Drone photography has become increasingly popular in recent years, and the lens used on the drone is a crucial component that determines the quality of the images and videos captured. From the field of view to the depth of field, the lens plays a significant role in the overall performance of the drone’s camera. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the technical details and quantifiable data related to lens for drone photography, providing you with a valuable resource to enhance your aerial photography skills.
Focal Length: The Key to Angle of View
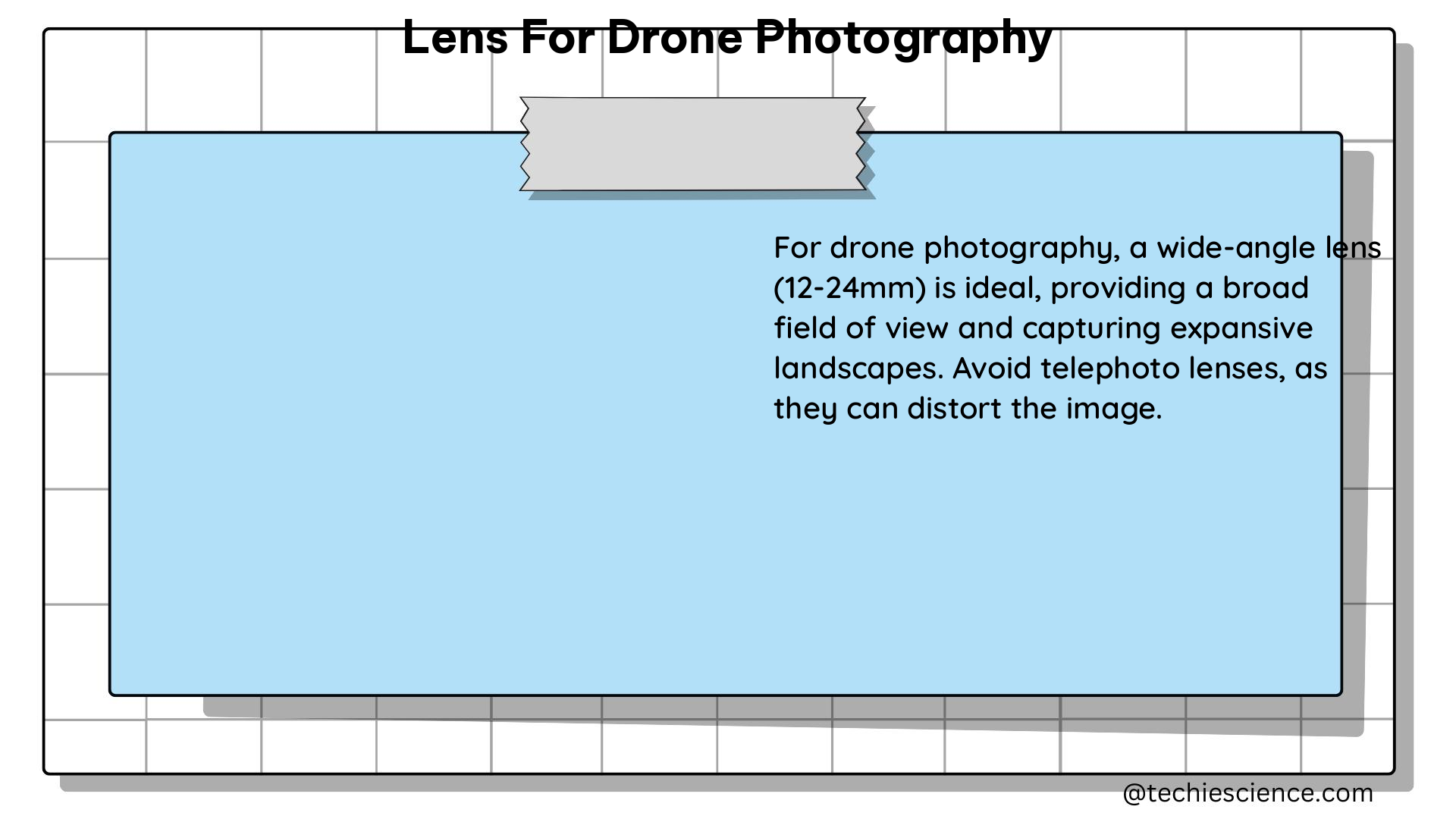
The focal length of a lens is the distance between the lens and the image sensor when the lens is focused on infinity. Measured in millimeters (mm), the focal length directly affects the angle of view and the magnification of the lens. A shorter focal length, such as 10-24mm, provides a wider angle of view, making it ideal for capturing landscape and architectural shots. Conversely, a longer focal length offers a narrower angle of view and higher magnification, suitable for capturing detailed images of distant objects.
