H2SO4 is a strong acid while Al2(CO3)3 is a salt. Let us discuss the reaction between them in detail in this article.
H2SO4 is the chemical formula of sulfuric acid. It is a strong and colourless mineral acid. It dissociates completely in water. Al2(CO3)3 is the chemical formula of Aluminium Carbonate. It is a basic salt. It is white powder with a melting point of 58 οC. The IUPAC name of Al2(CO3)3 is Dialuminium tricarbonate.
Let us explore how to balance and other facts related to the reaction between Sulfuric acid and Aluminium Carbonate in this article.
What is the product of H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3?
H2SO4 reacts with Al2(CO3)3 to form the product Aluminium sulphate [Al2(SO4)3], carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) so the chemical equation for the above reaction is –
3H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + 3CO2 + 3H2O
What type of reaction is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3?
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is an acid-base or a neutralization reaction.
3H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2CO3
How to balance H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3?
To balance the reaction between H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 , the following steps needs to be followed.
- Write the skeletal chemical equation.
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + H2O + CO2
- Note the number of moles of each element on the reactant and the product side.
| Elements | Reactant side | Product side |
|---|---|---|
| H | 2 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 3 |
| O | 13 | 15 |
| Al | 2 | 2 |
| C | 3 | 1 |
- Balance the number of moles of elements on reactant and the product side.
Start with the least balanced element. Multiply H2SO4 by 3 on the reactant side to balance sulfur. Multiply CO2 by 3 to balance carbon on the product side. Multiply H2O by 3 to balance the number of moles of oxygen and hydrogen
- The balanced chemical equation is as follows –
3H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + 3CO2 + 3H2O
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 titration
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is a type of acid-base titration. The end point of titration is the point at which there is a change in the colour of the indicator.
Apparatus used:
Burette, burette stand, conical flask, pipette, beaker, funnel
Indicator
Indicator used is methyl orange.
Procedure:
- Fill the burette with 25ml standardized solution of Al2(CO3)3 and note the initial reading.
- Take known concentration of H2SO4 in the burette.
- Take 10 ml of Al2(CO3)3 solution in a conical flask concentration is not known. Add 2-3 drops of methyl orange to its solution.
- Start titrating by adding dropwise H2SO4 to Al2(CO3)3 solution
- The point at which the colour of methyl orange changes to yellow is the end point of titration.
- Repeat the steps to get the concordant readings.
- Initially the solution is yellow as the pH is high. But as acid is added the pH decreases and the colour changes to red. That is the end point of titration.
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 net ionic equation
The net ionic equation for H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3is as follows –
6H+ (aq) + Al2(CO3)3 (s) –> 2Al3+ (aq) + 3H2O (l) + 3CO2 (g)
Following are the steps to be followed to write the net ionic equation –
- Write the complete equation
- 3H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + 3CO2 + 3H2O
- Write the chemical state of each compound
- 3H2SO4 (aq) + Al2(CO3)3 (s) –> Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
- Strong electrolytes will dissociate completely in aqueous solution
- 6H+ (aq) + 3SO42- + Al2(CO3)3 (s) –> 2Al3+ (aq) + 3SO42- +3H2O (l) + 3CO2 (g)
- To obtain the net ionic equation cancel the spectator ions
- 6H+ (aq) + Al2(CO3)3 (s) –> 2Al3+ (aq) + 3H2O (l) + 3CO2 (g)
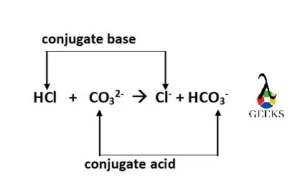
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 conjugate pairs
The conjugate pairs of H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 are as given below.
- The conjugate base of H2SO4 is SO42-.
- The conjugate acid of Al2(CO3)3 is H2CO3.
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 intermolecular forces
The intermolecular forces present in H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 are as given below.
- In Al2(CO3)3, electrostatic force of attraction is found.
- In H2SO4, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions and van der Waal’s dispersion forces are found.
- In Al2(SO4)3, electrostatic force attraction is present.
- In water, hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions are present.
- Between CO2 molecules, London forces of attraction are present.
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 reaction enthalpy
The enthalpy of the reaction H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 can be found out as below.
3H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 –> Al2(SO4)3 + 3CO2 + 3H2O
| Compounds | Enthalpy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| H2SO4 | -854.4 |
| Al2(CO3)3 | -579 |
| Al2(SO4)4 | -3440 |
| CO2 | -393.5 |
| H2O | -285.83 |
∆Hf(reaction) = ∑Hf(product) – ∑Hf(reactant)
={-3440 + 3*(-393.5) + 3*(-285.83)} – {3*(-854.4) + (-579)}
= -5,477.99 + 3,142.2
= -2,335.79 kJ/mol
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 a buffer solution?
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 is not a buffer solution because it contains a strong acid H2SO4 while buffer solution is a solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or weak base and its conjugate acid.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 a complete reaction?
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is a complete reaction as the reaction leads to the formation of stable product which do not breakdown further.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is an exothermic reaction as the enthalpy of the reaction is -2,335.79 kJ/mol which means heat is liberated in the reaction.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 a redox reaction?
H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 is not a redox reaction because the oxidation state of each element is same on the reactant and the product side.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 a precipitation reaction?
The reaction H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is not a precipitation reaction as the reaction between them does not lead to the formation of any solid product.
What Are Some Common Uses of Phosphorus Triiodide?
Phosphorus triiodide applications cover a variety of fields including organic synthesis, manufacturing pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing organic iodides. Its ability to convert alcohols to alkyl iodides makes it a valuable reagent. Additionally, it is used in the production of chemicals like flame retardants and catalysts, making it an important compound in various industries.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 reversible or irreversible reaction?
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is an irreversible reaction because there is a formation of gas (CO2) increases the entropy of the reaction so making the reaction irreversible.
Is H2SO4 and Al2(CO3)3 displacement reaction?
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is a double displacement reaction. There is an exchange of ions between the reacting species.
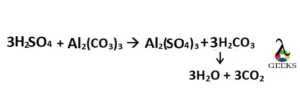
Conclusion
H2SO4 + Al2(CO3)3 is an acid-base reaction. It is an irreversible reaction. It is an exothermic reaction with heat of enthalpy as -2335.79 kJ/mol.