In this article we will discuss about the relationship of Mass Flow Rate to Velocity.
The concept of flow rate(Mass Flow rate and Volume Flow Rate) measurement in a industry is very much essential for accurate and cost effective running of a process. Velocity indicates how fast a fluid is moving a distance per unit time.
Whenever we calculate flow rate of a fluid flowing through a pipe line certain terms like mass flow rate, volumetric flow rate, Molar flow rate, velocity, density, volume ,temperature , pressure etc come into the picture.
Flow rates and all the above mentioned physical properties are inter related and we can determine one quantity from the other by using different formulas associated with them.
Velocity=Distance traveled /Time
Volume Flow Rate, Q= Area x Velocity
Mass Flow Rate, ṁ=Density x Area x Velocity
Mass Flow Rate
Mass Flow Rate is the measurement of mass of a fluid passing through a passage per unit time.
Mass Flow rate can be expressed as,
ṁ=mass/time=m/t
SI unit of mass flow rate is Kg/s and it is denoted by ṁ.

Accurate measurement of Mass flow rate is necessary in an industry to control the different operations smoothly. Efficiency of an equipment and product quality also depends on mass flow rate of a fluid.
Mass is neither created nor destroyed and Mass flow rate is not affected by temperature and pressure change during the process so in case of precision measurement mass flow measurement is always advisable.
Mass Flow Rate to Velocity relationship
Flow rate measurement of different fluids is an important aspect of pipe line industries.
Velocity is the measurement of how fast a fluid is moving per unit of time. Mass Flow Rate is associated with the amount of fluid passing through a passage per unit time.
Mass Flow Rate can be expressed as ṁ=mass/time=m/t Eq1
And Volume Flow rate can be expressed as Q= volume/time= V/t Eq2
From Eq(1), ṁ=mass/volume . volume/time Eq3
Now, mass/volume=Fluid density ρ
And volume/time=Volumetric Flow Rate=Q
From Eq(3) , ṁ= ρ.Q Eq4
The above equation relates Mass Flow rate and Volumetric Flow Rate of a fluid. If we know the density of the fluid and discharge through a pipe, then we can determine the amount of fluid passing through the pipe in terms of Kg/s i.e. mass flow rate of the fluid.
From the Continuity Equation applicable for incompressible fluid we can write,
Here A is the cross sectional area of the passage and bar(v) is the average velocity of the fluid.
So Eq(4) becomes,
From the Eq(5) it is clear that mass flow rate of a liquid is directly proportional to the density of the liquid, velocity of the liquid and the cross sectional area.
How to Calculate Mass Flow Rate from Velocity?
The Flow rates, velocity, pressure, density all these terms are interrelated to each other.
If we know the velocity(v)of a flow through a pipe of cross sectional area(A), then we can calculate the volume flow rate of the fluid by using following formula,
Where Q=Volume Flow rate
A= Cross sectional area of the pipe
= Average velocity of the fluid
Now Mass Flow Rate is the density ρ multiplied by the Volume Flow Rate
ṁ=ρ. Q or,
As per the law of conservation of mass, in case of incompressible fluid passing through a channel of non uniform cross sectional area, the Mass flow rate maintains a constant value.
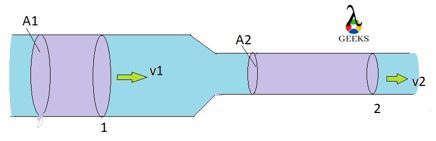
In the above figure we can observe a pipe with different cross sectional area A1 and A2 (where A1>A2) through which water(incompressible in nature) is flowing.
Even though the diameter of the pipe is not same, due to continuity same amount of water is passing through the point 1 and 2. The speed of the fluid is less at the wider area of the passage than the speed at the narrow region to keep the flow constant.
At point 1 and 2,
Q_{1}=Q_{2} or,
This is the famous Continuity Equation applicable for Incompressible fluids.
Difference between Mass Flow Rate and Velocity
The difference between Mass Flow Rate and Velocity as follows:
| Mass Flow Rate | Velocity |
| Volume Flow Rate(ṁ) is the amount of mass(m) of a fluid flows through a cross sectional area (A) per unit time (t). | Velocity bar(v) of a fluid is defined as the distance(d) travelled by a fluid within a time period( t). |
| Mathematically, ṁ= m/t | Mathematically, bar(v)=d/t |
| Units: kg/s( SI unit), gm/s(CGS unit) | Units: m/s(SI unit), cm/s(CGS unit) |
Problems Related to Mass Flow Rate
Problem 1: A fluid with density 650 kg/m3 is flowing through a duct of inner cross sectional area 25 cm2 with a velocity of 30 m/s. Find the mass flow rate of the fluid.
Solution: Here, Density, ρ=650kg/m3
Cross sectional Area, A=25 cm2=0.25m2
Velocity, v=30m/s
The formula for calculating mass flow rate ṁ= ρVA
\dot{m}= 650× 30 × 0.25m = 8400 kg/s
The mass flow rate m for the above-given data is 4875 kg/s
Problem 2:The mass flow rate of a fluid flowing through a circular pipe is 3600 kg/s, the velocity of the flow is 25 m/s and cross sectional area of the pipe is 10 cm2. Calculate the density of the fluid inside the pipe.
Solution:
From the given data,
\dot{m}= 3600 kg/s,
Velocity,v = 25 m/s and
Area of the cross section,A = 10 cm2 = 0.10m2
To determine the density of thefluid from the above-given values, we can use the formula,
Density ρ= m/vA
ρ = 3600 / ( 25 * 0.10 ) = 3600 / 2.5
ρ = 1440 kg/m3
The density of the liquid ρ of the fluid passing through the pipe is 1440kg/m3
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1: Write the differences between Mass Flow Rate and Volume Flow Rate.
Answer: The Differences between Mass Flow Rate and Volume Flow Rate are mentioned below:
| Mass Flow Rate | Volume Flow Rate |
| Actual mass of a fluid which travels through a measuring instrument per unit of time | Volume of fluid that passes through a measuring instrument per unit time. |
| Preferable in case of high accuracy with a high pressure rating | Generally preferred when high accuracy isn’t necessary. |
| There is no change in mass flow rate with changing pressure and temperature. | Changes in Flow rate occurs with pressure and temperature is changed. |
| Formula for mass flow rate, ṁ = Density x cross sectional area x velocity | Formula for volume flow rate, Q=Cross sectional area x Av. velocity |
| Mass flow is measured in kilogram/second | Volume flow rate is measured in litre/second or cubic metre/second. |
To know more about Mass Flow Rate(Click here)

I am Sangeeta Das. I have completed my Masters in Mechanical Engineering with specialization in I.C Engine and Automobiles. I have around ten years of experience encompassing industry and academia. My area of interest includes I.C. Engines, Aerodynamics and Fluid Mechanics. You can reach me at