Benzaldehyde, a clear, colorless to yellow liquid with a bitter almond odor, is a widely studied organic compound with diverse applications in the chemical industry. Understanding its solubility properties is crucial for various industrial and research applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of benzaldehyde’s solubility, providing a wealth of technical information for science students and professionals.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde is a member of the aldehyde family, with the chemical formula C6H5CHO. It has a molar mass of 106.12 g/mol and a boiling point of 178-179°C at atmospheric pressure. The compound has a flash point near 145°F and is denser than water, with a density of 1.0436 g/cm³ at 20°C.
Solubility of Benzaldehyde in Water
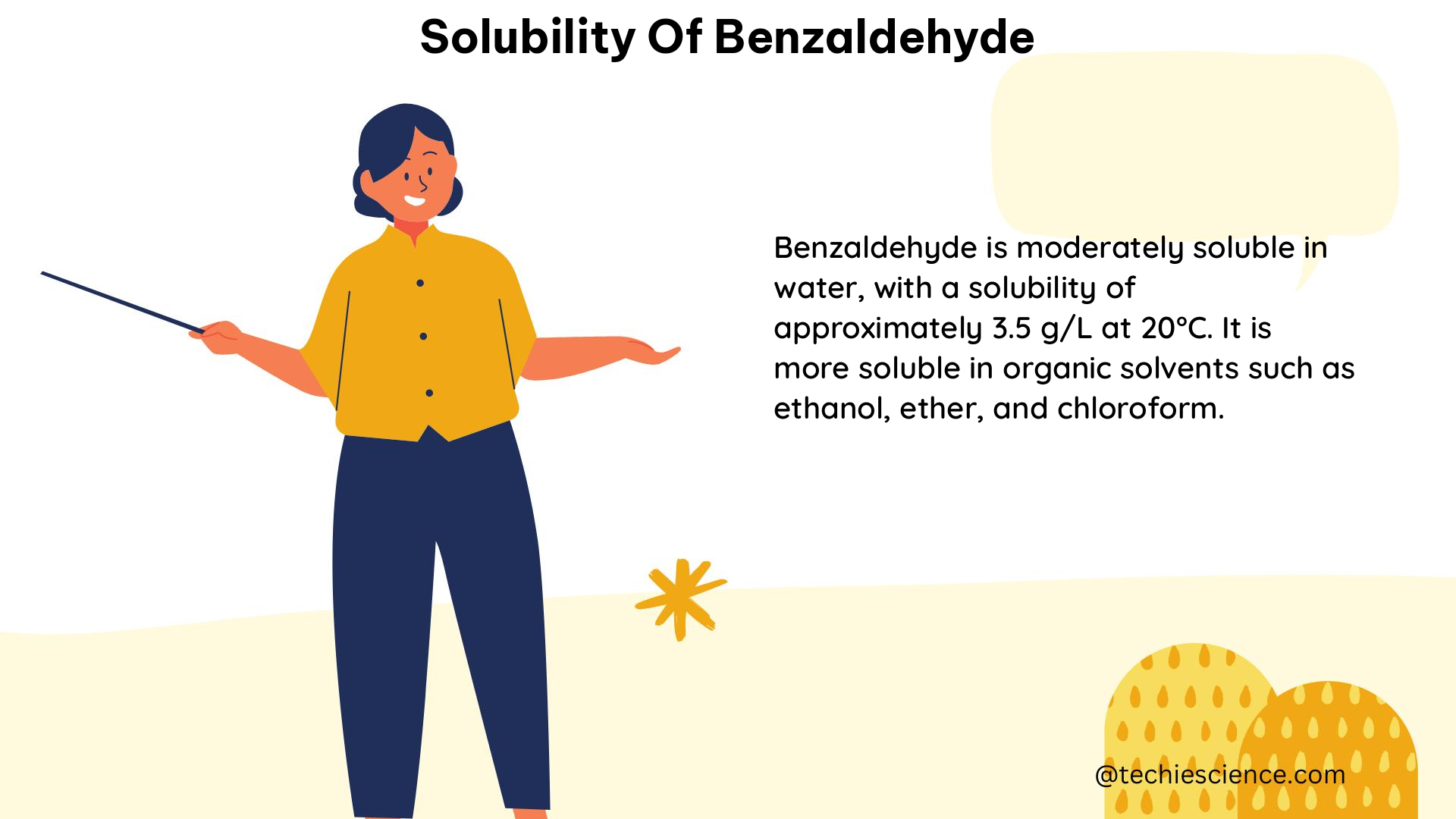
Benzaldehyde is considered insoluble in water due to its non-polar nature. The solubility of benzaldehyde in water at 25°C is reported to be approximately 3.4 g/L, or 0.032 mol/L. This low solubility is attributed to the lack of strong intermolecular interactions between the water molecules and the benzaldehyde molecules.
Solubility of Benzaldehyde in Organic Solvents
In contrast to its poor solubility in water, benzaldehyde exhibits excellent solubility in various organic solvents. The following table provides the solubility of benzaldehyde in common organic solvents at 25°C:
| Solvent | Solubility (g/L) |
|---|---|
| Ethanol | Miscible |
| Diethyl ether | Miscible |
| Acetone | Miscible |
| Chloroform | Miscible |
| Hexane | 26.0 |
As shown in the table, benzaldehyde is completely miscible (soluble in all proportions) in polar protic solvents like ethanol and polar aprotic solvents like acetone. It also exhibits high solubility in non-polar solvents like chloroform and hexane.
Solubility Enhancement through Bisulfite Adduct Formation
The solubility of benzaldehyde in water can be increased by forming a bisulfite adduct. The bisulfite adduct is prepared by reacting benzaldehyde with sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) in an aqueous solution. This reaction produces a water-soluble compound, the sodium salt of the benzaldehyde-bisulfite adduct.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
C6H5CHO + NaHSO3 → C6H5CH(OH)SO3Na
The resulting adduct is highly soluble in water, with a solubility higher than that of the original sodium bisulfite. However, the adduct is not miscible in water, and its solubility is still lower than that of the original sodium bisulfite.
Solubility and Metastable Zone Width Measurement
A study on the solubility and metastable zone width measurement of benzophenone herniated disc (BPH) specimen found that the material crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with a solubility of 0.0022 mol/L at 25°C. The metastable zone width, which is the temperature difference between the solubility curve and the nucleation curve, was also determined for this system.
Analytical Techniques for Detecting Trace Levels of Benzaldehyde
Sensitive analytical techniques have been developed to detect and quantify trace levels of benzaldehyde in various matrices, particularly in pharmaceutical formulations. One such method involves solid-phase microextraction (SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-flame ionization detection (GC-FID).
This method has been validated and found to have a limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 50 ng/mL and a limit of detection (LOD) of 16 ng/mL for benzaldehyde in injectable pharmaceutical formulations. This high sensitivity allows for the accurate determination of benzaldehyde levels in complex matrices, which is crucial for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
In summary, this comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the solubility properties of benzaldehyde, covering its solubility in water, organic solvents, and the enhancement of solubility through bisulfite adduct formation. Additionally, the guide has discussed the solubility and metastable zone width measurement of benzophenone herniated disc (BPH) specimens, as well as the analytical techniques used for the detection of trace levels of benzaldehyde in pharmaceutical formulations.
This information is invaluable for science students and professionals working in the fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and pharmaceutical sciences, as it offers a deep understanding of the fundamental aspects of benzaldehyde’s solubility behavior and its practical applications.
References
- PubChem. Benzaldehyde. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Benzaldehyde
- Sciencemadness Forum. Solubility of Benzaldehyde Bisulfite Adduct. http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=64970
- Science.gov. Benzaldehyde Solubility. https://www.science.gov/topicpages/b/benzaldehyde
- Gao, Y., et al. (2016). Solubility and metastable zone width measurement of benzophenone herniated disc (BPH) specimen. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 221, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.05.057
- Jiang, Y., et al. (2015). Determination of trace benzaldehyde in injectable pharmaceutical formulations by solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-flame ionization detector. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 107, 434-439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.01.028

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.