The word “osmosis” is passive transport that is used to transport substances without the use of energy. There are some common type of osmosis example which are always spontaneous, along the solutes concentration gradient. It also involves simple diffusion, and facilitated diffusion and filtration.
Not take a look at the different types and examples of Passive transport
- Osmosis
- Endosmosis
- Exosmosis
- Simple Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Filtration
Osmosis
This type of passive transport, explains the movement of water but not the solute, water travels from areas with a lower solute concentration to areas with a higher solute concentration. Fatty acids and steroids are all diffuse passively across the cell membrane.
It will stop moving across the selectively permeable membrane once the water and solute concentration become an equal. It doesn’t require that the cell use any energy to move substances either into or out of the cell.There are two most common type of osmosis are Endosmosis and Exosmosis.
Endosmosis
It is the most common type of osmosis example in which the concentration of solute inside the cell is higher than the outside of the cell which will cause the water to move in or inside the cell.The cells are swell up due to the entry of water inside which cause cell to become turgid.there is a highest need of osmostic pressure during the endoosmosis becuase the pressure require for the prevention of the flow of water across the semi-permeable membrane.The most common example of endosmosis is root absorb capillary water from the soil and move towards xylem.
Exosmosis
The direction of solvent or water is outside of the cell in such a type of osmosis process.In a surrounding cell, the concentration of solute is higher than in the cytoplasm. It is the most common type of osmosis example.The flow of water molecules is outward from the cell which is completely opposite to the endosmosis mechanism.In such kind of situation cell will start to become shrink rather than become turgid,the process named Plasmolysis.
The most common example of exosmosis is, it exemplifies endosmosis during water move from the root to the xylem vessels of the plant.
Some other most common osmosis examples with the important roles are:
- The root absorb water from the plants via osmosis,it can control this absorption via the root hairs
- Transport of water in plant via osmosis
- It regulate the flow of liquid,gases and dissolved solids
- It can used to remove dirt or some other contaminants from water,osmotic power generation ,waste water treatments methods via forward osmosis and reverse osmosis mechanism.
Simple Diffusion
In this type of passive transport, the solution transverse the semipermeable cellular membrane. The membranes are usually uncharged, non-polar, smaller, and can easily pass through the phospholipid bilayer. The solutes travel along their concentration gradient or the passive movement of solute from an area of higher concentration to an area of low concentration rate.
It will stop moving across selectively permeable membrane once the solute concentration becomes equal or reach equilibrium. Passive transport is just simple diffusion of the molecules but not water.The Gas exchange is the most common example of diffusion. It can also describe as moving solute down to the concentration gradient.
Some factors that can affect the rate of diffusion include
- Solvent density-If solvent density rise, it will affect the diffusion and reduce the rate of the movement across the membrane
- Mass of the molecules-if the concentration of the molecules arising and more massive. It will move slowly and that will affect the faster rate of diffusion because a very slow rate of movement temperature-The temperature can also affect the rate of diffusion. If the temperature is high the movement will rise due to an increase in the rate of diffusion. at very less temperature it can affect the rate and movement of the molecule
- Concentration gradient-If the difference in conventions is high, the diffusion will go rapidly.if the distribution is closely related it can reach the equilibrium point and become stable thus there is no movement at this stage. The rate of diffusion becomes zero at this stage.
Facilitated Diffusion
This type of passive transport contains some transmembrane integral proteins or specific transport proteins that are embedded in the plasma membrane. The carrier proteins or protein channels do not require any energy as it facilitates the diffusion of a solute from the area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
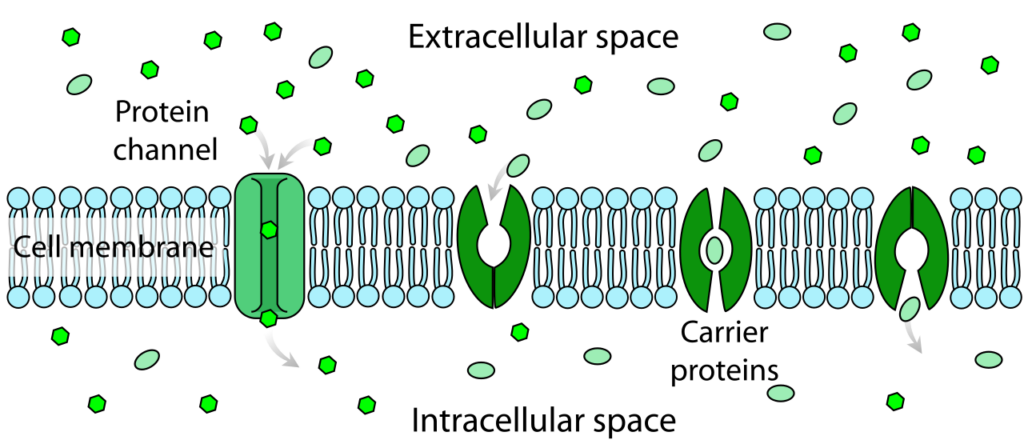
Image from Wikipedia
This type of diffusion is also known as carrier-mediated osmosis. The most common example of this kind of transport is ion channels, aquaporins, and a Glucose transporter. The glucose transporter is also known as a GLUT2-Glucose transporter 2.
