The solubility of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a crucial parameter in various fields, including chemistry, geology, and environmental science. Calcium carbonate is a common mineral found in nature, and understanding its solubility behavior is essential for applications such as water treatment, soil management, and the study of geological processes. This comprehensive guide will delve into the factors that influence the solubility of calcium carbonate, provide quantitative data, and offer a step-by-step approach to determining its solubility in different scenarios.
Factors Affecting the Solubility of Calcium Carbonate
Temperature
The solubility of calcium carbonate is known to be temperature-dependent. As the temperature increases, the solubility of CaCO3 generally increases. According to the study published in the Journal of Fluid Phase Equilibria, the solubility of CaCO3 in pure water at 50°C is approximately 0.025 g/L, while at 100°C, it increases to around 0.06 g/L.
Pressure
The solubility of calcium carbonate also depends on the pressure of the system. As the pressure increases, the solubility of CaCO3 tends to increase. The study in the Chemical Engineering Science journal found that the solubility of CaCO3 increases with increasing pressure, with a maximum solubility observed in the presence of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Concentration
The presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the solution can significantly affect the solubility of calcium carbonate. As the CO2 partial pressure increases, the solubility of CaCO3 also increases. The study in the Journal of Fluid Phase Equilibria reported that in the presence of 10 bar CO2 partial pressure, the solubility of CaCO3 in pure water at 50°C increases to around 0.1 g/L, and at 100°C with 40 bar CO2 partial pressure, the solubility increases to approximately 1.2 g/L.
pH
The pH of the solution can also affect the solubility of calcium carbonate. The study in the Chemical Engineering Science journal found that the solubility of CaCO3 shows a maximum in the presence of sodium chloride (NaCl), which is likely due to the influence of pH on the ionic species present in the aqueous solution.
Ionic Strength
The presence of other ions in the solution, such as sodium chloride (NaCl), can also impact the solubility of calcium carbonate. The study in the Chemical Engineering Science journal reported that the solubility of CaCO3 shows a maximum in the presence of NaCl, indicating that the ionic strength of the solution can influence the solubility behavior.
Quantitative Data on the Solubility of Calcium Carbonate
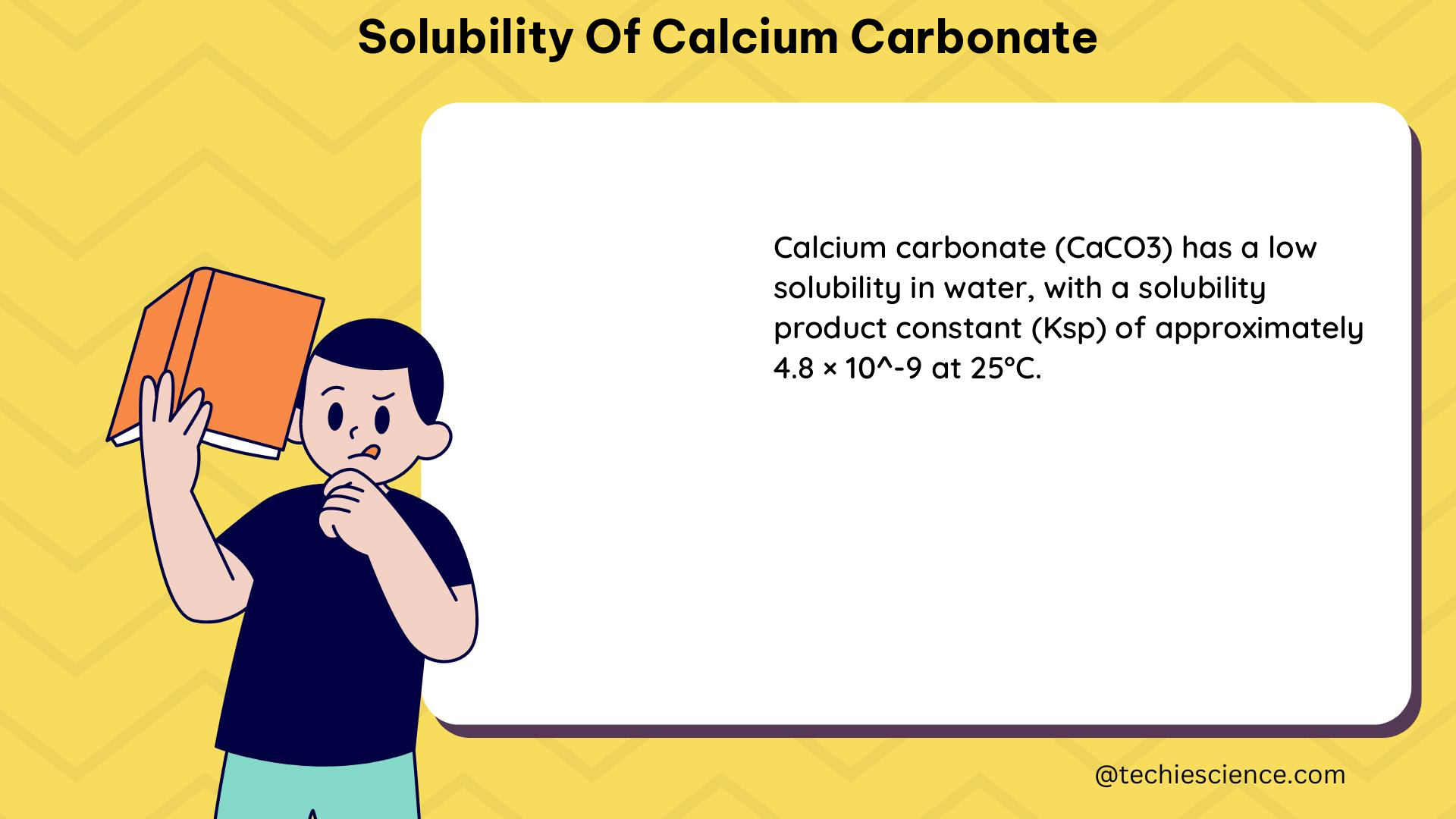
The solubility of calcium carbonate can be expressed in various units, such as grams per liter (g/L), moles per liter (M), or parts per million (ppm). The following table provides some quantitative data on the solubility of CaCO3 under different conditions:
| Condition | Solubility (g/L) | Solubility (M) |
|---|---|---|
| 25°C, 1 atm, pure water | 0.013 | 0.0013 |
| 50°C, pure water | 0.025 | 0.00025 |
| 50°C, 10 bar CO2 partial pressure | 0.1 | 0.001 |
