Argon is a colorless odorless gas, and it exhibits a violet glow after placing in an electric field. Let us discuss the different chemical properties of argon in detail.
Argon is the 3rd most abundant element in earth’s atmosphere and is considered a chemically inert gas. Most of the argon gas is formed during the decay process of potassium-40 in the atmosphere but industrially it is extracted by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is 2.5 times more soluble in water than N2.
Let us focus on the isotopes, melting as well as boiling point, ionization energies, radius, and the position in the periodic table of argon elaborately.
Argon Symbol
The symbol of argon used in chemistry is “Ar” which is the first two alphabets of the word “argon”. It comes from the Greek word “Argos” which means lazy or inactive.
Argon Group in Periodic Table
Argon belongs to group 18 which is a group of noble gases. It is placed between neon (Ne) and krypton (Kr).
Argon Period in Periodic Table
Argon belongs to the 3rd period in the periodic table between chlorine (Cl) and potassium (K).
Argon Block in Periodic Table
Argon is a p-block element because it has a fulfilled p-orbital and the last electron of argon enters into the p-orbital.
Argon Atomic Number
Argon has an atomic number of 18 because it has 18 protons and 20 neutrons in its nucleus.
Argon Atomic Weight
Argon has an atomic mass of 39.948 amu (atomic mass unit) which is regarded as the mass of one argon atom.
Argon Electronegativity according to Pauling
There is no electronegativity data of argon in the Pauling scale. But it shows different electronegativity of 3.31 and 3.20 in Sanderson’s electronegativity scale and Allred Rochow’s electronegativity scale respectively.
Argon Atomic Density
Argon has an atomic density of 1.40 Mg/m3.
Argon Melting Point
Argon possesses a very low melting point of 83.81 K or -189.340 C.
Argon Boiling Point
The boiling point of argon is also very low 87.302 K or -185.8480 C like its melting point.
Argon Van der Waals Radius
Argon has a Van der Waals radius (half of the distance between two unbounded atoms) of 188 pm and it has an atomic radius of 98 pm.
Argon Ionic/Covalent Radius
Argon has a covalent radius (half of the distance between two atoms attached through covalent bonds) of 106 pm. But it has no ionic radius because it does not form ions under standard conditions.
Argon Isotopes
Isotopes have the same number of protons, but they differ in the number of neutrons. They also have the same position in the periodic table. Let us find out the isotopes of argon.
| Isotopes | Abundance (in %) | Decay mode |
| 36Ar | 0.334 | stable |
| 37Ar | syn | ε |
| 38Ar | 0.063 | stable |
| 39Ar | trace | β– |
| 40Ar | 99.604 | stable |
| 41Ar | syn | β– |
| 42Ar | syn | β– |
Argon Electronic Shell
Electronic shells are defined as the different energy states for placing electrons outside the nucleus. Let us find out the electronic shells of argon.
Argon has a total of 18 electrons in its three electron shells. They are arranged in these three shells in 2,8, and 8 fashion. It means the first two electrons enter in the 1st shell followed by 8 electrons in the 2nd and the last 8 electrons in its 3rd shell.
Argon Energy of First Ionization
Argon has the first ionization energy of 1520.6 KJ/mol.
Argon Energy of Second Ionization
Argon has the 2nd ionization energy of 2665.8 KJ/mol which means it needs 2665.8 KJ/mol energy to remove the 2nd electron from its valence shell.
Argon Energy of Third Ionization
Argon has the third ionization energy of 3931 KJ/mol. Due to the complete shell electron configuration, all of the ionization energies of argon are very high.
Argon Oxidation States
Argon can exist in only one oxidation state which is 0. Therefore, the formation of argon compounds is not possible.
Argon Electron Configurations
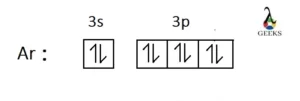
Argon has a closed-shell electron configuration which is [Ne] 3s2 3p6. Therefore, it is considered chemically inert.
Argon CAS Number
Argon has the CAS registry number (authentic numeric identifier which can contain upto10 digits) 7440-37-1.
Argon ChemSpider ID
Argon has the ChemSpider ID (ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database) 22407.
Argon Chemical Classification
Argon can be chemically classified as a p-block element which is also known as a noble gas or inert gas.
Argon State at Room Temperature
Argon is a gaseous compound at room temperature (200 C). It is the 3rd most common gas in the earth’s atmosphere.
Is argon paramagnetic?
Paramagnetism is proved by the presence of unpaired electrons and these electrons are weakly attracted by the external magnetic field. Let us explain it in detail.
Argon is not a paramagnetic substance because all of its electrons are paired up. Therefore, it is known as a diamagnetic compound.
Conclusion
Argon is used in welding and other high-temperature industrial methods to build up an inert atmosphere like in graphite electric furnaces to prevent graphite from burning. It is also applied in incandescent along with fluorescent lights and gas-discharge tubes.

Hello,
I am Aditi Ray, a chemistry SME on this platform. I have completed graduation in Chemistry from the University of Calcutta and post graduation from Techno India University with a specialization in Inorganic Chemistry. I am very happy to be a part of the Lambdageeks family and I would like to explain the subject in a simplistic way.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditi-ray-a7a946202