Summary
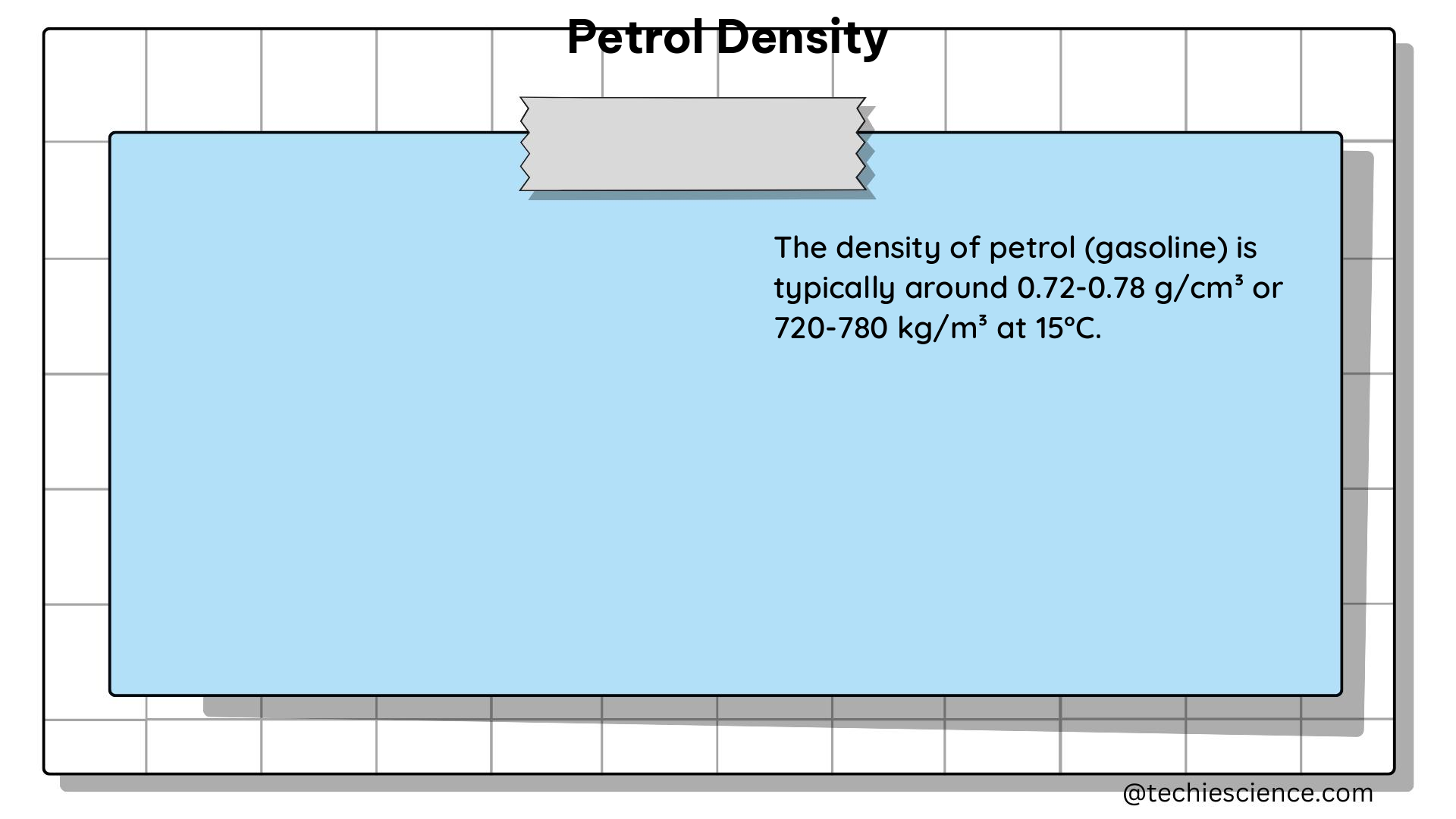
Petrol density, also known as the density of gasoline, is a crucial physical property that is measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per milliliter (g/ml). It is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume and can vary depending on factors such as temperature, pressure, and the specific type of gasoline. This comprehensive guide will delve into the technical details of petrol density, covering everything from the underlying physics principles to the advanced applications in the petroleum industry and beyond.
Understanding Petrol Density
Density and Its Relationship to Mass and Volume
Density is a fundamental physical property that describes the mass of a substance per unit volume. It is mathematically expressed as:
Density = Mass / Volume
where density is measured in kg/m³ or g/ml, mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g), and volume is measured in cubic meters (m³) or milliliters (ml).
