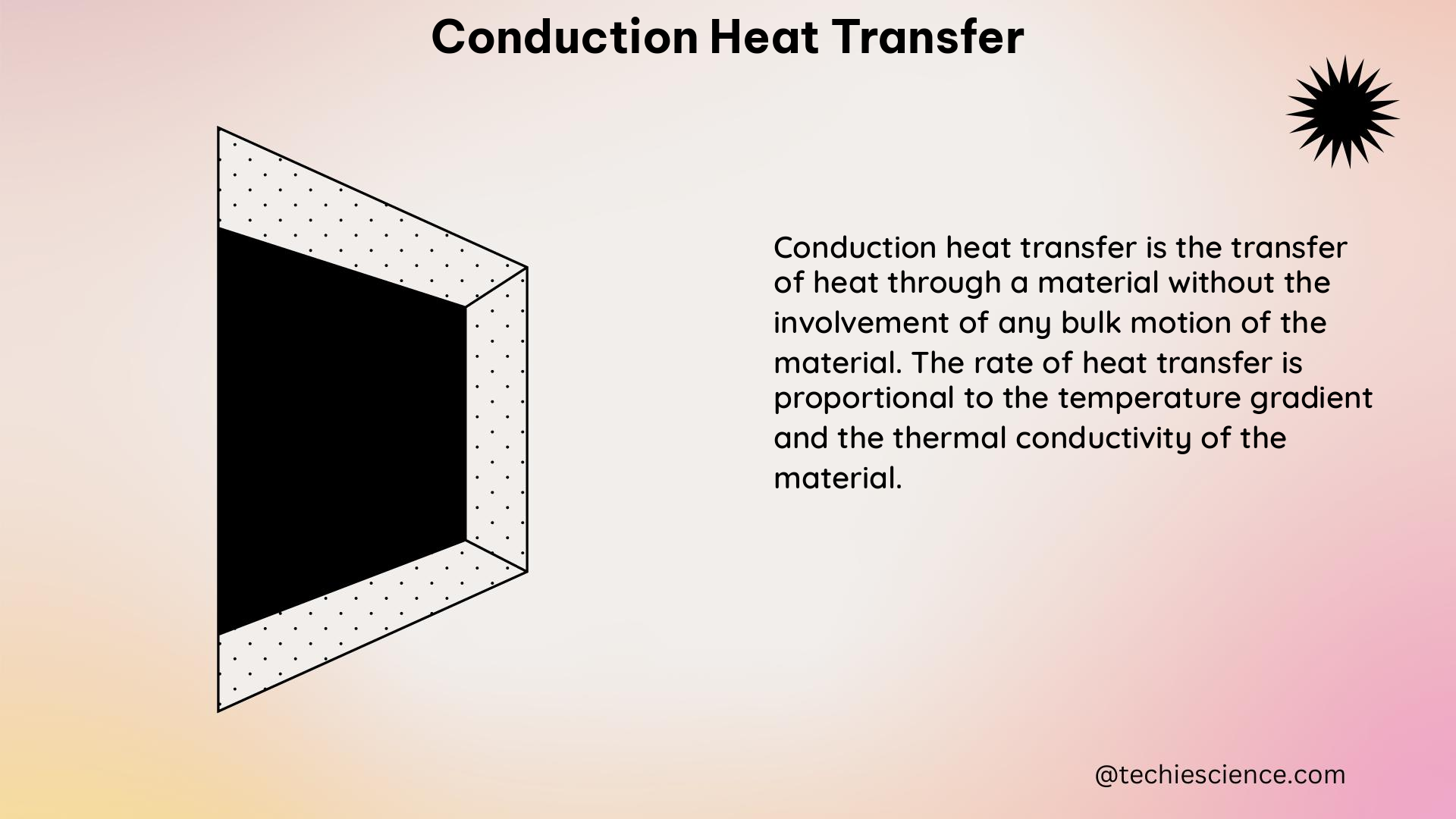
Nature:
- Oceanic Convection Currents: Warm ocean water rises at the equator and cold water sinks at the poles.

