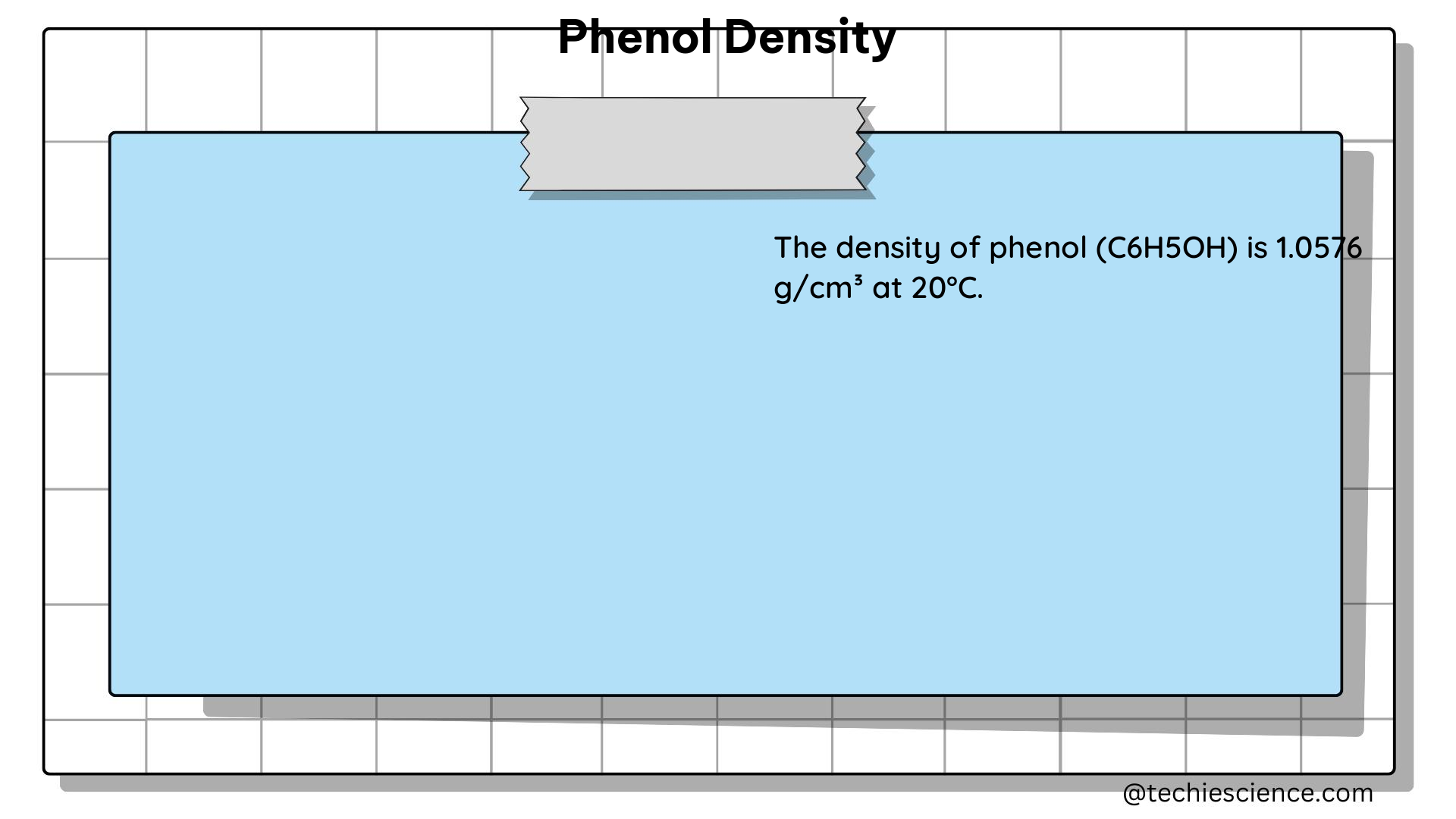
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid or hydroxybenzene, is a widely used chemical compound with a density of 1.07 g/cm³. This means that one cubic centimeter of phenol has a mass of approximately 1.07 grams. The density of a substance is a crucial physical property that can significantly impact its behavior in various applications, such as its solubility in other liquids, boiling and melting points, and viscosity.
