The pathogenic and parasitic fungi together form the relationship known as symbiotic, with the other living organisms in the environment. Though they gain an advantage at the expense of their hosts. Many trees and some other plants can get affected by these species. Some fungi parasite examples:
- Cryphonectria parasitica
- Puccinia sparganioides
- Candida albicans
- Claviceps purpurea
- Trichoderma reesei
- Ophiostoma ulmi
- Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Aspergillus flavus
- Septobasidium bogoriense
- Botrytis cinerea
- Pseudogymnoascus destructans
- Trichophyton violaceum
- Hypmyces lactifluorum
- Sparassis crispa
- Olpidium brassicae
- Phaeolus schweinitzii
- Puccinia graminis
- Beauveria bassiana
- Metarhizium robertsii
We will discuss a few fungi parasite examples here. Specially the plant parasitic fungus is the most harmful disease causing fungi. These are species of different fungi parasite that belong to different genus:
Cryphonectria parasitica
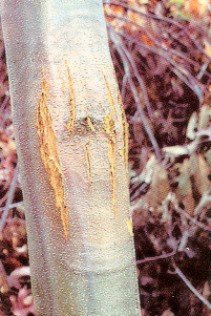
Cryphonectria parasitica is a kind of parasitic fungus that belongs to the trees of chestnut. Thus, this disease is popularly known as the chestnut blight.
The disease causing fungus Cryphonectria parasitica was previously known as the Endothia parasitica, which is a member of the Ascomycota that is a sac fungus. This is a necrotrophic fungus that means it kills the living cells of the host first and then gets their food from the dead organism.
The fungus carried by the C. parasite rapidly spread across both regions, causing severe tree loss. It enters infected trees through wounds that are usually filled with dead or damaged cells. It then kills the tree’s cambium by burrowing under the bark. The first sign of the infection is an orange-brown colour on the tree’s bark.
The inner bark are the first tissues of plant that are being targeted by the fungus. This is a part that contains the conductive tissue and also the cambium. This cambium is a sheet or coating of cells that are active in dividing. These cells help in giving rise to the secondary vascular tissues.
Puccinia sparganioides
The parasitic fungus named Puccinia sparganioides has an ash like texture that is responsible for causing rust disease in plants, and alsoincluds Spartina alterniflora.
Most ash species found in the east side of the Rocky Mountains are affected by the infection ash rust. It’s worse near the seaside, where it has alternative hosts such as cord and marsh grasses (Spartina spp.), that are present in huge amount.
The fungus consists of five stages of spores, out of which two need to develop on different hosts so that they can infected by the ashes. Telio-spores invade the existing tissues of ashes in the season of spring, that results in producing spermogonia and ultimately the aecia start to grow.
Candida albicans
Candida albicans is a kind of pathogenic yeast that has a quite aggressive nature. It is a well-known member which is present in the gut flora of humans. It can also exist independently of the human body.
In roughly amount of 40% to 60%, Candida albicans is present in the gastrointestinal tract as well as the mouth of adults who are healthy. This species is a member of the genus known as Candida, which is accounatble for the human ailment named Candidiasis.
