Arsenic is a metalloid, and it is found in minerals in combination with sulfur and metals. Let us explain the chemical properties of arsenic in brief.
Arsenic is a silver-grey, brittle, crystalline, and naturally occurring solid which is widely found in the earth’s crust. It is a common n-type dopant in semiconductors. It burns rapidly in the air at elevated temperatures and forms a white cloud of arsenic trioxide.
Let us discuss the position of arsenic in the periodic table as well as melting point, boiling point, allotropes, isotopes, radius, and ionization energies in detail.
Arsenic Symbol
The name of each chemical element is abbreviated to a short form for the convenience of writing. These are known as the chemical symbol. Let us see the symbol of arsenic.
The symbol of arsenic used in the periodic table is As. The name “arsenic” has come from the Greek word “Arsenikon” which means yellow pigment.
Arsenic Period in Periodic Table
The chemical elements belonging to the same period (horizontal row) have the same number of electron shells. Let us find the period of arsenic in the periodic table.
Arsenic belongs to the 4th period of the periodic table between germanium and selenium.
Arsenic Group in Periodic Table
The chemical elements belonging to the same group (vertical column) have similar type of physical and chemical properties. Let us check the group of arsenic.
Arsenic is a group-15 element and all these group-15 elements are known as pnictogens.
Arsenic Block in Periodic Table
Block in the periodic table is known as the set of elements grouped by their outermost shells. Let us see the block of arsenic in the periodic table.
Arsenic is a p-block element because it has an incompletely filled p-orbital in its electron configuration (4p3).
Arsenic Atomic Number
The atomic number (total number of protons) helps to identify any ordinary element as it is different for every element. Let us find it.
The atomic number of arsenic is 33 because it has a total of 33 protons in its nucleus.
Arsenic Atomic Weight
Atomic weight, the average weight of an element, is calculated to solve stoichiometry problems. Let us see the atomic weight of arsenic.
Arsenic has an atomic weight of 74.92 amu (atomic mass unit). This is considered to be the mass of one arsenic atom.
Arsenic Electronegativity according to Pauling
Electronegativity, measured through different scales, is the tendency of any atom to pull the electron pairs of a covalent bond toward itself. Let us discuss it in detail.
Arsenic has an electronegativity value of 2.18 on the Pauling scale. But this electronegativity value is 2.82 on the Sanderson electronegativity scale and 2.20 on the Allred Rochow electronegativity scale.
Arsenic Atomic Density
Atomic density is the ratio of atomic mass and atomic volume which is expressed as kg/m3 or g/cm3. Let us calculate the atomic density of arsenic.
Arsenic has an atomic density of 5.727 g/cm3.
Arsenic Melting Point
The melting point or liquefaction point (at which the solid starts melting) depends upon the standard pressure. Let us find out the melting point of arsenic.
Arsenic has a melting point of 816.80 C at 36 atmospheric pressure (atm). The liquid state of arsenic can only be possible at very high pressure.
Arsenic Boiling Point
The boiling point refers to a definite temperature at which the vapor pressure of an element becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. Let us comment on this.
Arsenic has no boiling point rather it has a sublimation point which means solid arsenic is directly converted into gaseous arsenic. It has a sublimation point of 6130 C.
Arsenic Van der Waals Radius
Van der Waals radius is one-half of the distance between two atoms, that are not attached through bonds and belong to two neighboring molecules of an element. Let us measure it.
Arsenic has a Van der Waals radius of 185 pm but it has a much lesser atomic radius of 115 pm.
Arsenic Ionic/Covalent Radius
Ionic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell of an ion whereas the covalent radius is one-half of the length of the covalent bond. Let us explain it.
The covalent radius of arsenic is 119 pm and the ionic radius of As (III) is 72 and As(V) of 60 pm.
