Uranium (U) is a radioactive silvery-grey chemical element that belongs to the actinide series of the periodic table with atomic number 92. Let us look into the uses of uranium.
The applications of uranium in different fields are listed as follows:
- Defense Manufacturing Industry
- Civilian Industry
- Industrial Sector
- Food-processing Industry
- History and Culture
- Other Uses
Defense Manufacturing Industry
- Depleted uranium (uranium which has a lower content of the fissile isotope) is alloyed with 1-2% additional elements such as molybdenum or titanium.
- The military utilizes uranium to power nuclear submarines.
- Certain containers used for storing and transporting radioactive materials utilize depleted uranium as a shielding component.
- Uranium, for its high density (19.1 g/cm3) is used in gyroscopic compasses, navigation systems and sensors.
Civilian Industry
- Enriched uranium (U-235) is utilized as a primary fuel source in nuclear power plants for the generation of electricity.
- Uranium-235 is used as a source of thermal power in the nuclear reactors that run navy ships and submarines.
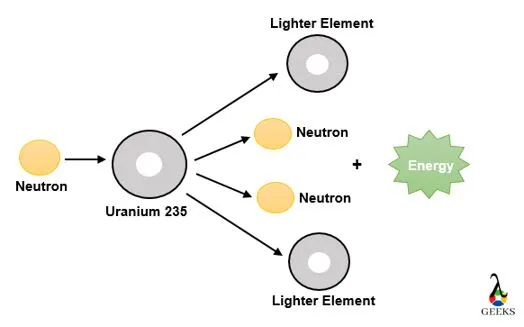
Industrial Sector
- High energy X-rays are created using uranium, which is also utilized as an X-ray target.
- The radioactive isotopes of uranium are frequently utilized in aeronautics, metallurgy, and automobiles for safety and quality control.
Food-processing Industry
Irradiation destroys parasites, bugs, and bacteria, hence isotopes of uranium are employed to sterilize and preserve food products.
History and Culture
The isotope uranium-238’s long half-life makes it well-suited for estimating the age of the archaeological remains of the earliest igneous rocks as well as other methods of radiometric dating, such as uranium-uranium dating, uranium-thorium dating, and uranium-lead dating.
Other Uses
- Uranium serves as a toner in photographic chemicals (particularly uranium nitrate)
- Uranium is utilized in lamp filaments for bulbs in stage lighting.
- The wood and leather industries use uranium for dyes and stains.
- In earlier times, uranium was used largely as a colorant in pottery and ceramic glazes and for coloration in early photography.
Conclusion
Uranium, with an atomic mass 238.028 u, is one of the Earth’s heaviest naturally occurring elements. It is malleable and ductile in nature. It is well-known for being a rich source of concentrated energy. There are 3 major isotopes of natural uranium: uranium-238, uranium-235, and uranium-234.

Hello, I am Padmakshi Kotoky working as a Subject Matter Expert on this platform. I have completed my post-graduation from the Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai. I have always found Chemistry an intriguing subject and enjoy exploring more on it. I would like to utilize this platform to explain the subject in an easy and precise manner making it simpler for the readers to understand the concepts with clarity. I engage myself in Singing, Dancing, and nature photography during my leisure time.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/in/padmakshi-k-b54679132