Understanding Phenol Density
Phenol density is a measure of the mass of phenol per unit volume. It is calculated by dividing the mass of a sample of phenol by its volume. The density of phenol can be expressed using the following formula:
Density of Phenol = Mass of Phenol / Volume of Phenol
The density of phenol is affected by several factors, including temperature and pressure. As the temperature of phenol increases, its density typically decreases due to the expansion of the molecular structure. Conversely, as the pressure on phenol increases, its density will increase as the molecules are compressed.
Factors Affecting Phenol Density
-
Temperature: The density of phenol is inversely proportional to its temperature. As the temperature of phenol increases, its volume expands, leading to a decrease in density.
-
Pressure: The density of phenol is directly proportional to the pressure applied to it. As the pressure increases, the molecules of phenol are compressed, resulting in an increase in density.
-
Molecular Structure: The arrangement and packing of phenol molecules within the substance can also influence its density. Factors such as the presence of hydrogen bonding and the orientation of the hydroxyl group can affect the overall density.
-
Impurities: The presence of impurities in phenol can alter its density. Impurities can occupy space within the phenol matrix, leading to changes in the overall density.
Calculating Phenol Density
To calculate the density of phenol, you can use the following formula:
Density of Phenol = Mass of Phenol / Volume of Phenol
For example, if you have a sample of phenol with a mass of 10 grams and a volume of 9.35 cubic centimeters, the density of the phenol can be calculated as follows:
Density of Phenol = 10 g / 9.35 cm³ = 1.07 g/cm³
Physical and Chemical Properties of Phenol
In addition to its density, phenol has several other physical and chemical properties that are relevant to its use and handling. These properties include:
Melting and Boiling Points
Phenol has a melting point of 43°C (110°F) and a boiling point of 182°C (359.6°F). These properties are important in determining the appropriate storage and handling conditions for phenol, as well as its potential applications.
Solubility
Phenol is soluble in water and most organic solvents, such as ethanol, ether, and acetone. This property makes phenol useful in a variety of chemical processes and applications.
Molecular Weight
The molecular weight of phenol is 94.11 g/mol. This property is important in understanding the behavior of phenol in chemical reactions and processes.
Hazardous Properties
Phenol is a hazardous substance that can pose risks to human health and the environment. It can cause skin and eye irritation, and prolonged exposure can lead to more serious health effects, such as damage to the liver and kidneys. Therefore, it is essential to handle phenol with care and follow appropriate safety precautions when using it.
Applications of Phenol
Phenol has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
-
Chemical Industry: Phenol is used as a raw material in the production of various chemicals, such as phenolic resins, bisphenol A, and caprolactam.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Phenol is used in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds, such as aspirin and acetaminophen.
-
Disinfectant and Antiseptic: Phenol is used as a disinfectant and antiseptic due to its antimicrobial properties.
-
Plastics and Resins: Phenol is used in the production of phenolic resins, which are used in the manufacture of various plastic products, such as electrical components, adhesives, and coatings.
-
Herbicides and Pesticides: Phenol is used as a raw material in the production of certain herbicides and pesticides.
-
Dyes and Pigments: Phenol is used in the synthesis of various dyes and pigments.
Safety Considerations
Phenol is a hazardous substance that requires careful handling and storage. When working with phenol, it is essential to follow appropriate safety protocols, such as:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat, to minimize exposure.
-
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the work area to prevent the buildup of phenol vapors.
-
Spill Containment: Have a plan in place for containing and cleaning up any spills or leaks of phenol.
-
Waste Disposal: Dispose of phenol waste in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines.
-
Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training to all personnel who may come into contact with phenol to ensure they understand the risks and proper handling procedures.
Conclusion
Phenol density is a crucial physical property that can significantly impact the behavior and applications of this versatile chemical compound. By understanding the factors that affect phenol density, as well as its other physical and chemical properties, researchers and industry professionals can optimize the use of phenol in a wide range of applications, while also ensuring the safe handling and storage of this hazardous substance.
Reference:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK214904/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Phenol
- https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp115.pdf

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.