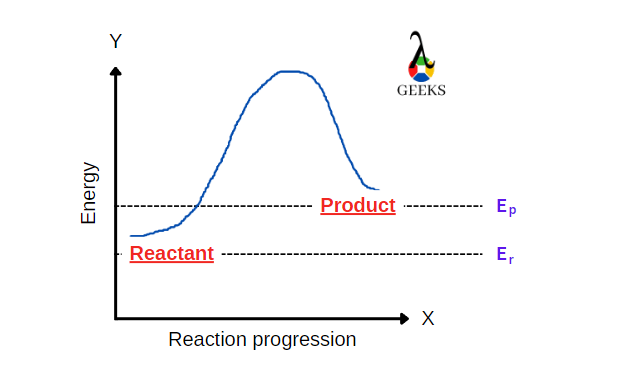
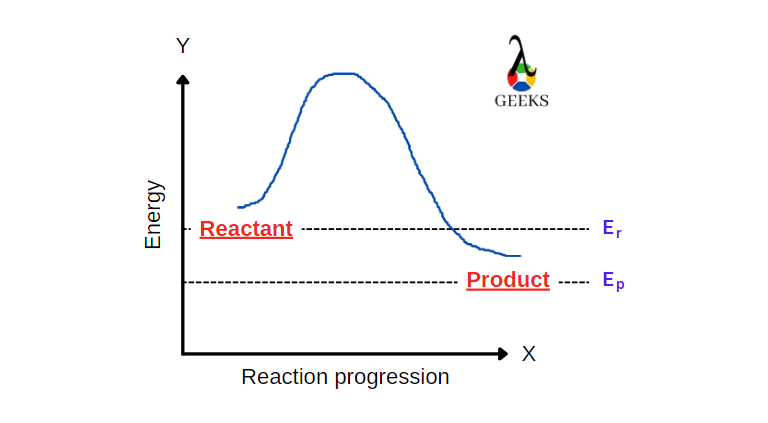
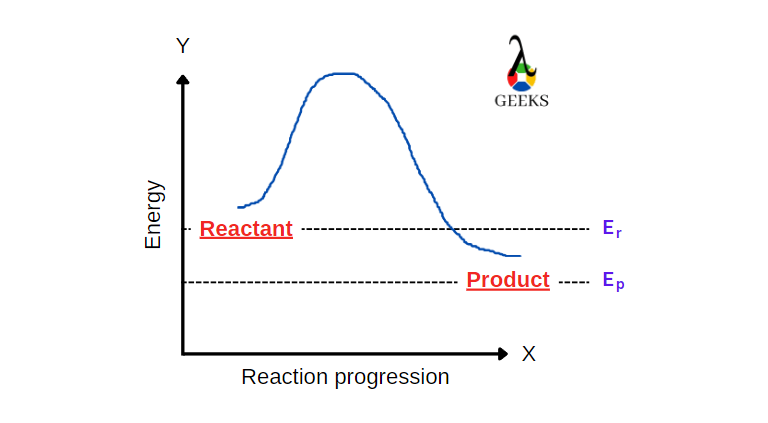
The Chemistry Behind HNO3 + Cl2: 15 Facts You Should Know
Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas with a suffocating smell which is not good for long-term inhalation. Let us see how chlorine reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) in the article below: Nitric acid (HNO3) and chlorine (Cl) react to chloric acid, nitrogen monoxide and water. Nitric acid (HNO3) is a strong corrosive metal acid and is … Read more