Anaerobic respiration is the type that includes the use of electrons accepting the rest molecules of oxygen. Oxygen is not the only one that gets accepted.
The anaerobic respiration stages include-
The electron transfers with also combining oxidative phosphorylation. Anaerobic respiration is of two types being alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Respiration is the chemical process that takes place in the living cells and then sets to release energy from the glucose. Anaerobic respiration takes place without the presence of oxygen and then releases not so much of the energy and is quick in aerobic respiration. the sum total of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which oxygen is conveyed to tissues and cells, and the oxidation products.
Respiration and breathing are not similar terms. The name for respiration being scientific is given to be ventilation. Respiration release the stored energy in order to have the cells to stay alive. There are two types of respiration-
- Aerobic respiration- This respiration takes place in the presence of the oxygen and is seen in all the cells mostly all the time.
- Anaerobic respiration– This takes place with no oxygen and is much less seen that the aerobic one.
Respiration takes place within the mitochondria and they are seen inside the cytoplasm. The cells that need more of the energy just like the sperm cells that tend to swim. Another example can be the muscle cells that need to relax and contract and thus have more of mitochondria. Other like bacteria and yeast perform fermentation type.
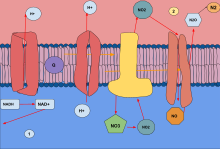
Humans tend to use both types of the perspiration process. They do aerobic respiration till they run short of oxygen and then they need the urge to switch to anaerobic respiration and then it where the anaerobic respiration stages come to play. The anaerobic respiration inside the microbes is called to be fermentation. In physiology, respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues, and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction
Some example of anaerobic respiration can be the lactic acid fermentation. The decomposition of the organic matter and the alcohol fermentation. Humans only use up the anaerobic respiration stages while they lack oxygen and this case is little. This type of respiration takes place in the muscles. It gives energy for cell to function.
Making of ATP without oxygen (anaerobic respiration step)
ATP is the short term linked with adenosine triphosphate and is the power provider of cell for its functions.
All of the living beings make up ATP in the cells from the glucose and in the method during the time of cellular respiration. This process takes up in phases and can be termed to be the anaerobic respiration stages.
The process of Krebs cycle and the electron transport need the use of oxygen that makes the cell respiration a process called the aerobic process. The time when oxygen is not available inside the cells, the ETA is quick to shut down. There are yet many ways to make ATP from glucose that are anaerobic and this method is called anaerobic respiration.
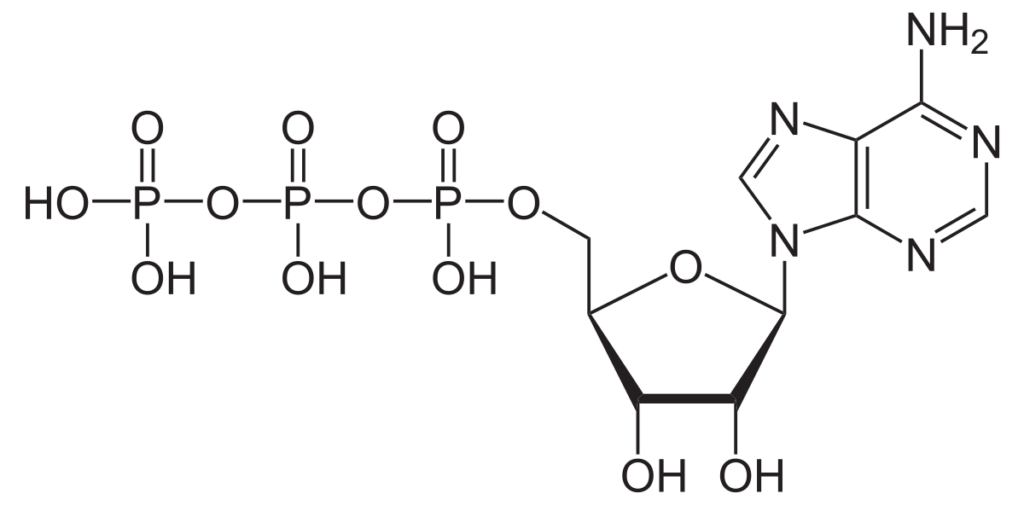
Adenosine triphosphate–Wikipedia
One also vital way of forming ATP with no use of oxygen is by fermentation. The method of fermentation starts up with the glycolysis that uses up no oxygen. Fermentation is said to be of two types being the lactic acid and the alcoholic. There is a use of both types with only lactic acids taking place in humans.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a linear path for all the reactions making the use of enzyme as a catalyst converting glucose to pyruvate.
