Polymerase is any enzyme that helps in synthesizing the large chains of nucleic acids or the polymers. RNA polymerase helps in copying of the DNA sequence.
There are different types of RNA polymerase in both for prokaryotes and eukaryotes. All of the eukaryotes have several polymerases that can help in getting the genes transferred. There is RNA polymerase I, RNA polymer II and also the RNA polymerase III. Thus the types that are found are-
RNA polymerase I
This complex is used up for the production of ribosomes which is vital for the synthesis machine of cellular proteins that helps in its growth along with getting to underline may of the other functions. The accurate transcription of human rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I requires two transcription factors, upstream binding factor. Pol I is a 590 kDa enzyme that consists of 14 protein subunits.
RNA polymerase II
It is responsible for transcription of nuclear genes encoding messenger RNA and some small nuclear RNAs. Twelve of its subunits have identical or related counterparts in RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and RNA polymerase III (Pol III). The other two subunits are related to Pol II initiation factors and have structural homologues in Pol III. RNA polymerase allows in copying of the DNA sequence.
RNA polymerase III
RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcribes a variety of small, stable RNAs that are essential for multiple cell signaling pathways, including premRNA splicing (U6 snRNA) and protein synthesis. The last for the eukaryotes is the polymerase III that gets the 5S ribosomal RNA gens and the tRNA transcribe.
RNA polymerase IV
RNA polymerase IV is an enzyme that synthesizes small interfering RNA that suppresses gene expression in plants. The RNA polymerase I gets the genes of ribosomal RNA transcribed, RNA polymerase II helps in getting the snRNA, the miRNA and the messenger RNA gets itself transcribed. RNA polymerase is seen in all types and kinds of organism and thus yet the composition and the number of the DNA.
RNA polymerase V
Determining the composition and diversity of the Pol IV and Pol V RNA subunits is an important step in understanding their function. The ones that are being used in two different types of species are a bit different from each other. The data is kept inside the molecule of the DNA and is made to copy in a new molecule for the messenger RNA. Just for taking an example the entire organism needs methods by which they can carry on transcription.
RNA polymerase is said to be an enzyme that makes to take part in copying of the sequence in DNA and help in get converted to a sequence of RNA at the time of a method called transcription. It is same as that of the molecule that is made of the protein subunits and is much complex. The enzyme called as RNA polymerase helps in controlling its acting to get flowed with transcription at the time where the information is kept stored.
Considering an example for just one type of bacteria has only a small type of RNA polymerase while in the yeast and the multicellular organism often said to be the eukaryotes do have three types of it and are all different. Despite these not so similar features there are also many other characters that make them alike by which they can come hands on with the method of transcription.
Types of RNA polymerase in prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are the organism that have only one cell and cannot be seen under naked eye. They are single called along with being unicellular and having either flagella or cilia for their movement. Bacteria and archaea can be its example.
Within the bacteria or the prokaryotes, the polymerase is seen in two phases. One of them being called the core enzyme that helps in getting the RNA synthesized but is not able to link the DNA with the targeted promoter.
The second part of it is the holoenzyme which helps in two ways one being the synthesis of RNA and the other gets to recognize the promoter. Along with this, the prokaryotes use a single type of RNA polymerase for its use. The organism being prokaryotes helps themselves by suing the same polymerase of type RNA to get the genes transcribed.
Four if the units in them are denoted by α, α, β, and β′ and these are a part of the core enzyme. These units kink all the time into a genes and then is transcribed and disassemble it after transcription is done. While the eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerase in use it also uses up there of the DNA polymerase.

RNA polymerase–Wikipedia
How many types of RNA polymerase in eukaryotes
The cells of the eukaryotes are one of the complex materials found in several ways that also consists of the term of the process transcription. These are the organism that have a nucleus and is covered inside the nuclear envelope.
Thus out of all the types of RNA polymerases eukaryotes take the use of three types of them. These types are typical in view to carry other types of organelles that have membranes just like the Golgi body and the mitochondria and also the chloroplasts that can be found in the algae and plants.
They are different in their type of unit they carry and also vary in number. There is also a variation seen in the type of class the three of each belong to. The three of them used are RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II and RNA polymerase III. The RNA polymerase I helps with the ribosomal RNA, the RNA polymerase II help with the transcription of messenger and the RNA polymerase III goes with the transfer RNA.
The RNA polymerase II helps with the encoding of the gens in proteins it is of more importance to the researchers that spy on the gene expression of the eukaryotes and its use. Taking into consideration, it is said that RNA polymerase II gets to bind the DNA with the promoter genes called as the TATA box that helps in the initiation of transcription.
All together having same motif for getting a small sequence of DNA these are the ones that have the core promoter. Despite these the changes in polymerase II gets to influence the genes that surround the DNA while recruiting the factors for transcription. Although they method of transcription is quite vital, they are contracted in the area of just effectiveness.
Types of RNA polymerase in bacteria
Bacteria are said to be organism having single cell and are microscopic that can be seen in millions of places in millions of forms covering in and out of a species.
Inside the bacteria despite being so many types of RNA polymerase there is the similar enzyme that helps in getting the messenger RNA synthesize and also the RNA that is not coded like that of ncRNA. There is a large size molecule that is called the RNAP.
The base of the enzyme contains of five units in it. In the bacteria they are just in one form of the rest for they are the prokaryotes. Bacteria are the organism that are actually ubiquitous and are almost free living ones. They have only one cell and have a large domain in its space.
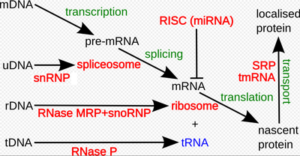
In the bacteria, one polymerase stays function. It has four subunits for catalyst and only one regulatory unit called the sigma. With the curious fact, there are many factors of sigma that have been found and each of them looks at transcription fir a unique set of genes. Thus the factor for sigma are said to be discriminatory with each of them binding to a specific sequence of promoter. .
Types of RNA polymerase in enzyme
In defining this enzyme in much similar terms it helps in synthesizing the RNA from any DNA template with using the help of helicase.
It is much vital for sustaining life and is seen in all the living beings and many other microbes. Based on the species, a polymerase of RNA can be a complex of protein or also a small unit or subunit that by each shows a lineage that is not dependent.
One is located in the archaea, bacteria and the eukaryotes and also shares a same base structure and method. Each of the eukaryotes has multiple polymerase of RNA that functions on its own style in synthesizing. RNA polymerase is said to be an enzyme that helps copy a DNA sequence and convert it into an RNA sequence by a method called transcription.
It is composed of protein subunits and is the same as a very complex molecule. An enzyme called RNA polymerase helps control the action of information stored in a DNA molecule so that it flows with transcription when it is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA. One is found in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes and shares the same basic structure and methods.
Also Read:
- Bacterial chromosome structure
- Sea anemone characteristics
- Do mitochondria have enzymes
- Is exocytosis active
- Brain anatomy
- Are bacteria herbivores
- Example of prokaryotic cell
- Protein denaturation examples
- What is the function of ribosomes
- Do humans have plant cells
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.