By the use of this transporter, a concentration gradient can drive glucose across the membrane. The major difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion is that simple diffusion doesn’t require any transport protein while facilitated diffusion, for the movement across the membrane, requires transport protein to assist or facilitate the substances.
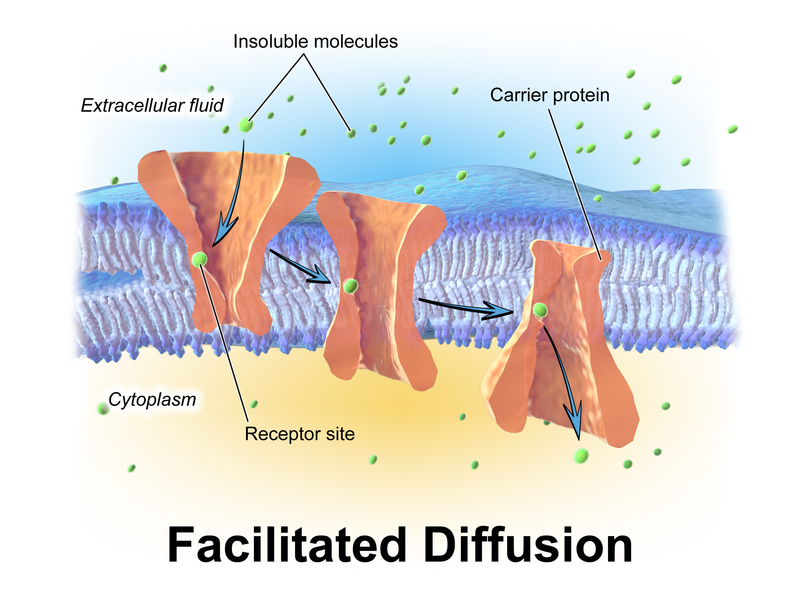
Image from Wikipedia
Filtration
Filtration is non-specific and also come in the category of passive transport in which the hydrostatic pressure or some other physical pressure pushes fluid or solute molecules and water across the cell membrane and that mainly depends on the size of the pore.
The osmosis and filtration mainly depends on the concentration gradient while filtration has a pressure gradient via which molecule move from an area of higher pressure to the area of lower pressure.
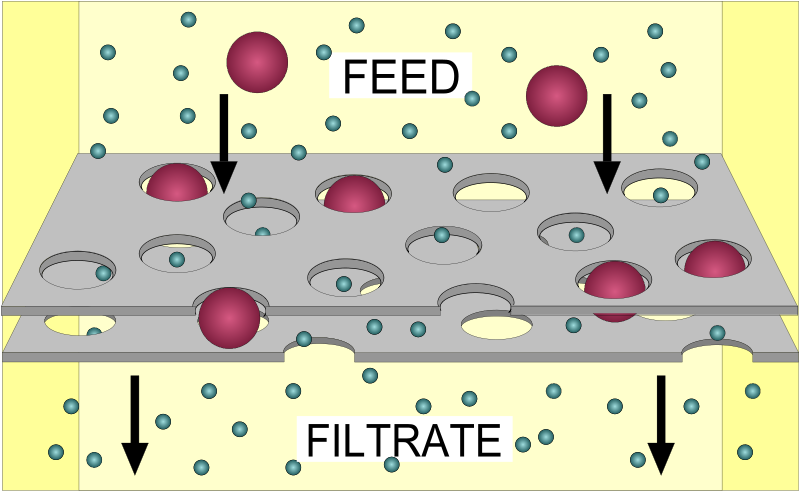
Image from Wikipedia
Some other most common example of passive transport is a voltage-gated ion channel in nerve cells. There is a concentration difference between NA+ and K+ inside and outside nerve cells.
On the membrane of a nerve cell, there is a voltage-gated channel that opens during the changes of voltage caused by other nerve cells.Osmotic balancing of salt concentration across the membrane is also an example of passive transport.
Conclusion
Passive transport is always energy-independent process that can able to transport the important material or substances across the membrane via the different type of transport mechanisms that uses energy-independent career proteins.
Also Read:
- Cellular respiration cycle
- Is lipase an enzyme
- What are the polymers of carbohydrates
- Mesophilic bacteria examples
- Dna transcription process
- Lichen examples
- Is fermentation anaerobic respiration
- Channel protein transport
- Is endocytosis pinocytosis
- Obligate anaerobes

Hello, I am Bhairavi Rathod, I have completed my Master’s in Biotechnology and qualified ICAR NET 2021 in Agricultural Biotechnology. My area of specialization is Integrated Biotechnology. I have the experience to teach and write very complex things in a simple way for learners.