All the living species use up the energy that is released from respiration for the life process. There are two types of it.
The enzymes are a part of the cell components. The process of ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration takes place via there of the ways being-
Birds and the mammals need to have their energy maintained at a constant temperature in the body. Energy is thus needed for having the good synthesis of protein, for cell division. Have good active transport, better muscle contraction, good growth and nerve impulse. Respiration is the method that consists of several chemical process to have a breakdown of nutrients for energy.
Aerobic respiration takes place with the witness of oxygen. It gets to release quite a lot amount of the energy inside the cells by having the food materials to break with the use of the gas oxygen. The chemical equation for it refers with having glucose, oxygen and water with carbon dioxide as its results. The equation is C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O. It is the process of cell respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food

Aerobic respiration–Wikipedia
This type of respiration takes place all the time and thus the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration is also continues in both the plants and animals. Respiration and breathing both are not the same term. Most of the reactions in this type of respiration takes place in the cells in side he mitochondria called the power house of the cell. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products.
The energy that is meant to be released by using oxygen aids in the formation of a chemiosmosis potential, which is used to drive ATP synthesis across the membrane in aerobic respiration by pumping up protons. This advantage is then leveraged to have phosphate and ADP drive ATP production in aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is a series of enzyme controlled reactions that release the energy stored up in carbohydrates and lipids during photosynthesis and make it available to living organisms.
Glycolysis
It is said to be the very first step in ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration. It includes the breaking down of glucose to have the energy needed.
It is termed to be chain of equations and reactions that help in making of energy needed by the body. It is done by having the three molecules of carbon compound pyruvate broken down. It is an old way.
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms. Glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration, which occurs in all organisms. Glycolysis is followed by the Krebs cycle during aerobic respiration.

Glycolysis–Wikipedia
If we have only one molecule of the glucose and another is given to the lactobacillus acidophilus the bacterium that help in turning the milk to curd, then the outcome of both with the molecule of glucose shall be different. The metabolism of both the molecules shall be different with regards to the owner of the glucose molecules. In the absence of oxygen, the cells make small amounts of ATP as glycolysis is followed by fermentation.
The very first step in both the cases shall be same and that would be heling the molecules of glucose to split into two by getting them the method of glycolysis. This method is seen to be in use from long way and is seen in major part in the organism that is alive today. In all the organism that use up cellular respiration as a part of its process, glycolysis is the first step.
Glycolysis is the primary stage of cellular respiration. This metabolic pathway occurs when the glucose or sugar molecules break to release energy for cellular metabolism. The overall chemical reaction of glycolysis takes place within the cytoplasm of the cell. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C₆H₁₂O₆, into pyruvic acid, CH₃COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate.
Yet, with being every first phase for ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration it does not need any oxygen to perform and in many organisms that are anaerobic the organism does not tend to use oxygen and yet has its own way to have this method run well. Both of the types of respiration take up this process to be their first. This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists were Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century.
Citric acid cycle
This cycle is also said to be Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. It is actually a series of reactions that is chemical in nature.
On addition to its being the second phase in the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. The cycle uses up the precursors to of few amino acids and also the reducing product like NADH and then used in the other reactions.
The cycle isn’t all branded and is not vital for all the metabolites to get to follow specific rules at least with three of the alternate segments of the Krebs cycle that has been recognized. The name of this path is generated from the citric acid and is consumed and then makes by this sequence of the reaction to have the cycle completed. The citric acid cycle is a key metabolic pathway that connects carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism.

