The behavior of waves traveling from one medium to another medium is different. The difference in the behavior of waves gives the phenomena of diffraction and refraction.
Diffraction and refraction are the processes of change in the direction of the wave. Both the light and sound waves can undergo diffraction and refraction. In this post, we will learn the differences between diffraction vs refraction in both light and sound and learn various facts involved in diffraction vs refraction.
Diffraction vs refraction of light
The comparative analysis of diffraction vs refraction briefly summarizes the nature of propagation light waves in the various mediums. In this section, let us discuss the comparison of diffraction vs refraction of light.
| Diffraction | Refraction | |
| Definition | Diffraction is the bending of light at the corner of the hurdle when the light ray passes through the slit giving geometrical shadow. | Refraction is the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another of different refractive indices. |
| Wavelength | The diffraction corresponds to the wavelength; as the wavelength is more, the amount of diffraction will be more. | Refraction is also wavelength-dependent; the amount of refraction increases if the wave with a shorter wavelength is incident on the medium. |
| Nature of the image or pattern | Diffraction of light produces spots or fringes as the diffraction pattern. The pattern is nothing but the shadow of the obstacle. | Refraction of light produces realistic visual illusions or images, not the fringes or shadows. |
| The appearance of the image or pattern | The diffracted pattern appears where they are, and they do not look closer than their original position. | The refracted image of the object appears to be closer than its original position. |
| Splitting up of light wave | When white light is diffracted by passing through an obstacle, it splits the light into its prominent colors giving the diffraction pattern. | The refraction also has the ability to splitting up white light into its prominent colors. |
| Intensity | The intensity of the diffraction fringes depends on the nature of incident light and the width of the slit. | The refracted light’s intensity depends on the light’s velocity and the refractive indices of the medium. |
| Examples | At the edge of the door or window, the bending of the light ray produces the shadow of the window or door. | Water in a swimming pool looks less deep is due to the refraction of light. |

Diffraction vs refraction sound
The change in the direction of the sound wave can produce diffraction as well as refraction depending on the nature of the medium and material. The differences between acoustic diffraction vs refraction is listed as follows:
| Diffraction | Refraction | |
| Definition | The diffraction of sound waves involves a single medium where the bending of the sound wave takes place, and then the sound wave spreads out. | The refraction of the sound waves involves the bending and spreading of the wave, and hence the speed of the sound wave changes. The speed may increase or decrease depending on the nature of the medium. |
| TemperatureThe diffraction of sound waves is generally a temperature-independent phenomenon. | The refraction of sound waves generates a natural temperature gradient for the atmosphere. | |
| Wavelength | The wavelength of the sound wave plays a vital role in the diffraction of sound. The greater wavelength sound wave diffracts more than, the shorter wavelength wave. | If the wavelength is shorter, the frequency will be high; this makes the sound wave attain a higher pitch, and thus the refraction will be greater. |
| Size of the passage | The size of the passage contributes to the diffraction. The diffraction of the sound wave is more if the passage is smaller. | Since the refraction of a sound wave is caused by traveling from one medium to another, the size of the passage or medium does not matter; the only thing that matters how dense the medium is. |
| The velocity of the wave | The velocity of the sound wave remains the same before and after the diffraction. | Refraction is caused due to change in direction, and thus, the velocity also changes when the refraction of a sound wave happens. |
| Examples | Forest-dwelling birds hear the sound of other birds in the long-distance is due to the diffraction of the sound wave at the edge of the trees. | The thunder sound created during lightning is a good example of the refraction of the sound wave. |

Is refraction same as diffraction?
Diffraction and refraction are very important properties of the wave where bending or spreading of the wave occurs. These are natural phenomena that can be observed everywhere around us. Though both properties encounter bending phenomena, they differ from one another.
Refraction is a bulk phenomenon; it occurs when the wave hits a surface and travels through the bulk of another medium of different densities, and the bending of the wave takes place. While the diffraction is an edge phenomenon, where the wave hits the corner of the obstacle, which is placed in the path of the propagation of the wave, and then bending or spreading of the wave takes place.
Though both diffraction and refraction are the characteristics of the wave, their result is also different as the refraction produces the visual image, whereas the diffraction produces the fringes or geometrical shadows.
Is it a rainbow diffraction or refraction?
Rainbow is a naturally occurring process in the sky when the light ray from the sun passes through the water droplet.
Even though the rainbow looks like the cause of diffraction as the water droplet acts as a grating because water is a transparent medium, diffraction does not play any role in the rainbow formation. As the light ray travels from the water droplet to air, there is a change in the light ray’s propagation medium. The refractive indices of air and water are different. As the water medium is denser than the air medium, there will be refraction, not diffraction.
The cause of the rainbow
- The cause of the rainbow is due to the refraction, and reflection also plays a part in causing the rainbow. When the light ray enters the water droplet, the ray gets reflected inside the droplet more than once; this is called total internal reflection, which causes the rainbow to look shiner. When the ray leaves the droplet, the rays are double refracted, and they disperse into a cone of seven constituent colors of various wavelengths.
Is a prism refraction or diffraction?
The prism has the ability to disperse the white light into its constituent colors when white light is passed through the prism. The dispersion of white light in the prism is due to refraction, not diffraction.
When the white light ray is encountered on the prism, the bending of the light ray takes place at the surface of the prism. Since prism is made up of a particular type of glass-like material, the refractive index of the prism is more than the air; the splitting up of colors takes place inside the prism of a different wavelength.
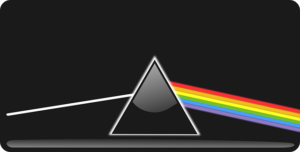
The spectrum we obtained from the prism of different frequencies is not the diffraction pattern. Prism is refraction, not diffraction.
Each spectral line emerges out of the prism, and the rainbow has a different wavelength in the order of red, yellow, green, blue-green, blue, and violet. Red has the longest wavelength, and violet has the minimum wavelength.
Some interesting facts of diffraction and refraction
- The refraction is the property of the wave that obeys “Snell’s law”.
- Not only light and sound waves, electromagnetic can also undergo refraction and diffraction.
- The amplitude of the wave decreases after the refraction and diffraction, as there is a change in the direction of the wave; hence during the process, some amount of energy may get lost; as a result, there will be an amplitude decrease.
- Water can undergo both refraction and diffraction as it is a transparent medium. For example, if we place a straw in a glass of water, it looks like the straw is cut off; in this case, water acts as a refractive medium. While if a light wave hits the island and bends, it produces the shadow of the island due to diffraction.
- On the earth, we can able to visualize maximum of ¾th of the rainbow cone; a pilot can visualize the complete rainbow.
Also Read:
- Telescope diffraction limit formula
- Diffraction vs dispersion
- Reflection vs diffraction
- Lens diffraction limits
- Microscope diffraction limit formula
- Diffraction in telescopes
I am Keerthi K Murthy, I have completed post graduation in Physics, with the specialization in the field of solid state physics. I have always consider physics as a fundamental subject which is connected to our daily life. Being a science student I enjoy exploring new things in physics. As a writer my goal is to reach the readers with the simplified manner through my articles.
