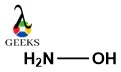NH3O Lewis Structure & Characteristics (17 Complete Facts)
NH3O is a parent class of the aminoxyl group. Let us discuss its characteristics in a detailed manner. NH3O or hydroxylamine involves bonding between N, O and H by a single covalent bond. Here the lewis structure is formed by sharing of electrons which fulfills octet rule at every aspect. The typical bonding is between … Read more