CO32- is a chemical formula for carbonate ion which is a polyatomic anion. It is an carbon oxoanion. Here we are learning about CO32- lewis structure and characteristics.
Carbonate (CO32-) is an anion which consists of two elements i.e. one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms. CO32- is an conjugate base of hydrogen carbonate. Most of the carbonic acid ions and salts have CO32- functional group in it. Alkali metal carbonates are miscible in water rather other carbonates are not soluble.
How to draw CO32- lewis structure?
Lewis structure of any molecule is drawn with the help of some steps to follow:
Step – 1 Predict the group positions of C and O atoms present in CO32- and note the valence electrons present on C and O atoms.
Step – 2 Determine the total valence present in the CO32- lewis structure.
Step – 3 Place the least electronegative atom in central position or if polyatomic molecule place the two atoms besides each other.
Step – 4 Other remaining atoms bonded to central atoms with a single covalent bonds in which two valence electrons are present.
Step – 5 After doing bonding the left over valence electrons get placed on outer atoms to complete the octets.
Step – 6 Check the complete or incomplete octets of all atoms present in CO32- lewis structure.
Step – 7 Calculate the lone electron pairs and formal charge present on CO32- lewis structure.
Step – 8 Last is to determine shape, hybridization and bond angle of CO32- lewis structure.

CO32- valence electrons
The CO32- lewis structure, it is a diatomic anion, in which only two element are present that is carbon and oxygen atoms. Carbon atom do lies in 14th periodic table group and oxygen atom lies in 16th periodic table group. Thus they both contain 4 and 6 valence electrons respectively.
Let calculate the total valence electrons present on CO32- ion.
Valence electrons present in C atom of CO32- = 04 x 01 (C) = 04
Valence electrons present in O atom of CO32- = 06 x 03 (O) = 18
Here we will add extra two electrons for 2- charge present on CO32- ion.
Valence electrons due to 2- charge of CO32- = 02
Hence total valence electrons present on CO32- ion = 04 (C) + 18 (O) + 02 = 24
Therefore, total valence electrons present on CO32- lewis structure is twenty four.
If we count the total electron pair present on CO32- lewis structure we have to divide total valence electrons by two.
So, total electron pairs on CO32- = 24 / 2 = 12
Thus, total twelve electron pairs are present on CO32- ions.

CO32-lewis structure octet rule
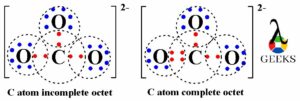
In CO32- lewis structure, carbon atom occupies the central position in CO32- ion as it is least electronegative atom. Later it gets bonded with three oxygen atom with three single covalent bonds. Each single (C-O) covalent bond possesses two electrons from total valence electrons.
As three are three C-O single bonds then 6 valence electrons are being bond pairs in formation of three covalent bonds. Now, we have remaining 18 valence electrons for further sharing of electrons in CO32- ion. Thus these 18 valence electrons get shared between all three bonding O atoms.
Each oxygen atom can possess more six – six valence electrons, so all the 18 valence electrons is on three O atoms. Now, each O atom has six non- bonding electrons present on it. Thus, with single bonds central C atom has only six bond pairs so it has incomplete octet rather three O atoms has complete octet with eight electrons i.e. two bond pair electrons and six non- bonding electrons.
To complete the octet of central C atom we have to move two electrons from one of oxygen atom to form a double bond within carbon and oxygen (C=O) atoms. Thus the central C atom now has total eight electrons i.e. complete octet and also all three O atoms also has eight electrons means complete octet.
CO32- lewis structure lone pairs
CO32- lewis structure has total 24 valence electrons out of which six valence electrons being bond pairs forming three single C-O covalent bonds within central C atom and outer bonded three O atoms. The remaining 18 electrons are being which are placed on all the three outer oxygen atoms and each O atom has six non- bonding electrons present on it.
Thus, these six non- bonding electrons on each carbon atom get paired into the pair of two electrons. Therefore, there are three lone electron pairs are present on each oxygen atom of CO32- lewis structure. Thus, the CO32- lewis structure has total nine lone pair electrons present on it.