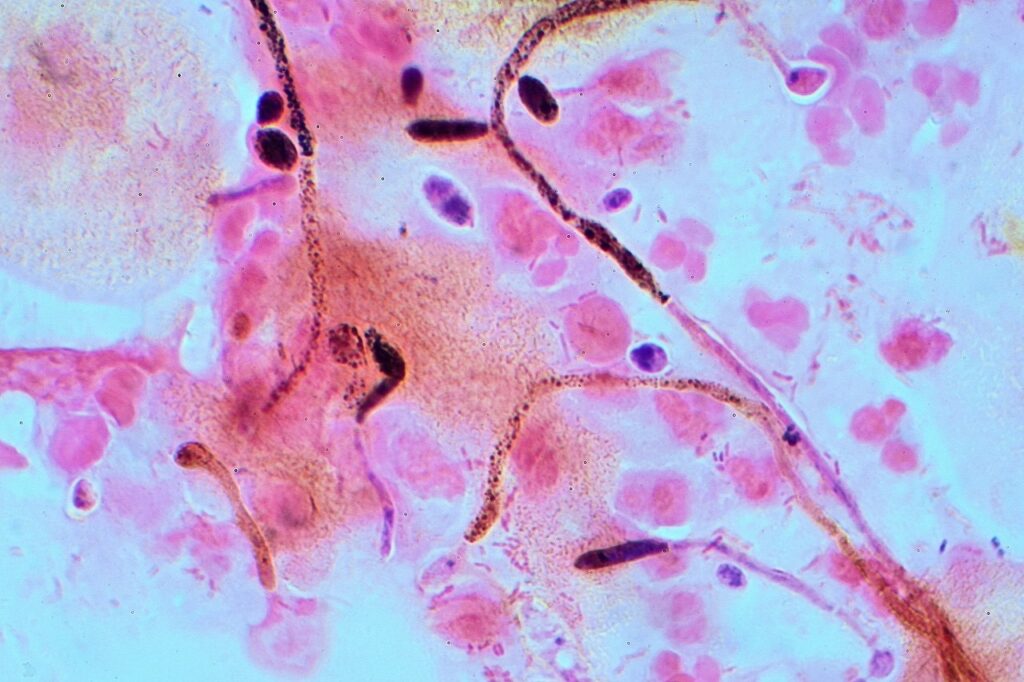
The infection Candidiasis takes place when there is an over growth of Candida albicans. This kind of diseases is generally seen in patients those are positive with HIV.
Candida albicans is a fungal pathogen that is frequently used as a model organism. It is also known as a dimorphic fungus since it can develop as a form of yeast as well as the form of filamentous cells.
Claviceps purpurea
Claviceps purpurea is a kind of ergot fungus that has the ability to grow on the ears of rye and some similar cereal and plants that are used to feed animals (forage plants).
Ergotism can be result of this fungus in humans and some other mammals by consuming grains or seeds that are contaminated with survival structure of the fungus, which is known as the ergot sclerotium. Only a small percentage of oats are affected by Claviceps purpurea.
Ergotism is a term used to describe a group of often severe clinical disorders that affect humans and animals after they consume plant materials that contain alkaloid with ergot, just like the grains that are contaminated with ergot.
Trichoderma reesei
Trichoderma reesei is a kind of mesophilic fungus with filaments. As it can produce cellulase, this fungus is a significant commercial and industrial microbe.
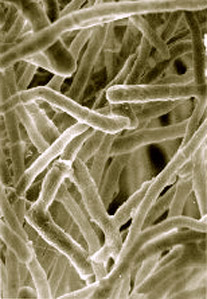
Ophiostoma ulmi
The fungus named Ophiostoma ulmi belongs to the family of Ophiostomataceae. It’s one of the substances that is responsible for causing Dutch elm disease.
Only the elm trees and Zelkova carpinifolia are attacked by this fungus. Thus, Ophiostoma ulmi has a limited range of host. The susceptibility of elms as hosts for Dutch elm disease is largely determined by the nature where they grow.
The bark and xylem tissue of the elm trees get infected by Ophiostoma ulmi. The vast majority of elms invaded by Ophiostoma ulmi are found in Europe, west central Asia, and North America. Ophiostoma ulmi has the ability to reproduce both by mating and without mating. disease.
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
The fungus named Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, that is generally known as Bd or the amphibian chytrid fungus, is responsible in causing the disease in amphibians named chytridiomycosis.
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infects amphibians who has keratinized skin. A thallus consists of a combination of rhizoids and smooth-walled, approximately spherical in shape, inoperculate, that is, without an operculum, sporangia in the epidermis. For every sporangium there is a one tube that helps in discharging the spores.
The fungus generates aquatic zoospores and mainly develops on the skin of amphibians. It can be found everywhere, ranging from the forests of lowland to the coldest mountain peaks.
Histoplasma capsulatum
Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus. Ajellomyces capsulatus is the name of its mating form. The disease named histoplasmosis is caused by this species and it can develop in lungs (pulmonary), and spread throughout the body.
Blastomyces dermatitidis is closely linked to Histoplasma capsulatum, which is an ascomycetous fungus. It’s dimorphic in nature that changes from a form of mould-like (filamentous cells) growth in the environment to a tiny, budding form of yeast in the warm-blooded animal host.