One of the anaerobic respiration stages include the method of glycolysis. It is a path that helps in converting of the glucose into the two molecules of the pyruvate with the use of oxygen or also in two lactate molecules with no oxygen.
In this very process the glucose is broken down to make energy. It makes up molecules of pyruvate, water, NADP and ATP. This method is seen inside the cytoplasm of any cell and also does not need any oxygen. It takes place in both the organism that are anaerobic and aerobic. Glycolysis means breakdown or dissolution.
It is vital in most of the living cells and is a good source of energy and also a source for the precursors for several other metabolic methods. The rate of getting the carbon flown via glycolysis is mostly glucose that is converted to per unit pyruvate and meets the basic needs of the cells. Yet, from energy, this anaerobic respiration stage is inefficient.
In mostly all the animals, the muscles tend to exhibit the anaerobiosis that is based on activity and can work without oxygen for short time. No only animals but also athletes that work put intense need ATP that exceed the work of the body to provide oxygen to the muscles. Thus, here the muscles tend to function for a shorter time in the mode of anaerobic respiration.
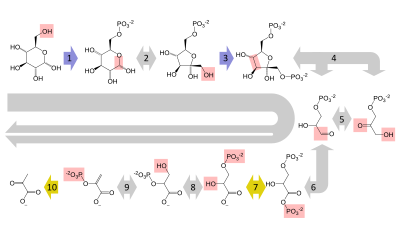
Glycolysis–Wikipedia
Other example can be an eye part called the cornea that has a poor vascular tissue. It can also be said that the process of glycolysis shall play a good role as an energy sources. It is the only energy giver to the sperm cells, the red blood cells, the brain that uses ketone for fuel and at least for the adrenal medulla.
The link reaction
If there is a presence of oxygen while respiration, glycolysis if followed up by chain of reactions to oxidase pyruvic acid molecules.
The step 2 of the anaerobic respiration stages is called the link reaction. This is also as it connects the method of glycolysis with the next step being the Krebs cycle that helps in complete oxidation.
The very starting component of the link reaction is said to be the pyruvic acid and is the molecules that comes out of the glycolysis. Here are generation of two pyruvates for each of the molecule of glucose that shall enter the process of glycolysis. Via this, glucose is pretty worked upon at glycolysis along with enzymes used to bond chemically.
The enzymes make two NADHs and two again ATP, while there is enough pyruvic acid for energy that is kept intact in the cell. The storage begins at the link reaction where it is placed in their ways. The number of ways that help the link reaction described well or work is three. During aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid which is formed during glycolysis enters the mitochondrial matrix. It undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to produce CO2 and NADH.
The link reaction starts with pyruvic and diffuses in mitochondria. As it enters the enzymes slips the carboxyl group. Snipping carbon dioxide helps make one third of the CO2 made in cell respiration. Pyruvate has a double bond and one oxygen and is linked with the second molecule of oxygen having negative charge.
The second step here leaves the pyruvate and then gets it oxidase. The energy in the electrons get harvested in the flow of oxidation to move the NAD which is the electron carrier and then reduces the NADH. The outcomes of tis is being left with two molecules of carbon called the acetyl chain. The product combines with sulfur-containing co-enzyme A to form acetyl CoA.