CO32- lewis structure formal charge
Formal charge is the positive or negative charge present on the atoms of any structure. As least the charge more stable form of the structure it is. Formal charge is being calculated with the help of a particular formula given below:
Formal charge = (valence electrons – non-bonding electrons – ½ bonding electrons)
Formal charge calculation of CO32- lewis structure is done by calculating the formal charge present on a single C and O present on it. Hence, let we have to calculate the formal charge of C and O atom of CO32- ion to know the total formal charge present on CO32- lewis structure.
Carbon atom: Valence electrons on C atom of CO32- ion = 04
Non- bonding electrons on C atom of CO32- ion = 00
Bonding electrons on C atom of CO32- ion = 06
Carbon atom of CO32- lewis structure has formal charge = (4 – 0 – 6/2) = +1
Thus, formal charge present on carbon atom of CO32- ion is plus one (+1)
Oxygen atom: Valence electrons on O atom of CO32- ion = 06
Non- bonding electrons on O atom of CO32- ion = 06
Bonding electrons on O atom of CO32- ion = 02
Oxygen atom of CO32- lewis structure has formal charge = (6 – 6 – 2/2) = -1
Thus, formal charge present on each oxygen atom of CO32- ion is minus one (-1)
Therefore, the overall formal charge present on C and O atoms of CO32- lewis structure is +1 and -1 respectively.

CO32- lewis structure resonance
While drawing resonance structure we have to manage the same valence electrons number. Also we have to maintain same lone electron pairs in the molecule with only moving electrons from one atom to another to form double or triple bond within a molecule. In CO32- lewis structure there are three form of resonance structures can possible.
In the resonance structure of CO32- lewis structure, the one lone electron pair on each oxygen atom moved inside to form a double bond with central carbon atom. Alternately one lone electron pair on the entire three O atom moved to form C=O double bond one by one. The O atom from which the electron pair moved has zero formal charge on it i.e. the moving of electrons minimize the charge on that oxygen atom.

CO32- lewis structure shape
CO32- lewis structure consists of one central atom and three outer bonded atoms attached to it. Thus VSEPR notation for this kind of molecules says, the molecule having one central atom with three outer bonded atoms attached to it with no lone electron pairs on central atom has AX3 generic formula. Where, A is central atom and X is bonded atoms to central atom.
According to this notation, these kinds of molecules have trigonal planar shape and molecular geometry. Thus the CO32- lewis structure follows AX3 generic formula of VSEPR theory. Hence the CO32- lewis structure has trigonal planar moleculear shape and electron geometry.