Factors Affecting Petrol Density
The density of petrol can be influenced by several factors, including:
-
Temperature: As the temperature of petrol increases, the volume of the fuel expands, leading to a decrease in density. Conversely, as the temperature decreases, the volume contracts, resulting in an increase in density.
-
Pressure: Changes in pressure can also affect the density of petrol. Higher pressures tend to compress the fuel, leading to an increase in density, while lower pressures result in a decrease in density.
-
Fuel Composition: The specific type of gasoline, such as 1D, 2D, or 4D fuel, can have different densities due to variations in their chemical composition and the refining process.
Measuring Petrol Density
There are several methods for measuring the density of petrol, including:
-
Graduated Cylinder Method: This involves weighing an empty graduated cylinder, filling it with a known volume of petrol, and then weighing the cylinder again. The mass of the petrol can be calculated by subtracting the empty cylinder’s mass, and the density can be determined by dividing the mass by the volume.
-
Digital Density Meters: Modern digital density meters use oscillating U-tube technology to measure the true density of a petrol sample with high accuracy and precision. These meters are often calibrated using the density of air and water.
-
Specific Gravity: The density of petrol can also be expressed in terms of its specific gravity, which is the ratio of the density of the fuel to the density of water at a specific temperature (typically 4°C, where the maximum density of water is 1 g/ml).
Density Calculations and Conversions
To convert between different units of density, you can use the following formulas:
Density (kg/m³) = Density (g/ml) × 1000
Density (g/ml) = Density (kg/m³) / 1000
For example, if the density of a petrol sample is 850 kg/m³, the equivalent density in g/ml would be:
Density (g/ml) = 850 kg/m³ / 1000 = 0.850 g/ml
Petrol Density in the Petroleum Industry
ASTM Standards and Regulations
In the petroleum industry, the density of gasoline or diesel fuel is an important quality indicator that is governed by ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards. These standards ensure the consistency and reliability of fuel products, which is crucial for the efficient operation of engines and other equipment.
Density Measurement in Fuel Trading and Transportation
Accurate density measurement is essential in the trading and transportation of petrol and other fuels. Discrepancies in density can lead to disputes over the quantity and quality of the fuel, as well as potential financial losses. Digital density meters play a crucial role in ensuring the precise measurement of fuel density during these processes.
Density and Fuel Quality Characterization
In addition to its use in fuel trading and transportation, density measurement is also employed in the petrochemical industry to characterize and define the quality of various products, such as fuels, lubricating oils, and crude oils. Density is a key parameter in understanding the physical properties and performance characteristics of these materials.
Advanced Applications of Petrol Density
Density and Engine Performance
The density of petrol can have a significant impact on engine performance. Denser fuels, such as 4D gasoline, tend to have higher energy content per unit volume, which can result in improved fuel efficiency and power output. Understanding the relationship between fuel density and engine performance is crucial for optimizing engine design and operation.
Density and Emissions
The density of petrol can also influence the emissions produced by internal combustion engines. Denser fuels may result in incomplete combustion, leading to increased emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). Monitoring and controlling fuel density is essential for meeting stringent environmental regulations and reducing the environmental impact of petrol-powered vehicles.
Density and Fuel Blending
In the production of alternative fuels, such as biofuels or synthetic fuels, the density of the blended fuel is a critical parameter. Maintaining the appropriate density range is necessary to ensure compatibility with existing engine and fuel system designs, as well as to meet regulatory requirements.
Density and Academic Research
Density measurement is also a fundamental tool in professional academic research, where it is used to characterize the physical properties of a wide range of substances, including fuels, lubricants, and other materials. Accurate density data is essential for understanding the behavior and performance of these materials in various applications.
Conclusion
Petrol density is a complex and multifaceted physical property that plays a crucial role in the petroleum industry and beyond. This comprehensive guide has explored the fundamental principles of density, the factors that influence petrol density, and the various methods for measuring it. Additionally, it has highlighted the importance of petrol density in the petroleum industry, including its role in fuel trading, quality characterization, and engine performance. Finally, it has delved into the advanced applications of petrol density, such as its impact on emissions and fuel blending, as well as its significance in academic research.
By understanding the intricacies of petrol density, professionals in the petroleum industry, as well as researchers and students in the field of physics, can make informed decisions, optimize processes, and advance the understanding of this critical physical property.
References
- ISO/TR 19441:2018(en), Petroleum products — Density versus temperature correlation for distillate fuels, ISO, 2018.
- How to Measure the Density of Gasoline, Sciencing, 2020.
- Significance of true Density measurement in an Industry … – LinkedIn, LinkedIn, 2021.
- Density: a core parameter at key points – Jan 11 2019 – Petro Online, Petro Online, 2019.
- Measuring the density of fuels when trading and transporting, Anton Paar GmbH, 2021.

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.