Potassium chloride is an inorganic compound and the solid combination of this is called sylvinite, a mineral. Let us discuss the properties of potassium chloride.
Potassium chloride is a metal halide salt mainly used for making fertilizers for plants as potassium is an important source for plants to grow known as muriate of potash (MOP). The KCL is also used to maintain the low blood potassium in the human body and as salt in food.
In this article, we will discuss the molar mass, chemical formula, melting and boiling points, viscosity, and color with detailed explanations
Potassium chloride IUPAC name
The IUPAC name (international union of pure and applied chemistry) of potassium chloride is potassium chloride itself.
Potassium chloride chemical formula
Potassium chloride has the chemical formula KCl. In this formula there are only two atoms potassium is a metal that donates the electron and chloride is a halide that accepts the electron and forms an ionic bond by attending the charges as metal attends positive and negative charge.
Potassium chloride CAS number
The CAS registry number of potassium chloride is 7447-40-7 which is authentic numeric identifier which contains up to 10 digits.
Potassium chloride ChemSpider ID
Potassium chloride has the ChemSpider ID is a free chemical structure database 4707.
Potassium chloride chemical classification
- Potassium chloride is classified as an electrolyte and a mineral.
- Potassium chloride used to cure hypokalemia which occurs in the human body because of the deficiency of potassium.
- Potassium chloride can also be used as a substitute for common salt in food and beverages.
Potassium chloride molar mass
The molar mass of potassium chloride is 74.55 g/mol.
Potassium chloride color
Pure potassium chloride is white in color and is in white powder forms like common salt and present in the ancient dried lakes of earth and easily dissolves in water like common salt.
Potassium chloride viscosity
- The viscosity of potassium chloride is 1.1975 mPa/s if one mole of KCl is dissolved in water as it is less
- Potassium chloride is highly soluble in water because of its ionic nature it has the ability to dissociate in water and forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Potassium chloride molar density
The molar density of potassium chloride is 74.5513 g/mole as it has a density of 1.98 g/mL.
Potassium chloride melting point
Potassium chloride has a melting point of 1,418°F or 770°C.
Potassium chloride boiling point
Potassium chloride has a boiling point of 2,588°F or 1,420°C. The boiling point of potassium chloride is high because of the ionic bond they are highly soluble in water.
Potassium chloride state at room temperature
The potassium chloride state at room temperature is a crystalline solid form or in a powdered form called fekabit.
Potassium chloride ionic bond
There is one ionic bond present in 1 atom of potassium chloride salt.
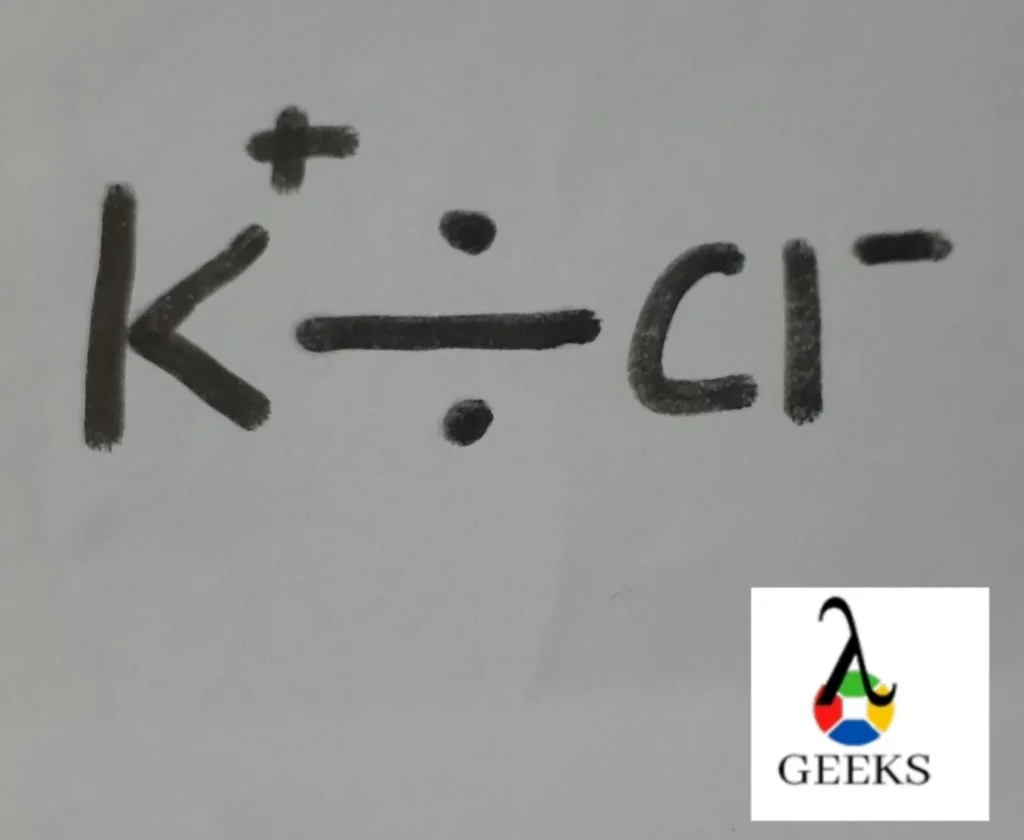
Potassium chloride ionic radius
The ionic radius of potassium chloride is 159.5 pm.