CO32- hybridization
As per the VSEPR theory notations, CO32- lewis structure comes under the generic formula AX3 in which A is a central atom and X is bonded atoms attached to central atom. Here, no lone electron pair present on central atom. Thus there is no notation of E.
As the CO32- ion has follows AX3 generic formula of VSEPR theory module, it has trigonal planar molecular shape and electron geometry. Because three bonded oxygen atoms are linked with central C atom in CO32- lewis structure. Thus, CO32- ion has sp2 hybridization according to VSEPR theory.
CO32- lewis structure angle
As per the module or notations of VSEPR theory, CO32- lewis structure comes under AX3 generic formula in which the central carbon atom gets joined with three outer bonded oxygen atoms. Thus in AX3 A = central atom and X = bonded atom to central atom.
Hence CO32- lewis structure has trigonal planar molecular shape and electron geometry according to VSEPR theory. Also it has sp2 hybridization of central carbon atom. Thus the bond angle between oxygen carbon oxygen (O-C-O) atoms is 120 degree. Therefore, the overall bond angle within all carbon and oxygen atoms of CO32- ion is 120 degree.
CO32- solubility
Carbonates (CO32-) ions are soluble in:
- Salts of 1st group elements
- Salts of Na+ ions
- Salts of K+ ions
- Salts of NH4+ ions (ammonium ion)
Carbonates (CO32-) ions are mostly insoluble ions and also it is not soluble in water.
Is CO32- ionic?
Yes, CO32- ions are ionic in nature because it is an anion which we can see already due to the presence of 2- charge present on its structure.
Why CO32- is ionic?
Carbonate (CO32-) has an overall electrically negative charge on it i.e. 2-. It can easily form ions when reacts with positively charged cations. Also it is a polyatomic ion in which the same number of electrons and protons are not present. So, it has a strong capability of forming ions with other positively charged cations. Thus it is an ionic compound.
How CO32- is ionic?
In CO32- carbonate ion, there is the central C atom gets attached with three oxygen atoms. Out of these three oxygen atom one O atom has a double bond with zero formal charge rather the two O atoms has -1 negative charge present on it. Thus, these negatively charged O atoms can accept (H+ ions) protons from other cations and can form OH- ions.
Is CO32- acidic or basic?
Carbonate (CO32-) ions are a conjugate bas in nature. Thus, it is being a moderately basic ion, due to its capacity to form OH- ions by accepting H+ ions from acidic compounds.
Why CO32- is basic?
Carbonate (CO32-) ions have 2- negative formal charge and also it has quite sufficient lone electron pairs present on three O atoms out if which two O atoms have -1 negative charge. Thus it can easily gain or accepts H+ ions from an acid solution and thus CO32- ions are being a strong base or conjugate base in nature.
How CO32- is basc?
Conjugate base are the compounds or ions which can reacts with acids and accepts proton from acid solution. Thus CO32- carbonate ion is an conjugate base because when it get reacts with acids to gain H+ ions or protons to form the compounds like HCO3- I.e. bicarbonate ions.
Is CO32- polar or nonpolar?
CO32- ions are non – polar in nature due to the presence of polar bond in its symmetrical shape with equal charge distribution.
Why CO32- is non – polar?
The CO32- ion has trigonal planar molecular shape which is symmetrical in nature. Thus the CO32- ions have equal charge distribution on all atoms due to which the dipole creates get cancel out each other and having the overall zero dipole moment. Thus, CO32- is non- polar ion.
How CO32- is non – polar?
In CO32- ion the central C atom attached with three O atoms in a symmetric manner having trigonal planar molecular shape and geometry. Also it has polar bonds and the dipole generates on atom get cancel out one another due to its symmetric geometry. Hence, CO32- is a non- polar ion.
Is CO32- symmetrical or asymmetrical?
CO32- ion is symmetrical ion as it has four atoms i.e. one C atom centrally placed and three O atoms bonded to it are arranged in a symmetrical manner in its shape. Thus CO32- is symmetrical in nature.
Why CO32- is symmetrical?
CO32- ion has AX3 generic formula as per the VSEPR theory due to which it has a trigonal planar molecular shape and geometry. In trigonal planar shape all the atoms get arranged in symmetrical manner thus CO32- is a symmetrical ion.
How CO32- is symmetrical?
As the CO32- ion has comes under AX3 generic formula of VSEPR theory, so it has no lone electron pair present on central c atom and no repulsion between the atoms. All the atoms arranged in symmetric manner with equal electron distribution. Hence CO32- is symmetric ion.
Conclusion:
Carbonate (CO32-) ion has 24 total valence electrons out of which 8 are bonding electrons and 16 are non- bonding electrons. It has nine lone electron pairs. All the C and O atoms has complete octet with -2 formal charge present on it. It has three resonance structures. CO32- ion has trigonal planar shape, sp2 hybridization and 120 degree bond angle. It is basic, non- polar and a symmetrical ion.
Also Read:
- Xe lewis structure
- Formaldehyde lewis structure
- Cf2h2 lewis structure
- Bei2 lewis structure
- Lif lewis structure
- Cas lewis structure
- Hclo3 lewis structure
- Hydrochloric acid lewis structure
- Nhf2 lewis structure
- Ch3i lewis structure

Hello everyone, I am Dr. Shruti M Ramteke, I did my Ph.D. in chemistry. I am passionate about writing and like to share my knowledge with others . Feel free to contact me on linkedin