DNA is also referred to as deoxyribonucleic acid and is a molecule made up of two chains of polynucleotide which has coils around each of them making a double helix.
With concern to the question of what is conservative DNA replication, it is the whole original double helical structure of DNA that acts as a template for the new helix that is formed. It is made in such a way that each of the way of cell division makes one daughter cell with a whole new helix and another daughter cell.
The DNA is supposed to be that molecule which carries all the genetic data inside it so that the feature can pass via the parent to the new ones. It helps in growth, the function and the development of the organism along with also having the part in its reproduction. It is a type of nucleic acid. Nucleic acid is one of the vital types of macromolecules needed for life.
There are two strands in the DNA and is thus said to be double stranded. The two of the strands in DNA are called as polynucleotides and is made of tiny simple monomeric units known as the nucleotides. Each of the nucleotide is made up of one of the four bases of nitrogen having the nucleobases. DNA and RNA have the same kinds of nuclobases except one.
The nucleobases seen in the DNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. It also has a sugar in it called the deoxyribose and a group of phosphate. They are joined to each other in a chain like format by the covalent bonding. This bond is seen in between the sugar and one of the nucleotide with the next being phosphate that results in a formation of an alternating phosphate-sugar backbone.
The conformation of the DNA can be in many possible ways which insist on B-DNA, A-DNA and also Z-DNA. The ones that have been seen now are the B and the Z DNAs. The adoption of the conformation of the DNA is based on the level of hydration, the sequence of DNA, the process of supercoiling and its way, the modification in the chemical composition of bases.
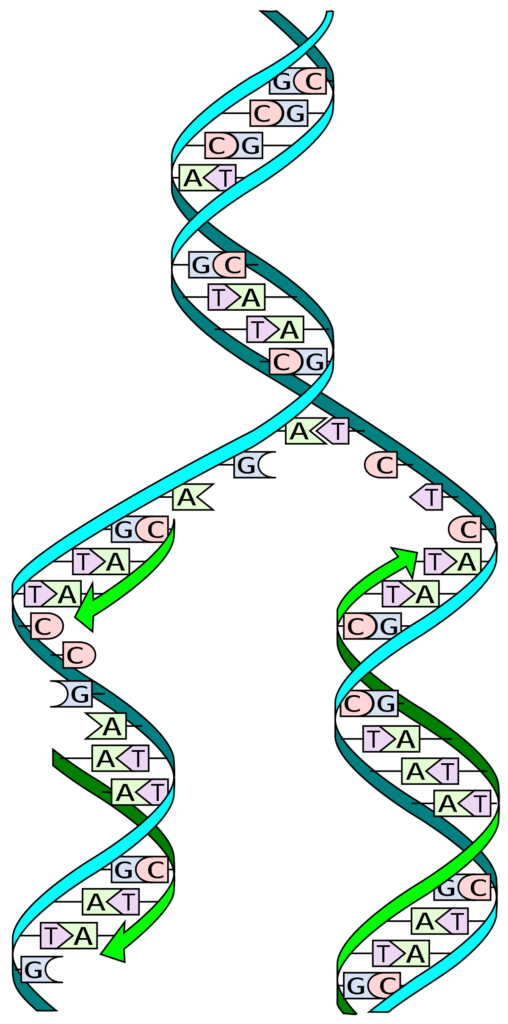
The series for the steps in DNA replication for most of the organism are-
- Initiation
- Primer Synthesis
- Leading Strand Synthesis
- Lagging Strand Synthesis
- Primer Removal
- Ligation
- Termination
Is the process of replication called conservative DNA replication?
DNA replication is the method that takes place in all the living beings and is based on the concept of biological inheritance.
The process of DNA replication is called to be a semi conservative process and it is so cause of the one that is newly made DNA strand. One of them is the original and the other is new made from the original.
The method of getting the DNA replicated is actually semi conservative as each of the helix that is made have only single strand from the helical form that has been copied. It is also said to be conservative for the half of the portion of the each original helix is conserved in each of the new formed strand. They are ubiquitous enzymes in the cellular milieu functioning in diverse processes including DNA replication, DNA repair, RNA transcription and translation.
It has already been shown that the DNA that has been replicated by the process of semi-conservation method in the WT-4 cells has been grown at the 34 degrees or at the temperature of 38.5 degrees at the entire phase of log and into also the stationary phase. The initiation of DNA replication occurs in two steps. First, a so-called initiator protein unwinds a short stretch of the DNA double helix.
Helicases are enzymes that bind and may even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid protein complexes. DNA helicases are essential during DNA replication because they separate double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. It is a duplication process where exact copies of DNA within cells are replicated, with very low error rate.
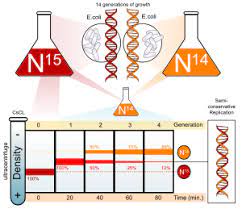
There was provision for three of the points to be kept in mind during the method of DNA replication. It was explained by Stahl and Meselson who established a way to get to the fact of knowing the process of DNA replication to be either of the three. They conducted an experiment to prove it via-
- There was suggestion for there of the model for DNA replication being dispersive, conservative and semi-conservative.
- The method that was conservative suggested that the original DNA stays same and hooked up and the one that is made new links up with the original.