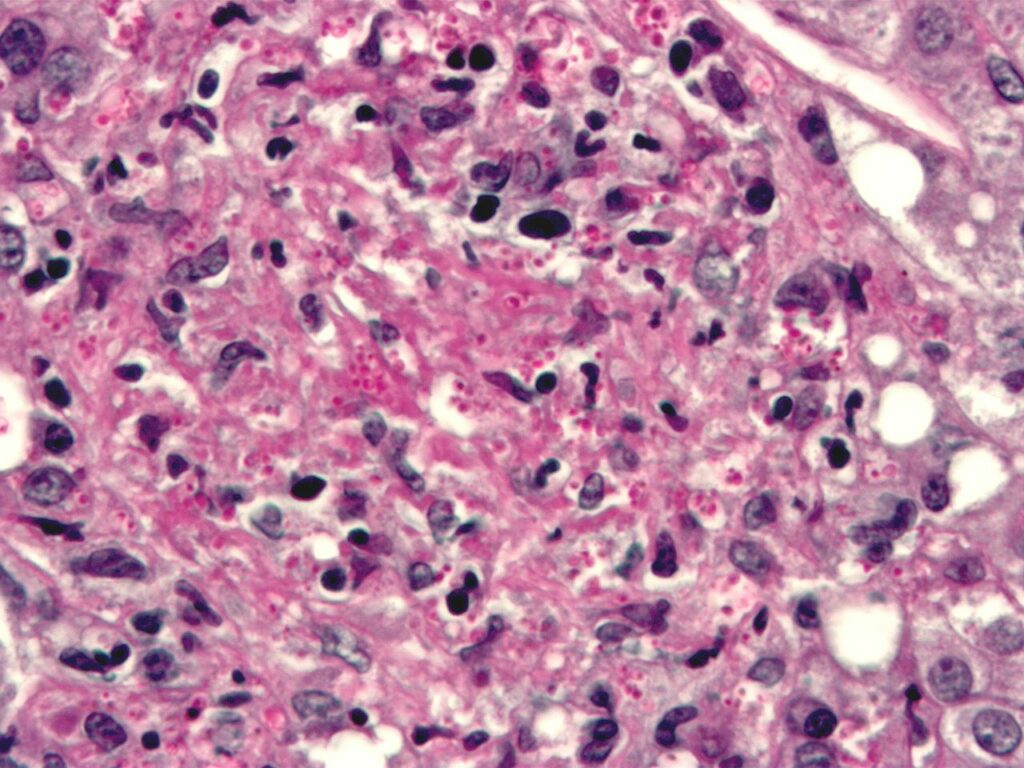
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection which is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum. Many people affected by histoplasmosis does not show any kind of visible symptoms. Histoplasma, on the other hand, can be responsible for causing diseases like acute or chronic lung disease.
Disseminated histoplasmosis, affects multiple organs. If left untreated, it can be lethal. Histoplasma with positive skin tests are found in up to 80% of people living in locations where Histoplasma capsulatum is prevalent, for example, the eastern and central United States.
Aspergillus flavus
The fungus named Aspergillus flavus is a type of global saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus. It is popularly recognised for the colonising of cereal grains, legumes, and other tree nuts.
Aspergillus flavus is a saprophyte that can be easily found in soils all over the world and causes illness in a variety of key agricultural crops. Ear rot in corn and yellow mould in peanuts are the diseases caused by Aspergillus flavus infection, which can either occur before or after harvesting.
Spores have the powdery textures of masses that is mainly of yellowish-green colour found on the upper surface and reddish-gold colour present on the lower surface of Aspergillus flavus colonies. Infection is limited to tiny areas in both grains and legumes, and infected areas generally loose its original colour that shows browning and roughness. Colonies have a downy or powdery appearance and grow quickly.
Septobasidium bogoriense
Septobasidium bogoriense is a type of plant pathogen that causes disease like “velvet blight” on tea plants. It is one of several fungi in the genus named Septobasidium that is responsible for the infection.
This fungus is unusual in that it has a mutualistic connection with its scale insect hosts instead of killing them. Despite the fact that it weakens the parasitized insects. The fungus gains profit from the interaction since it is fed by the waste materials produced by the insects.