- Cloud Formation: Warm air rises, cools, and condenses to form clouds.

Daily Household Usage:
- Boiling Water: Heat causes water at the pot’s bottom to rise, creating a circulation.

- Toasters: Heat from the coils rises, toasting the bread from the bottom up.

Equipment & Appliances:
- Refrigerators: Warm air rises and is cooled down by the freezer.

- Air Conditioners: Cool air released sinks, displacing the warmer room air.

Heating Systems:
- Radiators: Hot water or steam rises through the system, heating rooms.

- Underfloor Heating: Warm air from heated floors rises, warming the room.

Transportation:
- Car Radiators: Hot coolant is cooled by air passing through radiator fins.

- Hot Air Balloons: A burner heats the air inside, causing the balloon to rise.
Geological Phenomena:
- Geysers: Underground water heated by magma erupts.

- Volcanic Plumes: Magma heats the air above a volcano, causing it to rise with ash and gases.

Atmospheric Events:
- Thermals: Pockets of warm air rise, often used by birds for soaring.

- Dust Devils: Sun-heated ground causes air to rise quickly, picking up dust.

Recreational Activities:
- Saunas: Heated stones produce steam, warming the air.

- Jacuzzis: Warm water jets create circulation, maintaining even warmth.

Industrial Processes:
- Steel Quenching: Hot metal is cooled rapidly in a liquid, causing convection currents.
- Industrial Ovens: Circulating hot air ensures even heating of products.

Agriculture:
- Greenhouses: Sun heats the ground inside, causing warm air to rise and circulate.

- Grain Dryers: Warm air rises through the grains, drying them uniformly.

Marine Systems:
- Coral Bleaching: Warm ocean currents can raise temperatures, affecting coral health.

- Deep Sea Vents: Warm water rises from hydrothermal vents, supporting unique ecosystems.
Space & Astronomy:
- Solar Flares: Hot plasma rises from the sun’s surface, creating flares.
- Convective Zones in Stars: Hotter material rises while cooler material sinks, driving star’s energy.
Medical & Health:
- Infrared Saunas: Infrared heaters warm the body directly, causing sweat and circulation.
- Warm Compresses: Heat causes increased blood flow to the area, aiding healing.
Ecological Systems:
- Forest Canopy Gaps: Sunlight penetrates gaps in the forest canopy, heating the forest floor and causing moist air to rise, forming localized clouds.
- Wetlands: Sun heats shallow waters causing evaporation and upward movement of moist air, influencing local microclimates.
Urban Infrastructure:
- Skyscrapers: Tall buildings create wind patterns at their base due to differential heating and rising warm air.
- Subway Ventilation: Underground train systems use convection to circulate air, drawing in cooler air from above.
Fashion & Clothing:
- Ventilated Shoes: Designed to allow warm air from the feet to rise and escape, drawing in cooler air.
- Breathable Jackets: Allow warm air to rise and escape while drawing in fresh air, keeping the wearer cool.
Food & Cooking:
- Deep Frying: Hot oil causes rapid convection currents, cooking food evenly.
- Steam Cooking: Steam rises, cooking food from the bottom up.
Sports & Recreation:
- Paragliding: Pilots ride thermal updrafts to gain altitude.
- Sailing: Sailors utilize wind patterns created by differential heating of the Earth’s surface.
Art & Craft:
- Kilns: Used in pottery, where circulating hot air ensures even heating of clay items.
- Glass Blowing: Molten glass is shaped using tools and air, with convection playing a role in the cooling process.
Technology & Electronics:
- Computer Cooling Systems: Fans draw cooler air towards hot components, using convection to dissipate heat.
- Satellite Thermal Control: Space satellites use convection to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Hydrological Systems:
- River Eddies: Differential temperatures in river waters create swirling patterns or eddies.
- Glacial Melt Streams: Warm air causes glaciers to melt at certain points, creating streams where warmer water rises.
Also Read: