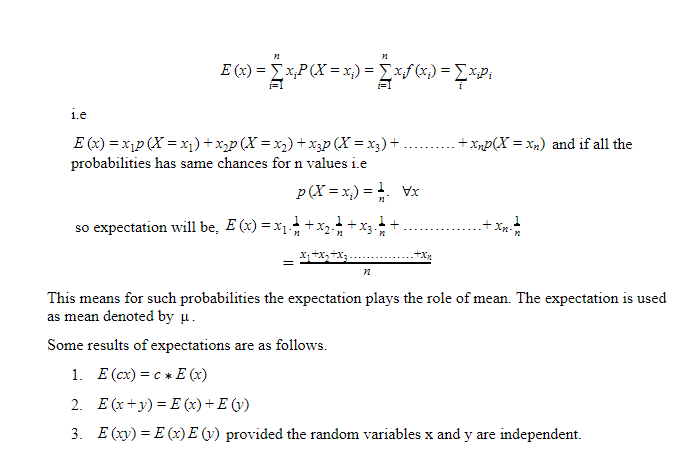
Mathematical expectation is very important concept for the probability theory as well as statistics point of view it is also known as the expectation or expected value, it can be defined as the summation of random variables and its probabilities in multiplication i.e if x1, x2, x3, x4, ……….xn are the values of discrete random variable X then P(x1),P(x2),P(x3),P(x4),……….P(xn) are the corresponding probabilities then mathematical expectation of random variable X denoted by E(x) as
Example: From a pack of 72 cards numbered from 1 to 72 at a time 8 cards are drawn, find the expected value of the sum of numbers on tickets drawn.
Solution:. consider the random variables x1, x2, x3, x4,……….xn representing the cards numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, ………, 72
so probability of any x out of 72 card is
P(xi)=1/n=1/72
since then expectation will be
E(x)=x1.(1/n)+x2.(1/n)+x3.(1/n)+……………+xn.(1/n)
E(x)=1.(1/n)+2.(1/n)+3.(1/n)+……………+72.(1/n)
={1+2+3+……………..+72}*(1/72)=72*(72+1)/2*(1/72)=73/2
Now the expected value for 8 such cards will be
E(x)=x1.(1/n)+x2.(1/n)+x3.(1/n)+……………+x8.(1/n)
E(x)=1.(1/n)+2.(1/n)+3.(1/n)+……………+8.(1/n)
={1+2+3+……………..+8}*(1/72)
=8*(8+1)/2*(1/72)=12
Variance, Standard deviation and Mean deviation by Mathematical Expectation
The important concepts of the statistics standard deviation and variance we can express in terms of mathematical expectation, so if the random variables x1, x2, x3, x4, ……….xn with the corresponding probabilities P(x1), P(x2), P(x3), P(x4), ……….P(xn) then variance will be

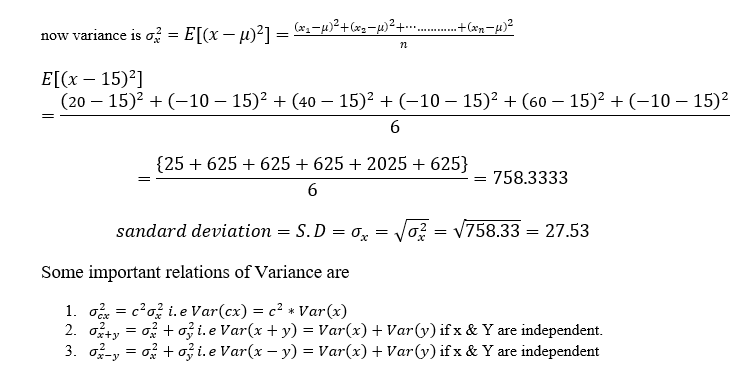
Example: In a game if a fair dice is used and player will win if any odd value come on dice and prize money will be given Rs 20 if 1 come, Rs 40 for 3, and Rs 60 for 5 and if any other face of the dice came Rs 10 loss for the player. find the expected money that can be won with variance and standard deviation.
Solution:
For the fair dice we know the distribution of the probabilities,
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| P(X=x) | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 |
Let X be the random variable for the dice convert as per the game requirement money won or loss when face came as follows,
| X | +20 | -10 | 40 | -10 | 60 | -10 |
| P(X=x) | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 |
so the expected amount won by any player will be
E(x)=(20).(1/6)+(-10).(1/6)+(40).(1/6)+(-10).(1/6)+(60).(1/6)+(-10).(1/6)=15
so the expected amount won by any player would be μ=15
The result of the mathematical expectation as well as variance can be generalized for more than two variables as per requirement.
Conclusion:
In this article we mainly discussed the discrete random variable, probability distribution and distribution function known as cdf cumulative distribution function, Also the concept of Mathematical Expectation for discrete random variable and what would be the mean deviation, variance and standard deviation for such discrete random variable is explained with the help of suitable examples in next article we will discuss the same for continuous random variable, if you want further reading then go through:
For more topic on Mathematics, please follow this link.
Schaum’s Outlines of Probability and Statistics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability

I am DR. Mohammed Mazhar Ul Haque. I have completed my Ph.D. in Mathematics and working as an Assistant professor in Mathematics. Having 12 years of experience in teaching. Having vast knowledge in Pure Mathematics, precisely on Algebra. Having the immense ability of problem design and solving. Capable of Motivating candidates to enhance their performance.
I love to contribute to Lambdageeks to make Mathematics Simple, Interesting & Self Explanatory for beginners as well as experts.