The fungus does not harm them, and it provides profit to the entire colony by helping to protect them from wasps that are parasitoid by generating a mycelial mat that helps in hiding the insects.
Botrytis cinerea
Botrytis cinerea is a type of necrotrophic fungus that cause diseases to various plant species, whereas its most significant hosts are the wine grapes.
Symptoms vary across plant organs and tissues. Botrytis cinerea is a soft rot that will have a collapsed and water soaked appearance on soft fruit and leaves. The fungus causes two various types of infections on grapes.
The first type is- grey rot which is the happens due to the presence of humid conditions that are humid and consistently wet, and typically results in the loss of the affected bunches. The second type of infection is the noble rot that occurs when the condition is mainly dry and can give rise to unique sweet dessert wines, just like the Sauternes.
Pseudogymnoascus destructans
Pseudogymnoascus destructans is a psychrophilic fungus that means cold-loving and it causes diseases like white-nose syndrome (WNS).
Earlier this fungus was known as the Geomyces destructans which is cause of WNS. This disease can also cause death that’s decimated bat populations in portions of the US and Canada.
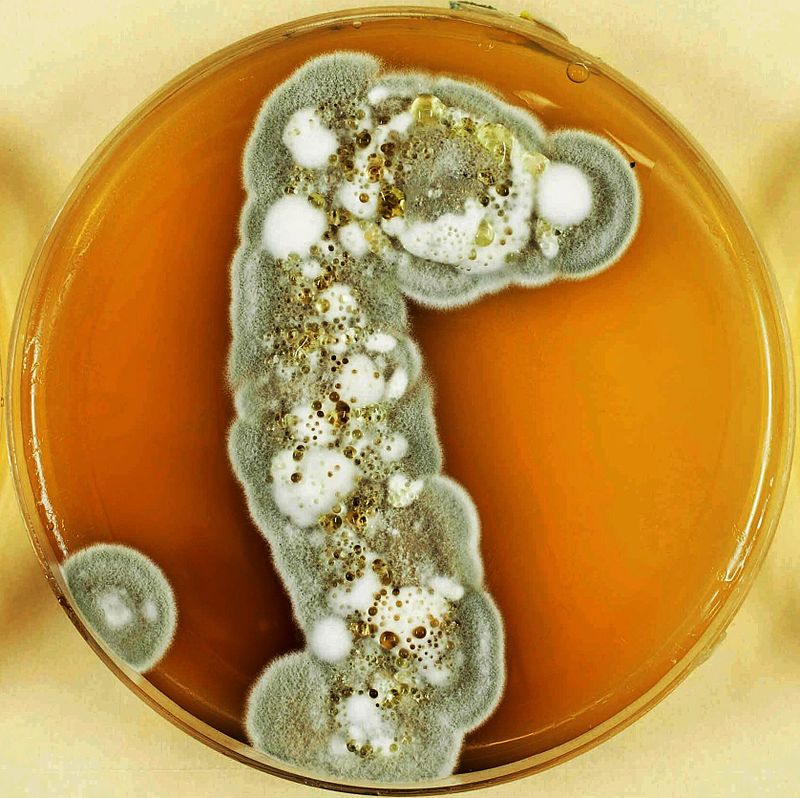
Pseudogymnoascus destructans is a slow growing fungus that grows an artificial media. This fungus cannot grow at temperatures which is above 20 °C. It can grow at a temperature between 4 °C to 20 °C, which includes the temperatures found in hibernacula for winter bats.
Trichophyton violaceum
Trichophyton is a fungus genus that comprises parasitic fungi that cause diseases or infections known as tinea just like athlete’s foot, ringworm, jock itch, and other diseases of nail, beard, skin, and scalp.
Dermatophytosis, or the fungal infection caused to the skin, is the result of the anthropophilic types of fungi. They are also keratinophilic in nature, that means they survive on keratin that are present in hair, dead skin and also nails. They can be spread through direct touch, contact with afflicted particles shed by the host (like nails, dead skin, hair), and also in contact with the spores of fungi.
These fungi usually grow in places that are warm, moist, dark in nature, for example, in between the toes of a foot that gets sweaty inside a tightly covered shoe, or in dead skin particles. Their spores are tough to eradicate and gets easily spread in the environment.