Potassium chloride electron configurations
The electronic configuration is the division of the electrons in the atomic orbitals. Let us explain the electronic configuration of potassium chloride.
Electron configuration of potassium 1s2 2s22p2 3s2 3p64s1 and for chloride 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6.
Potassium chloride oxidation state
The oxidation state of potassium in potassium chloride is +1. Potassium will behave as a central metal atom here because it is the atom donating the electron to chlorine to form the ionic bond.
Potassium chloride acidity/alkaline
Potassium chloride does not show any alkanity or acidity because of the absence of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions which are two important ions that shows the concentration of acid or base.
Is potassium chloride odourless
Potassium chloride is odourless and it does not produce any smell while heating too.
Is potassium chloride paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a phenomenon in which a single electron is left in the last shell. Let us explain the paramagnetic potassium chloride.
Potassium chloride is diamagnetic because of the paired electrons present in the last shell.
Potassium chloride hydrates
Potassium chloride rarely produce hydrates but potassium chloride react with water to produce hydrates with potassium.
KCl + HOH ——> KOH + HCl
Potassium chloride crystal structure
Potassium chloride has crystals of cubic shape called cubic crystal structure and they are very compact shaped too.
Potassium chloride polarity and conductivity
- Potassium chloride is a good conductor of electricity as it is an electrolyte while dissociation, because of the ionic bond potassium chloride is the conductor.
- Potassium chloride shows polarity because of the ionic bond.
Potassium chloride reaction with acid
Potassium chloride does not react with acids because of the lack of hydrogen ions and hydronium ions.
Potassium chloride reaction with base
Potassium chloride does not react with the base as it is a base itself and works as a neutralizer in some reactions too.
KCl + NaOH ——> KOH + NaCl
Potassium chloride reaction with oxide
Potassium chloride does not react with oxides directly as they produce some oxides while reacting with water.
2KCl + O2 —–> K2O +OCl2
Potassium chloride reaction with the metal
Potassium chloride does not react with metal as it is an ionic compound that cannot accept or donates any electron.
Conclusion
Potassium chloride has a different use in different fields. Most of the KCl is used as an electrolyte as well as a good fertilizer for the growth of plants and its medical use of it is to balance the concentration of potassium in the blood and can use as a substitute for common salt in food industries.

Hi….I am Soumya Chourasia, completed my Master’s in Chemistry. I am working as a Subject Matter Expert in Chemistry. Before this, I used to teach chemistry for competitive examinations and school as well.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn here,