Carbon Monoxide is a toxic gas that can be detrimental if inhaled in large quantities. Let us explore carbon monoxide’s different properties.
Carbon monoxide is a tasteless, odorless, combustible gas with a slightly lower density than air, and carbon monoxide is also very toxic. It is a crucial component in numerous industrial chemistry processes.
This article discusses the chemical formula, electron configurations, paramagnetic properties, and many more chemical properties of carbon monoxide.
Carbon monoxide IUPAC name
Carbon monoxide is the preferred IUPAC nomenclature. It is sometimes referred to as carbonic oxide or carbon oxide.
Carbon monoxide chemical formula
Carbon monoxide has the chemical formula CO. Here a carbon monoxide molecule is composed of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom with a triple bond.
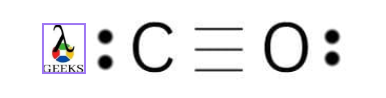
Carbon monoxide CAS number
The CAS number of carbon monoxide is 630-08-0.
Carbon monoxide ChemSpider ID
The ChemSpider ID of carbon monoxide is 274.
Carbon monoxide chemical classification
Carbon monoxide is classified as highly flammable gas and readily combines with air to create explosive combinations.
Carbon monoxide molar mass
A mole of carbon monoxide weighs 28.01 g/mol.
Carbon monoxide color
Carbon monoxide has no colour as it has insufficient oxygen for combustion which gives colour.
Carbon monoxide viscosity
The viscosity of carbon monoxide varies with the temperature.
| Temperature(◦C) | Absolute Viscosity(10-5 Pa S) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1.66 |
| 20 | 1.74 |
| 50 | 1.88 |
| 100 | 2.10 |
| 200 | 2.52 |
| 300 | 2.90 |
| 400 | 3.25 |
| 500 | 3.56 |
| 600 | 3.86 |
Carbon monoxide molar density
The molar density of carbon monoxide is 40.6997mol/m3 because it has a density of 1.14 kg/m3.
Carbon monoxide melting point
The melting point of carbon monoxide is -205.02°C
Carbon monoxide boiling point
Carbon monoxide has a boiling point of -191.5°C.
Carbon monoxide state at room temperature
Carbon monoxide exists in a gaseous state at room temperature.
Carbon monoxide covalent bond
In carbon monoxide, the carbon atom and oxygen atom are joined by three covalent bonds. One result of this is that one of the bonds is a coordinate covalent bond, and one of the atoms provides the shared pair of electrons.
Carbon monoxide covalent radius
The covalent radius of carbon is 0.67 Е and is calculated using the single-bond covalent radius.
Carbon monoxide electronic configurations
The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Let us see the electronic configuration of CO.
The ground state electronic configuration of the carbon monoxide molecule is 1σ2 2σ2 1π4 3σ2.
Carbon monoxide oxidation state
The oxidation states of oxygen and carbon in carbon monoxide are -2 and +2 respectively.
Carbon monoxide acidity/alkaline
Carbon monoxide is neutral oxide and does not exhibit basic or acidic characteristics when reacting with water.
Is carbon monoxide odorless?
Carbon monoxide (CO) has no smell as it is a byproduct of combustion.
Is carbon monoxide paramagnetic?
Unpaired electrons within the substance give it a paramagnetic property. Let us explain if carbon monoxide is paramagnetic or not.
Carbon monoxide is paramagnetic as the bonding molecular orbitals in carbon monoxide will resemble oxygen’s atomic orbitals more than they would because oxygen and carbon have different electronegativities.
Carbon monoxide hydrates
Carbon monoxide clathrate hydrate contains water molecules in the form of H2O molecules is known as hydrate is an example which is an essential constituent in the solar system.
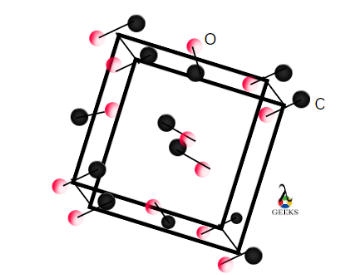
Carbon monoxide crystal structure
The crystal structure of carbon monoxide is rhombic and is given below. Here, black balls represent carbon and red balls represent oxygen.
Carbon monoxide polarity and conductivity
CO is polar and has a net dipole moment because of the unequal charge distribution of the carbon and oxygen atoms.
- The dielectric constant of carbon monoxide at 20°C and 1-atmosphere pressure (101.325 kPa) is 1.00065.
- The Permanent dipole moment of carbon monoxide, in Debye units, is 0.122.
- Thermal Conductivity of carbon monoxide at 25°C(77 °F, 298 K)and atmospheric pressure is -0.014, 0.024.
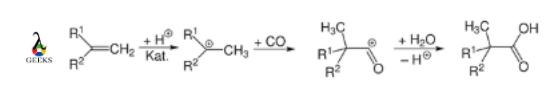
Carbon monoxide reaction with acid
The Koch-Haaf reaction transforms carbon monoxide into carboxylic acids from alkenes in the presence of strong acids and water. For example,
Carbon monoxide reaction with base
When heated under a pressure of 6 atmospheres, carbon monoxide combines with sodium hydroxide to form sodium formate.
NaOH(s) + CO(g) → HCOONa(s)
Carbon monoxide reaction with oxide
Carbon dioxide is produced when carbon monoxide and oxygen reacts. The following reaction occurs when iron(II) oxide and carbon monoxide are combined to produce iron and carbon dioxide.
FeO(s) +CO(g)→ Fe(s) + CO2 (g)
Carbon monoxide reaction with a metal
Metal carbonyls are produced when carbon monoxide reacts with some metals. For example; Carbon monoxide and nickel metal react directly to produce nickel carbonyl:
Ni + 4 CO → Ni(CO)4
Conclusion
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic gas that is colorless, tasteless, and odorless. It is made up of three covalent bonds. It has a paramagnetic property. The only metals that can combine with carbon monoxide ligands are those with lower oxidation states.

Hi … I’m Saina Naushad. I completed my Masters in science with a specialization in Chemistry. I worked with advanced research techniques during my science studies and possessed deep knowledge and expertise in different chemistry topics. I want to help learners better understand advanced Chemistry concepts by sharing my knowledge and skills. please reach out to me on LinkedIn.