Barium fluoride is found in nature in the form of frankdicksonite, which is a halide mineral. Let us see some important facts about Barium fluoride.
Barium fluoride is insoluble in water. In organic solvents such as methanol and ethanol, it is soluble. It is quite hard in texture. When barium fluoride comes in contact with moisture above 5000C, it undergoes corrosion, but we can use it up to 8000C in a dry environment.
Barium fluoride is a transparent compound. It shows ultraviolet to an infrared range of 150 – 200nm to 11 -11.5 µm. Let us focus on the IUPAC name, ChemSpider ID, Molar mass etc., and some more parameters of barium fluoride in this article.
Barium fluoride IUPAC name
IUPAC name of Barium fluoride is barium (2+) difluoride.
Barium fluoride chemical formula
The chemical formula of barium fluoride is BaF2. Barium fluoride is formed by combining Barium and two fluorine atoms.
Barium fluoride CAS number
The CAS number for barium fluoride was observed as 7787-32-8.
Barium fluoride ChemSpider ID
56421 is the ChemSpider ID for barium fluoride.
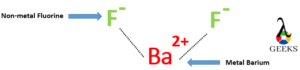
Barium fluoride chemical classification
Barium fluoride is a chemical compound. As barium fluoride does not contain carbon-hydrogen bonding, it comes under an inorganic compound. It is formed by combining metal barium and non-metal fluorine.
Barium fluoride molar mass
The molar mass of barium fluoride is 175.32 g/ mol.
Barium fluoride colour
Barium fluoride appears as white cubic crystals.
Barium fluoride viscosity
In the case of barium fluoride, dynamic viscosity is observed, which is listed below.
| Dynamic Viscosity | Unit | Temperature(K) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0021720 | Pa*s | 1620.20 |
| 0.0035600 | Pa*s | 1880.40 |
Barium fluoride molar density
The molar density value of barium fluoride is 4.893 g/cm3.
Barium fluoride melting point
Barium fluoride melt at 13680C (24940F, 1641K).
Barium fluoride boiling point
The boiling point of barium fluoride is found to be 22600C (41000F, 2530K).
Barium fluoride state at room temperature
Barium fluoride occurs solid at room temperature.
Barium fluoride ionic bond
The bond in barium fluoride is found to be ionic. It contains barium cation and fluoride anion. In barium fluoride transfer of electrons takes place from Barium to fluorine, forming an ionic bond between these two ions.
Barium fluoride ionic radius
The ionic radius of Barium Fluoride is 1.43 A0.
Barium fluoride electron configurations
Electrons are arranged in particular orbital around the nucleus. This arrangement is called electronic configuration. Let us see the electronic configuration of barium fluoride.
The electronic configuration of Barium and Fluorine in Barium fluoride is given below.
Ba ⟶ [Xe] 6s2
F ⟶ 1s2 2s2 2p5.
Barium fluoride oxidation state
The oxidation state of Barium in barium fluoride is +2, whereas, for fluorine, it is -1.
Barium fluoride acidity/alkaline
Barium fluoride is acidic in nature. As it partially dissociates in water, it is a weak acid.
Is barium fluoride odorless?
Barium fluoride is found to be odorless.
Is barium fluoride paramagnetic?
If an electron subshell contains paired electrons, it is diamagnetic, and if unpaired electrons it is paramagnetic. Let us see barium fluoride is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Barium fluoride is diamagnetic in nature as there is no unpaired electron. It is found that synthesized NP (nanoparticle) of barium fluoride is paramagnetic.
Barium fluoride hydrate
Barium fluoride, when reacted with water, gives oxide Barium and hydrogen fluoride. This reaction takes place above 5000C temperature.
BaF2 (s) + H2O (l) ⟶ BaO + 2HF
Barium fluoride crystal structure
Barium fluoride show Fluorite (cubic), cF12.
Barium fluoride polarity and conductivity
- Barium fluoride is a polar molecule. Barium fluoride contains Ba2+, which is a positively charged cation, and F–, which is a negatively charged anion-producing dipole.
- Barium fluoride is an ionic conductor. Its ion conduct electric charge. The thermal conductivity value of barium fluoride at 286 K is 11.72 Wm-1 k-1.
Barium fluoride reaction with acid
Barium fluoride reacts with hydrochloric acid to give barium chloride and hydrofluoric acid. Barium fluoride also reacts with sulphuric acid to give barium sulfate and hydrofluoric acid.
BaF2 (s) + 2HCl (aq) ⟶ BaCl2 (aq) + 2HF (aq)
BaF2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) ⟶ BaSO4(s) + 2HF (aq)
Barium fluoride reaction with base
Barium fluoride reacts with a base like NaOH and gives barium hydroxide and sodium fluoride the product.
BaF2 + 2NaOH ⟶ Ba (OH) 2 + 2NaF
Barium fluoride reaction with the metal
Barium fluoride reacts with zinc metal and forms barium and zinc fluoride.
BaF2 + 2 Zn ⟶ Ba + 2ZnF
Conclusion
Barium Fluoride is used in making lenses, optical glass and fibre optics. It is used in the metallurgical industry. It can be used as a preservative. Welding rods are coated with Barium fluoride. In positron emission tomography gamma photons are detected by barium fluoride.

Hello everyone I am Arti D. Gokhale. My master’s with a specialization in Organic Chemistry and I graduated with Chemistry, Biology, and Zoology. I have 3 years of work experience in water analysis at the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute Nagpur.