Aperture: Controlling Depth of Field
The aperture of a lens is the opening that allows light to enter the camera. Measured in f-stops, a lower f-stop value (e.g., f/2.8) indicates a larger aperture, allowing more light to reach the sensor. This larger aperture results in a shallower depth of field, creating a blurred background and emphasizing the subject. Conversely, a higher f-stop value (e.g., f/5.6) corresponds to a smaller aperture, providing a deeper depth of field. For drone photography, a larger aperture (f/2.8 – f/5.6) is often used to capture sharp images with a blurred background, creating a visually appealing and professional-looking result.
Resolution: Capturing Fine Details
The resolution of a lens refers to its ability to capture fine details in an image. Measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI), a higher resolution provides more detail and sharper images, while a lower resolution results in less detail and blurrier images. For drone photography, a lens with a high resolution, such as 4K or 5K, is often used to capture detailed and sharp images and videos, ensuring that the final product is of the highest quality.
ISO Sensitivity: Adapting to Lighting Conditions
The ISO sensitivity of a lens is a measure of its sensitivity to light. Measured in ISO values, a higher ISO value indicates higher sensitivity to light, allowing for better low-light performance. Conversely, a lower ISO value provides better image quality in well-lit conditions. For drone photography, a lens with a low ISO value (100-400) is often used to capture high-quality images in well-lit environments, ensuring that the images are free from noise and grain.
Optical Zoom: Magnifying the Details
The optical zoom of a lens is the ability to magnify the image without losing image quality. Measured in times (x), a higher optical zoom provides a higher level of magnification, allowing you to capture detailed images of distant objects. For drone photography, a lens with a high optical zoom (2x-10x) can be particularly useful for capturing close-up shots of subjects or distant landmarks.
Theorem and Physics Formulas
The physics formula that relates the focal length, sensor size, and field of view of a lens is:
Field of View (FOV) = 2 x arctan (Sensor Size / (2 x Focal Length))
Where the sensor size is the physical size of the image sensor in the camera, and the focal length is the effective focal length of the lens.
Example 1:
A drone camera with a sensor size of 1/2.3″ (6.17 x 4.55mm) and a lens with a focal length of 4.5mm will have a horizontal field of view of approximately 84 degrees.
Example 2:
A drone camera with a sensor size of 1″ (12.8 x 9.6mm) and a lens with a focal length of 8mm will have a horizontal field of view of approximately 51 degrees.
Numerical Problem 1:
A drone camera has a sensor size of 1/2.3″ (6.17 x 4.55mm) and a lens with a focal length of 4.5mm. What is the horizontal field of view of the camera?
Solution:
Using the formula above, the horizontal field of view is approximately 84 degrees.
Numerical Problem 2:
A drone camera has a sensor size of 1″ (12.8 x 9.6mm) and a lens with a focal length of 8mm. What is the horizontal field of view of the camera?
Solution:
Using the formula above, the horizontal field of view is approximately 51 degrees.
Figures, Data Points, and Measurements
- A lens with a focal length of 10mm provides a wider angle of view than a lens with a focal length of 50mm.
- A lens with an aperture of f/2.8 provides more light than a lens with an aperture of f/5.6.
- A lens with a resolution of 4K provides more detail than a lens with a resolution of 1080p.
- A lens with an ISO sensitivity of 100 provides better image quality in well-lit conditions than a lens with an ISO sensitivity of 1600.
- A lens with an optical zoom of 10x provides a higher level of magnification than a lens with an optical zoom of 2x.
Conclusion
In the world of drone photography, the lens is a critical component that can make a significant difference in the quality of your images and videos. By understanding the technical details and quantifiable data related to focal length, aperture, resolution, ISO sensitivity, and optical zoom, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right lens for your drone photography needs. This comprehensive guide has provided you with the necessary knowledge and tools to master the art of lens selection for your aerial photography endeavors.
Reference:
- What Does a Drone See?: How Aerial Data Resolution Impacts Data Privacy and GDPR Compliance
- Quantitative Remote Sensing at Ultra-High Resolution with UAV Spectroscopy: A Review of Sensor Technology, Measurement Procedures, and Data Correction Workflows
- Lesson 1: Measuring Distance Using a Drone Photo | DroneBlocks
- Drones Camera Resolution: Three Metrics You Should Know About
- comparison of photography behaviors using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for landscape photography

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.