Arsenic Isotopes
Elements having the same number of protons but a different mass number (proton+ neutron) are known as isotopes. Let us find out the isotopes of arsenic.
| Isotopes | Abundance (in %) | Decay mode |
| 73As | syn | ε, γ |
| 74As | syn | ε, γ, β+,β– |
| 75As | 100 | stable |
Arsenic Electronic Shell
Electronic shells are the different energy states at which the electrons are revolving, or it is defined by the outside part of the nucleus of an atom. Let us discuss it.
Arsenic has a total of 5 electronic shells and all 33 electrons are arranged in 2, 8, 18, and 5 manners in those 5 shells.
Arsenic Energy of First Ionization
The first ionization energy of an element can be quantitatively described as the equation X (g) + energy = X+ (g) +e–. Let us explain it.
The first ionization energy of arsenic is 947.0 KJ/mol.
Arsenic Energy of Second Ionization
The second ionization energy defines the energy needed to remove the least bound electron from an ion that is in a +1 oxidization state. Let us check it.
The second ionization energy needed to form As(I) to As(II) is 1798 KJ/mol.
Arsenic Energy of Third Ionization
The third ionization energy defines the energy required to pick up an electron from the +2 oxidization state of any atom. Let us find it for arsenic.
Arsenic has a third ionization energy of 2735 KJ/mol.
Arsenic Oxidation States
The oxidation state, the theoretical charge of an element, refers to the integral numbers which can be positive, negative, or zero. Let us explain it.
The following oxidation states of arsenic are possible-
- -3
- 0
- +3 (most organoarsenic compounds)
- +5 (most stable inorganic arsenic oxy compounds)
Arsenic Electron Configurations
Determination of electron configuration (arrangement of electrons in different shells) helps to describe the chemical bonds. Let us talk about this in detail.
The electronic configuration of Arsenic is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 because it has a total of 33 electrons.
Arsenic CAS Number
CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service) ID refers to a unique identification number written as three parts divided by two hyphens. Let us see the CAS number of arsenic.
Arsenic has a CAS registry number of 7440-38-2.
Arsenic ChemSpider ID
ChemSpider ID is a unique identification number that varies from element to element. Let us find out the ChemSpider ID of arsenic.
The ChemSpider ID of arsenic is 4514330.
Arsenic Allotropic Forms
Allotropic forms are the different forms of a chemical element. It also exists in those forms depending on their respective stability. Let us explain it.
There are 3 different allotropes of arsenic possible in the earth.
| Name of the allotropes | Structure |
| Grey arsenic (most stable) | Rhombohedral |
| Black arsenic | Orthorhombic |
| Yellow arsenic | Tetrahedral |
Arsenic Chemical Classification
Depending on the properties and position in the periodic table, the chemical classification of the element is done. Let us discuss it in detail.
Arsenic can be chemically classified as a nitrogen group element or pnictogen element.
Arsenic State at Room Temperature
The state of any compound can be generally three types. They are solid, liquid, and gas. Let us check whether arsenic is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature.
Arsenic is available in nature as a solid compound because it has a much higher melting and sublimation point.
Is arsenic paramagnetic?
The paramagnetism of any compound can be determined by the presence or absence of unpaired electrons. Let us check whether As is paramagnetic or not.
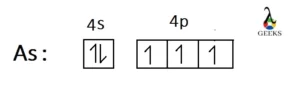
Arsenic is a paramagnetic compound because it has a total of 3 unpaired electrons in its 4p orbitals that are attracted by the external magnetic field and show weak magnetism.
Conclusion
Though arsenic is not so nature-friendly chemical element, it has various uses as a pesticide, herbicide, and insecticide. Few bacteria also use arsenic in their respiration.
Read more about Is Arsenic Malleable Or Brittle Or Ductile?

Hello,
I am Aditi Ray, a chemistry SME on this platform. I have completed graduation in Chemistry from the University of Calcutta and post graduation from Techno India University with a specialization in Inorganic Chemistry. I am very happy to be a part of the Lambdageeks family and I would like to explain the subject in a simplistic way.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditi-ray-a7a946202