- The method that was dispersive said that post the process of replication, the two of the daughter DNA that is formed have sugar segments in the alternate manner for both of the parents and the new one synthesized interspersed on two strands.
- The process being semi conservative suggested that the two DNA that acted as parents served to be a template for the new formed DNA and post replication, each of the double strands of DNA had one parental and other to be the nee called the daughter strand.
Is prokaryotic DNA replication conservative?
Watson and Crick had discovered the DNA to be double helix and provided a hint about how the DNA had been replicated.
There needs to be a replication process to ensure the process of gene transfer and hereditary. Just unlike the eukaryotes, the pyrimidine is made to synthesize. The replication in it is concerned to be semi-conservative and not being conservative.
On regard to the question of what is conservative DNA replication, at the time of cell duplication each of the molecules of DNA is copied at its best to ensure that all the molecules move to each of the daughter cells. The double structure suggests that at its replication time it serves as a template that the two of the strands meet to get separate. DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule.
In the process of conservative model of replication, the two of the pieces of DNA that is original is called the parent strands and appear to re base pair along with each other after being sued up as a template to get them synthesized and the two of the new ones are called as daughter strands acting as base pair. The double helix separates so that each old strand serves as a template for a new strand. Two new double helices result, each containing one new strand and one old strand.
One of the strands that are referred is called the old one and the other is referred to as the new one. In the process of semi-conservative one each of the two original strands act as a template for the new ones and after getting replicated each of the DNA strands make base pair with the complementary new one including the old one. The parental molecule directs synthesis of an entirely new double-stranded molecule.
Stahl and Meselson were quite interested in getting to know about the replication of DNA. They tested in the bacteria called E.coli for multiple generations in the medium that had heavy isotopes of nitrogen being 15N and 14N. N14 is said to be the light one and with the other being heavy form of isotope and thus the cell grew. In bacteria, the initiation of replication occurs at the origin of replication, where supercoiled DNA is unwound by DNA gyrate.
Is eukaryotic DNA replication conservative?
Eukaryotes are the organism that has nucleus covered inside a nuclear envelope. They have organelles having a membrane.
Within the eukaryotes, the majority of the synthesis in DNA takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle and the whole genome is said to untangled and copied to make the daughter cells. This process of DNA replication is semi conservative in eukaryotes.
The process of DNA replication in the eukaryotes is quote a conserved method that gets the restriction of replication per cycle. The central for replication is the chromosome and is vital for having the genome of the eukaryotes maintained. It is a process being semi conservative. A laboratory technique used to replicate, and thus amplify, a specific DNA segment.
The action of polymerase having to synthesize the strand of DNA complementing the original strand of DNA is said to be DNA replication. The cells of eukaryotes have within the organelles that have membrane like that of Golgi apparatus and mitochondria. Plants and the algae have chloroplasts in them. It contains one newly synthesized strand and one newly synthesized strand. The model of semi-conservative DNA was anticipated by Nikolai koltsov.
Eukaryotes–Wikimedia
DNA helicase helps in getting the DNA strands to unwound making a form of fork called the replication fork and have two of the template being single stranded. The process of replication entertains the copy of the single DNA into two helixes. The major use of enzyme is carried out by the replication fork and is much conserved from eukaryotes to prokaryotes.
One of the threads mentioned is called old and the other thread is called new. In semi-conservative analysis, each of the two original strands serves as a template for a new strand, and after replication, each DNA strand base-pairs with a new, complementary strand, including the old one. Both the eukaryotes and prokaryotic cells have replication process to be semi conservative.
Is bacterial DNA replication conservative?
Bacteria are the organism that have single cell and are microscopic and are found in millions of its forms and in every surrounding in and out of organism.
The method of DNA replication is anyhow seem conservation in any type of organism be it prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Thus bacteria have the process of replication being semi-conservative where one behaves as parents and the other is new.
While there was an experiment that said the process of replication to be semi conservative in bacteria, it has been said that it is just not in E.coli that the method is semi conservative but applies to other forms of bacteria as well. There has been no proof that says the process to be dispersive or conservative form of replication. DNA replication is the process of making copies of DNA. DNA replicates by semi-conservative replication.
this means which means that one strand of the parent double helix is conserved in each new DNA molecule. As for the question of what conservative DNA replication is, during cellular replication, each DNA molecule is copied in the best possible way to ensure that all molecules migrate to their respective daughter cells. The double structure suggests that the two strands meet and serve as a template for separation during replication.
The method used to replicate DNA is actually semi-conservative. This is because only a single strand of the spiral is copied to each generated spiral. This is also called conservative, as half of each original helix is preserved in each of the newly formed strands. The parental strands f DNA re always separated to make a new one. For most eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the process of DNA synthesis is done semi conservatively. Semiconservative replication for E. Coli is initiated by way of a replicon structure which behaves as an autonomous unit of DNA replication.
DNA replication is said to be semiconservative because each newly made DNA molecule has one original and one new strand of DNA. A laboratory technique used to replicate, and thus amplify, a specific DNA segment. This process is known as semi-conservative replication because two copies of the original DNA molecule are produced, each copy conserving (replicating) the information from one half of the original DNA molecule. The conservative method of replication suggests that parental DNA remains together and newly-formed daughter strands are also together.
Also Read:
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.