| 100°C, pure water | 0.06 | 0.0006 |
| 100°C, 40 bar CO2 partial pressure | 1.2 | 0.012 |
It’s important to note that the solubility of calcium carbonate can also be influenced by the presence of other ions, the pH of the solution, and the specific experimental conditions used.
Determining the Solubility of Calcium Carbonate
To determine the solubility of calcium carbonate in a given solution, you can follow these steps:
- Prepare a saturated solution of calcium carbonate by adding an excess of CaCO3 to the solution and allowing it to equilibrate.
- Filter the solution to remove any undissolved CaCO3 particles.
- Analyze the filtrate to determine the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) or carbonate ions (CO32-) using standard analytical techniques, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy or ion chromatography.
- Calculate the solubility of CaCO3 using the stoichiometry of the dissolution reaction and the concentration of the ions in the solution.
The solubility of CaCO3 can be calculated using the following equation:
Solubility (g/L) = [Ca2+] × 100.09 g/mol / 1000 mL/L
where [Ca2+] is the concentration of calcium ions in the solution, expressed in mol/L.
Alternatively, the solubility can be expressed in terms of the equilibrium constant (Ksp) for the dissolution reaction:
CaCO3 (s) ⇌ Ca2+ (aq) + CO32- (aq)
Ksp = [Ca2+] × [CO32-]
By measuring the concentrations of Ca2+ and CO32- in the saturated solution, you can calculate the Ksp value and use it to determine the solubility of CaCO3.
Conclusion
The solubility of calcium carbonate is a complex and well-studied topic, with various factors influencing its behavior. This comprehensive guide has provided detailed information on the factors affecting the solubility of CaCO3, including temperature, pressure, CO2 concentration, pH, and ionic strength. Additionally, it has presented quantitative data on the solubility of CaCO3 under different conditions and outlined a step-by-step approach to determining its solubility in a given solution. By understanding the principles and techniques discussed in this guide, you can effectively analyze and predict the solubility of calcium carbonate in a wide range of applications.
References:
- Calculated solubility index for calcium carbonate for membrane concentrate prior and after treatment. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Calculated-solubility-index-for-calcium-carbonate-for-membrane-concentrate-prior-and_fig6_41166263
- Calcium Carbonate. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Calcium-Carbonate
- Quantitative determination of calcite associated with carbonate rocks. https://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/am/vol37/AM37_211.pdf
- 2012 Fluid Phase Eq., CaCO3 solubility.pdf – University of Oregon. https://pages.uoregon.edu/chendon/coffee_literature/old_literature/2012%20Fluid%20Phase%20Eq.,%20CaCO3%20solubility.pdf
- Effects in the solubility of CaCO3: Experimental study and model description. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378381212001331

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.