Hypomyces lactifluorum
Hypomyces lactifluorum completely engulfs its host, making it unrecognisable. They’re widely consumed and sometimes loved raw and fresh. They have a strong, thick texture and a flavour of seafood.
Hypomyces lactifluorum, also known as the lobster mushroom, is a parasitic ascomycete fungus that develops on some types of mushrooms, that gives them a reddish orange colour that is similar to the outer covering of a cooked lobster.
Individuals should avoid consuming lobster mushrooms with other hosts as because H. lactifluorum could parasitize a poisonous host. Hypomyces cervinigenus, Hypomyces chrysospermus, and Hypomyces luteovirens are some of the similar species.
Sparassis crispa
Sparassis crispa is a fungal species that belongs to the genus named Sparassis. In modern English, it is popularly known as the cauliflower fungus.
Sparassis crispa forms a tangled globe with a diameter of up to 60 centimetres, that is, 24 inches. The smooth oval spores measure around 5–7 m by 3.5–5 m and have a cream spore print. Clamp connections can be found in the flesh.

Phaeolus schweinitzii
Phaeolus schweinitzii, is often known as the velvet-top or dyer’s polypore fungus, is a fungus that causes butt rot in Douglas-fir and other conifers.
As they expand, the part of the fungus that gives rise to the fruits, that mainly occur in the late summer, generally consist of blades of grass, twigs, or few needles of fallen pine. The spores typically seem to be white in colour, elliptical in shape, smooth in nature and inamyloid spores. Brown bruising occurs in the pores.
Phaeolus schweinitzii is domestically found in North America side and Eurasia, as well as New Zealand, Australia, and South Africa. Though Phaeolus schweinitzii is not fit to eat.
Olpidium brassicae
Olpidium brassicae is widely found in the root parts of the field crops, particularly those belonging to the Brassicaceae family, which also includes canola.
Olpidium brassicae is a fungal obligate parasite that is found on plants. A fungus epidemic of Olpidium brassicae infected clover. Clover is an important part of nutrition that belong to the horses.
Puccinia graminis
The fungus named Puccinia graminis causes illness named stem rust, which is also known as cereal rust, black rust, red rust, or red dust. This kind of infection is a serious disease that occurs in cereal crops.
The stem rust fungus attacks the parts of the plant that are above ground. Spores that land on green wheat plants form a pustule that invades the outer layers of the stalk. The fungus that is responsible for causing stem rust targets the portions of the plant that are above the ground. Spores that land on green wheat plants produce a pustule that infiltrates the stalk’s outer layers.

Stem rust caused in cereal crops reduces productivity in a variety of ways:
- Fungus consumes the essential nutrients that could be used to help the grains grow further.
- Pustules pierce the epidermis, disrupting the plant’s ability to control perfusion and perhaps causing dehydration or loss of moisture and getting infected by any other fungi.
- Shrunken grains is the result of interference with the vascular tissues of plant.
- The fungus wilts the stem of the plants, causing them to lodge that means falling or breaking down. The process of lodging may hamper the mechanical harvesting impractical in extreme circumstances.
Beauveria bassiana
Beauveria bassiana is an entomopathogenic fungus that genrally grows in soils in the environment and functions as a parasite on many arthropod species, that causes infection like white muscardine.
Metarhizium robertsii
This fungus was earlier called M. anisopliae, and before that as Entomophthora anisopliae (basionym).
This is a parasitic fungus that naturally expand in soils in nature and is responsible for many diseases in a several insects.
Characteristics of parasitic fungi
Every parasitic plants contain haustoria, which are modified roots that pierce the host plant and attach it to the conducting system- xylem, phloem, or maybe both. They can remove water and nutrients from the host by the system.
A parasitic fungus’s body is made up of mycelium’s branching multicellular filaments called hyphae. The spores of parasitic fungi can be of different of sizes and forms. Obligate parasitic fungus takes nutrients from living tissues and, mostly is not able to thrive in nutritional media that are made artificially.
Conclusion
The parasitic fungus assault live creatures, breach their outer defences, infiltrate the living organisms, and take food from their cytoplasm, that causes sickness to the host and, in some cases, the host may also die.
Also Read: