Sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda, is a versatile chemical compound with a wide range of applications in various industries, from food and pharmaceuticals to cleaning and personal care products. Understanding the solubility of sodium bicarbonate is crucial for its effective use and proper handling. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of sodium bicarbonate solubility, exploring the factors that influence its solubility, the methods used to quantify its presence in mixtures, and the practical implications of its solubility in various applications.
Sodium Bicarbonate Solubility in Water
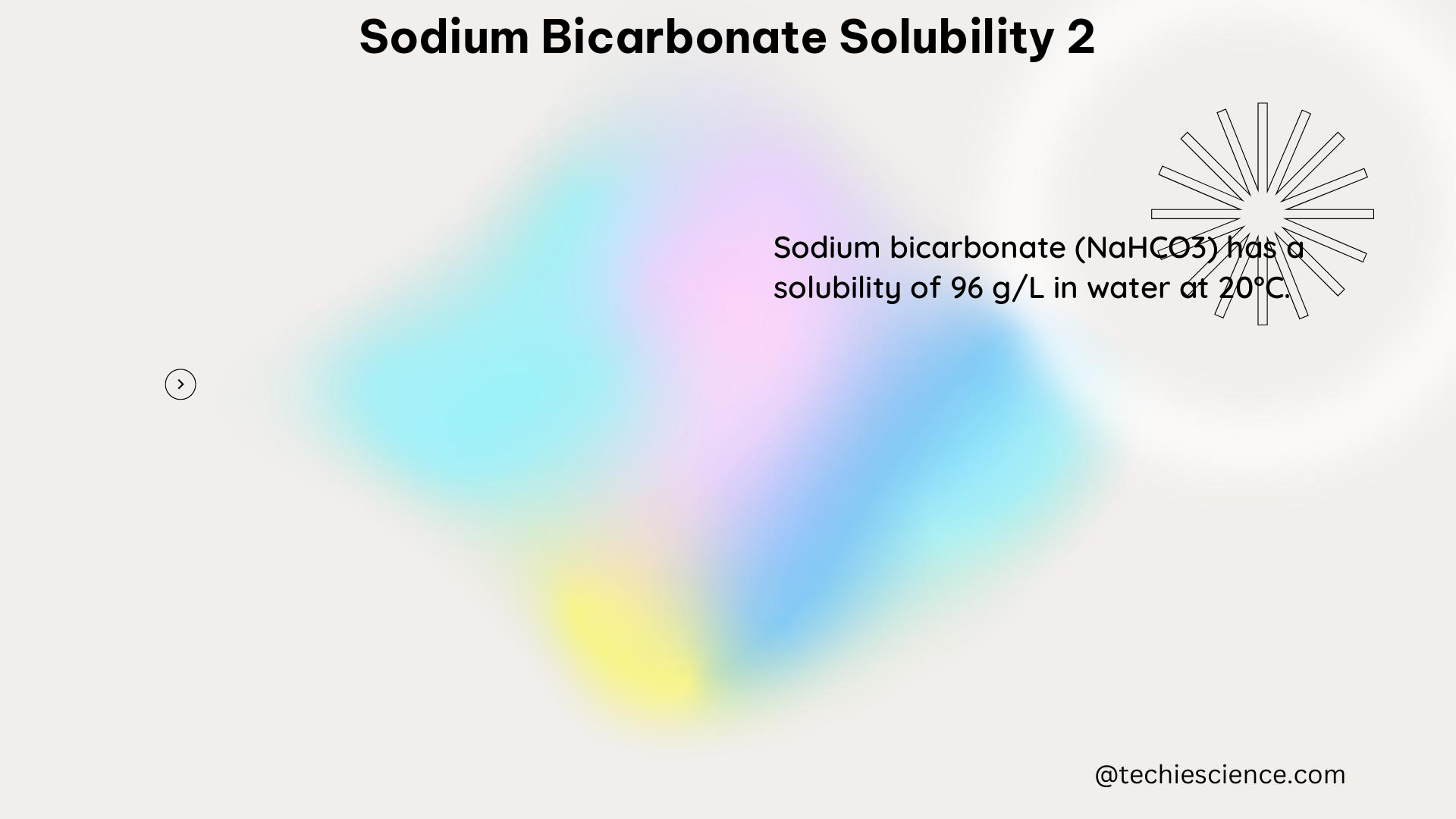
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is a highly soluble compound in water, with a solubility of approximately 6.8 g/100 mL of water at 25°C (77°F). This means that 6.8 grams of sodium bicarbonate can be dissolved in 100 mL of water at this temperature. The solubility of sodium bicarbonate in water can be expressed using the following equation:
NaHCO3(s) ⇌ Na⁺(aq) + HCO3⁻(aq)
The solubility of sodium bicarbonate in water is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of other ions in the solution.
Effect of Temperature on Solubility
The solubility of sodium bicarbonate in water increases with increasing temperature. This is due to the endothermic nature of the dissolution process, which is driven by the entropy change associated with the dissociation of the solid sodium bicarbonate into its constituent ions in the aqueous solution.
The relationship between temperature and the solubility of sodium bicarbonate can be expressed using the following equation:
ln(S) = -ΔH/RT + ΔS/R
where:
– S is the solubility of sodium bicarbonate (in mol/L)
– ΔH is the enthalpy change of dissolution (in J/mol)
– R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
– T is the absolute temperature (in K)
– ΔS is the entropy change of dissolution (in J/mol·K)
Experimental data has shown that the solubility of sodium bicarbonate increases from approximately 6.8 g/100 mL at 25°C to around 9.2 g/100 mL at 40°C.
Effect of Sodium Carbonate Concentration
The solubility of sodium bicarbonate in water decreases with increasing concentration of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) in the solution. This is due to the common-ion effect, where the presence of the carbonate ion (CO3²⁻) in the solution shifts the equilibrium of the sodium bicarbonate dissolution reaction towards the left, reducing the solubility of sodium bicarbonate.
The relationship between the solubility of sodium bicarbonate and the concentration of sodium carbonate can be expressed using the following equation:
[NaHCO3] = Ksp / [CO3²⁻]
where:
– [NaHCO3] is the solubility of sodium bicarbonate (in mol/L)
– Ksp is the solubility product constant of sodium bicarbonate (Ksp = 4.5 × 10⁻¹¹ at 25°C)
– [CO3²⁻] is the concentration of the carbonate ion (in mol/L)
This means that as the concentration of sodium carbonate in the solution increases, the solubility of sodium bicarbonate decreases, as the carbonate ion concentration rises and shifts the equilibrium towards the left.
Quantitative Analysis of Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Bicarbonate Mixtures
Determining the precise amounts of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate in solid mixtures is essential for various applications, such as in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. One method that has been developed for this purpose is the use of Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy.
Constant Ratio and Absorbance Correction Methods
The constant ratio and absorbance correction methods are two techniques used to quantify the amounts of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate in solid mixtures using FT-IR spectroscopy.
- Constant Ratio Method:
- This method is based on the fact that the ratio of the absorbances of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate is constant over a certain range of concentrations.
-
The ratio of the absorbances of the two compounds is determined experimentally and used to calculate the amounts of each compound in the mixture.
-
Absorbance Correction Method:
- This method takes into account the fact that the absorbance of a solution of sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate is proportional to its concentration.
- The absorbance of the mixture is measured, and the amounts of the two compounds are calculated using the known molar absorptivities of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate.
These methods have been shown to be effective in quantifying the amounts of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate in solid mixtures, with good accuracy and precision.
Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation and Exercise Performance
Sodium bicarbonate has been studied for its potential to enhance exercise performance, particularly in high-intensity activities lasting between 1 and 7 minutes.
Mechanism of Action
Sodium bicarbonate is believed to improve exercise performance by increasing the buffering capacity of the blood, which helps to neutralize the buildup of lactic acid and other acidic byproducts of high-intensity exercise. This, in turn, delays the onset of fatigue and allows the athlete to maintain a higher level of performance for a longer duration.
Optimal Supplementation Protocol
Studies have shown that the optimal protocol for sodium bicarbonate supplementation involves a multiple-day, progressive approach. Typical doses range from 0.025 g/kg per day to 0.100 g/kg per day, with the supplementation period lasting around 10 days.
This gradual increase in dosage allows the body to adapt to the higher levels of sodium bicarbonate, minimizing the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, which can be a common issue with sodium bicarbonate supplementation.
Practical Considerations
When using sodium bicarbonate as a performance-enhancing supplement, it is important to consider factors such as individual tolerance, timing of ingestion, and the potential for side effects. Proper hydration and monitoring of electrolyte balance are also crucial to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the supplementation protocol.
Conclusion
Sodium bicarbonate is a highly soluble compound in water, with a solubility of approximately 6.8 g/100 mL at 25°C. Its solubility is influenced by factors such as temperature and the presence of other ions, particularly sodium carbonate. Understanding the solubility of sodium bicarbonate is essential for its effective use in various applications, from quantitative analysis to performance enhancement in sports.
The constant ratio and absorbance correction methods using FT-IR spectroscopy have proven to be reliable techniques for quantifying the amounts of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate in solid mixtures. Additionally, sodium bicarbonate supplementation has been shown to improve exercise performance in high-intensity activities, with the optimal protocol involving a multiple-day, progressive approach.
By delving into the technical details and specific data points related to sodium bicarbonate solubility, this comprehensive guide provides a valuable resource for scientists, researchers, and industry professionals working with this versatile compound.
References:
- Linke, W. F., & Seidell, A. (1958). Solubilities of Inorganic and Metal-Organic Compounds (4th ed.). American Chemical Society.
- Lide, D. R. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). CRC Press.
- Bhandari, N., & Fechner, D. C. (2014). Quantitative Analysis of Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Bicarbonate in Solid Mixtures Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR). Analytical Chemistry Insights, 9, 29-35.
- Carr, A. J., Hopkins, W. G., & Gore, C. J. (2011). Effects of Acute Alkalosis and Acidosis on Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Medicine, 41(10), 801-814.
- Siegler, J. C., Marshall, P. W., Bray, J., & Towlson, C. (2012). Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation and Exercise Performance: A Dose-Response Study. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112(8), 2933-2943.

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.