In eukaryotes, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria, just like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. In prokaryotes, these steps both take place in the cytoplasm. The citric acid cycle is a closed loop, the last part of the pathway reforms the molecule used in the first step. In the first step of the cycle, acetyl combines with a four-carbon acceptor molecule, oxaloacetate, to form a six-carbon molecule called citrate. The reactions of the cycle are carried out by eight enzymes that completely oxidize acetate.
The NADH makes by the citric acid cycle is taken into the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. The net outcome of the closed link paths is the nutrients of oxidation to make usable chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate. The reactants of this cycle get to convert the equivalents of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide into the reduced NAD to one GDP.
One of the basic sources of Acetyl-CoA is taken from breaking down of sugars by the method of glycolysis which shall yield pyruvate that in turn gets in decarboxylase by the product pyruvate complex. The yield of the compound pyruvate is made via the following reaction being CH3C(=O)C(=O)O−pyruvate + HSCoA + NAD+ → CH3C(=O)S Co Aacetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2.
This cycle is said to start with the transfer of the two carbon group called acetyl from the acetyl CoA to the four carbon acceptor compound oxaloacetate to the final product being citrate. This citrate then runs via the series of certain chemical conversations that helps loosen the two groups of carboxyl as carbon dioxide. This donated carbon becomes the backbone.
Oxidative phosphorylation
This is also called to be an electron transport chain and is a series of the organic molecules and proteins that is found in the inside of the mitochondria.
Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that is common to both the types of respiration and is the third phase in the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration. It is after the Krebs cycle and is concerned with the transfer of electron.
The electrons are said to be passed from one member to the other via a chain of redox reaction. All of the energy that is released in the reactions is captured as a gradient of proton that is used to make ATP is the method known to be chemiosmosis. Combining both the methods they are said to be oxidative phosphorylation. It is s defined as an electron transfer chain driven by substrate oxidation that is coupled to the synthesis of ATP.
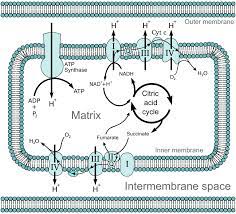
The key steps that this process consist of getting the electrons delivered by the FADH2 and NADH. There are the carriers of the reduced site of electrons from the rest of the steps for cellular respiration that helps to transfer the electrons to the molecules and then begin to have the chains transferred. In this method the process turned up to FAD and NAD that is reused.
Then there is the proton pumping along with electron transfers. As the electrons are passed via the chain, they are yet to move from the high level for energy to the low one that helps the release energy. Some of the energy that is used to get the hydrogen atoms pumped up is moved out of the space and then given to the intermembrane.
Next is the splitting up of the oxygen molecules to make water. The final stage of this chain, the electrons are converted to the oxygen molecules that gets to splits in the half and then takes up the hydrogen ion to make water. The last is the gradient that drives the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration that sues up ATP synthase. In the prokaryotes, this method is seen on the plasma membrane.
What is ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration?
Just unlike the aerobic process of respiration, this type of respiration is not bound with the use of oxygen.
It is the release of a small amount of stored energy inside the cells by having the food product broken down in the absence of the gas oxygen. Most of the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration is done by the method of oxidative phosphorylation.
The energy that is supposed to be released by suing of oxygen helps in making the making of a chemiosmosis potential which is used to have the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration driven across the membrane by having the protons pumped up. This advantage is then used to have the ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration driven from phosphate and ADP.
Anaerobic the of respiration is said to be seen in the muscles while having to work or exercise high. It shall involve lactic acid as outcome with glucose as its reactant and the equation is quite simple C6H12O6 → 2C3H6O3. Glucose is actually not fully broken in small parts thus there is less of the energy that is released that at the time of aerobic respiration.
In the equation of C6H12O6 → 2C3H6O3 lactic acid is seem to build up inside the muscles at the time of fast exercise. The lactic acids thus require to be repaid after the stopping of the workout. This is how one keeps on continues breathing deep for about a few time after one finishes their hard work out. In the process of anaerobic respiration, it results for about the production of 2 molecules of ATP.
Aerobic reparation is said to be divided into three of the main stages being the glycolysis, Krebs cycle and then the electron transport chain. In the first step of ATP synthesis in aerobic respiration called to be the glycolysis, the glucose is first made to split into molecules two in number of the glyceraldehyde phosphate with having 3 of them each.
After this it turns into having the compound called to be pyruvate that has 3 of the carbon molecules each. This results in having 2 ATP and then also 2 NADH. Glycolysis takes place inside the cytoplasm. The second step is being the Krebs cycle which is also termed as the citric acid cycle or the TCA cycle. This cycle is same for both the types of respiration methods.
The main and ultimate difference between the two type of respiration process is that aerobic uses up oxygen and anaerobic is done without the intervention of the gas oxygen. The main chemical that are seen in the Krebs cycle is a compound having two carbons called Acetyl CoA, citrate having 6 carbons and last the oxaloacetate having 4 carbons.
Krebs cycle results in making of carbon dioxide that one breathes out and take space inside the mitochondria. The last stage is the one that makes up energy is maximum way having 32 molecules of ATP than the rest having 2 each. This phase helps in getting the NADH and FADH2 converted to ATP. It also takes place in the power house of the cell like the Krebs cycle.
Also Read:
- Does bacteria have vacuole
- Unicellular fungi examples
- Do tissue cells have a nucleus
- Nucleic acid examples
- Are proteins inherited
- Zygote vs embryo
- Carbohydrates polymer examples
- Demosponge types
- Is exocytosis diffusion
- Are bacteria photosynthetic
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.