There is a compound of C2H30 left behind after the completed of the second phase of anaerobic respiration stages. The enzymes link to the acetyl group to the Coenzyme A, that helps by acting like a shuttle and then delivering the acetyl for the start of Krebs cycle. This combination is called the acetyl CoA. This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase. This step is called link reaction or gateway step as it links glycolysis with Krebs’ cycle
Krebs cycle
It is considered to be seen at the center part of the aerobic process. Aerobic process uses up oxygen as well.
This cycle can be called for in three names. Krebs cycle was the name given for Hans Krebs who was the scientist who researched out this cycle in the 1930s. He also won the Nobel award for the work in 1953.
It is also called as the citric acid cycle. It is called so for the presence of six carbon ring citrate that makes the beginning of this specific cycle. One can keep an eye on the formula of citric acid for this. Another name given to this is the TCA cycle which is an acronym for the tri-carboxylic acid. s a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
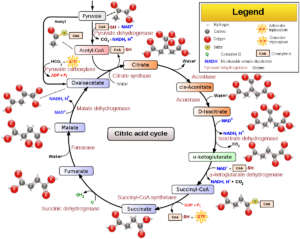
The Krebs cycle–Wikipedia
TCA cycle is the name given for the other from of citric acid. Acetyl CoA takes chemical energy in the cycle in the form of two groups of carbon acetyl. These two of carbos along with its link with the hydrogen atom are at a point same to that of the glucose portion. While at the start of the third phase of the anaerobic respiration stages, all the enzymes detach. The Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate.
There is a detachment of two groups of carbon from the Acetyl CoA and then links to the carbon molecule having four of it and is called the oxaloacetate. The outcome of it is the six molecule called the citric acid. The other part of the cycles involves enzymes that can arrange molecules, reduce the carboxyl groups, helps in the reduction and oxidation reaction and also for substrate level phosphorylation.
Energy in the form of two carbon molecule enter the cycle. This two molecule links with four carbon atoms called oxalic making a citric acid. At the time of the cycle, the cell stored one ATP. Three of the NADHs and one FADH2. Two of the carbon dioxide is released as waste. For all the entry of glucose, there is a run of twice Krebs cycle and this cycle take place in the mitochondria. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid that is a tricarboxylic acid, often called citrate.
Electron transfer
This takes place where there is a relocation of the electrons from any molecule or an atom to another entity being same.
It is defined as a methodical way of defining several kinds of the redox actions that consist of getting the electrons transferred. All of the electrochemical methods are said to be the electron transfer reactions. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, which are the basis of the ionic bond.
Most of the reactions that have electron transfer are related to mostly respiration or photosynthesis. They have one of the wider and most vital classes in the reaction of chemistry and more often in biochemistry. Here there are more than one element involved and an element seems to go oxidation and the other occurs reduction. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration.
There are three types of electron transfer for the anaerobic respiration and they are inner-sphere electron transfer, the outer sphere electron transfers and the heterogeneous electron transfer. The electrons are tending to be seen in the shells surrounding the nucleus of atom. They tend to move out if its shell to give energy with protons needing high energy to break the force.
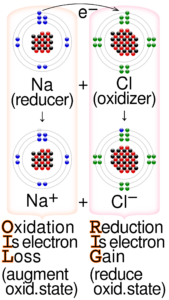
An example can be In the aluminum‐oxygen example, the aluminum was oxidized, and the oxygen was reduced because every electron transfer reaction involves simultaneous oxidation and reduction. The electron transport chain is a series of proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The proton gradient produced by proton pumping during the electron transport chain is used to synthesize ATP. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, which are the basis of the ionic bond.
Also Read:
- Types of rna splicing
- Chloroplasts in cytoplasm
- Endotoxin bacteria examples 2
- Cofactor examples
- Do bacteria have enzymes
- Types of rna polymerase
- Crustacean examples
- Parasitism examples
- Turbellaria characteristics
- Medusozoa characteristics
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.