The Boiling Point of CH3Cl: A Comprehensive Guide for Science Students
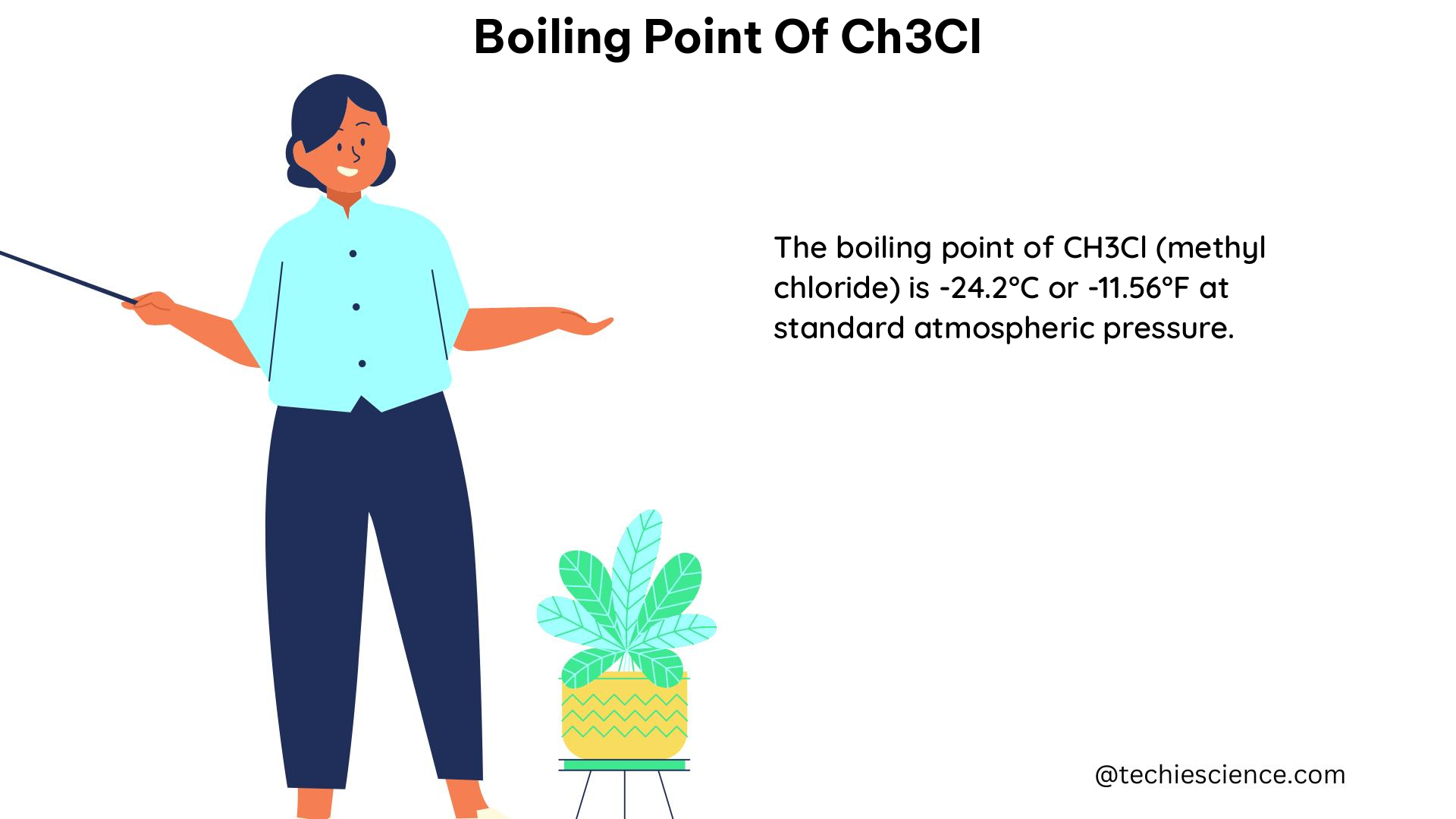
The boiling point of CH3Cl (methyl chloride or chloromethane) is a crucial physical property that plays a significant role in various scientific and industrial applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the boiling point of CH3Cl, providing a wealth of technical details and practical insights for science students. Understanding the Boiling Point of … Read more