Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of objects and systems. It refers to the energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. In simpler terms, potential energy can be thought of as stored energy, waiting to be released or converted into another form. This type of energy is not immediately apparent or visible, but it has the potential to do work or cause a change in the system. Understanding potential energy is essential for comprehending various phenomena in nature, such as the movement of objects, the behavior of fluids, and the operation of machines. In this article, we will explore the concept of potential energy in detail, examining its different forms, examples, and applications. So, let’s dive in and uncover the fascinating world of potential energy!
Key Takeaways
- Potential energy is a form of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition.
- It can be converted into other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy, when the object is in motion.
- Examples of potential energy include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy.
- Understanding potential energy is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and environmental science.
Chemical Potential Energy
Chemical potential energy is a form of potential energy that is stored within the chemical bonds of substances. It plays a crucial role in various natural and man-made processes, including combustion, photosynthesis, and digestion. Let’s delve deeper into the definition and explanation of chemical potential energy, as well as the energy stored in substances due to their composition.
Definition and Explanation
Chemical potential energy is the energy stored within the chemical bonds of a substance. It is a result of the arrangement and composition of atoms in molecules. When a chemical reaction occurs, these bonds are broken and new ones are formed, resulting in a release or absorption of energy.
To understand chemical potential energy, let’s consider a simple example: a molecule of glucose. Glucose is a carbohydrate commonly found in plants and serves as a source of energy. Within the glucose molecule, there are multiple carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds. These bonds contain potential energy, which can be released through chemical reactions.
When glucose is broken down through a process called cellular respiration, the chemical bonds are broken, and the stored potential energy is converted into other forms, such as heat and ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is a molecule that stores and transports energy within cells. This energy is then utilized by living organisms for various metabolic processes.
Energy Stored in Substances due to Composition
The energy stored in substances due to their composition is a result of the arrangement and types of atoms present in the substance. Different substances have different chemical compositions, and therefore, they possess varying amounts of potential energy.
For example, fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas contain a high amount of potential energy due to the carbon-hydrogen bonds present in their chemical structures. When these fuels are burned, the bonds are broken, and the stored potential energy is released as heat and light.
Similarly, food items such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats contain potential energy stored within their chemical bonds. When we consume these foods, our bodies break down the bonds through digestion, releasing the stored energy for use in various bodily functions.
It is important to note that the amount of potential energy stored in a substance depends on its chemical composition and the strength of the bonds between its atoms. Substances with stronger bonds tend to have higher potential energy.
In summary, chemical potential energy is a form of potential energy stored within the chemical bonds of substances. It is released or absorbed during chemical reactions, and its amount depends on the composition and arrangement of atoms within the substance. Understanding chemical potential energy is crucial in comprehending the energy transformations and conversions that occur in various natural and man-made processes.
Gravitational Potential Energy
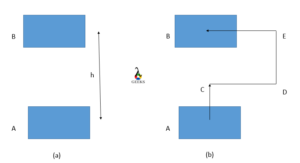
Gravitational potential energy is a form of potential energy that is stored in objects due to their position in a gravitational field. It is one of the many types of potential energy that exist in the world around us. In this section, we will explore the definition and explanation of gravitational potential energy, as well as how it is stored in objects.
Definition and Explanation
Gravitational potential energy can be defined as the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field. It is the energy that an object has by virtue of its height above the ground or any other reference point. The higher an object is above the ground, the greater its gravitational potential energy.
To understand this concept better, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine you have a ball on a shelf. When the ball is on the shelf, it has a certain amount of gravitational potential energy. This energy is stored in the ball and is waiting to be released. If you were to push the ball off the shelf, it would fall to the ground, converting its potential energy into kinetic energy as it accelerates due to gravity.
Energy Stored in Objects due to their Position in a Gravitational Field
The energy stored in objects due to their position in a gravitational field is directly related to their height above a reference point. The higher an object is, the more potential energy it possesses. This is because the object has the potential to fall and convert its potential energy into other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy.
The formula to calculate gravitational potential energy is:
Potential Energy = mass × acceleration due to gravity × height
Where:
– Mass is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg).
– Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by objects in a gravitational field, which is approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s²) on Earth.
– Height is the vertical distance between the object and the reference point in meters (m).
For example, let’s say we have a book with a mass of 2 kilograms (kg) placed on a shelf that is 2 meters (m) above the ground. Using the formula, we can calculate the gravitational potential energy of the book:
Potential Energy = 2 kg × 9.8 m/s² × 2 m = 39.2 joules (J)
Therefore, the book has 39.2 joules of gravitational potential energy when it is on the shelf.
In summary, gravitational potential energy is a type of potential energy that is stored in objects due to their position in a gravitational field. The higher an object is above a reference point, the more potential energy it possesses. This energy can be converted into other forms of energy when the object falls or moves in response to gravity.
Potential Energy in Lifting a Basketball
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage
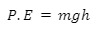
When we talk about potential energy, we are referring to the energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. It is a form of stored energy that has the potential to do work. In simpler terms, potential energy is like a “stored” energy waiting to be released.
There are various types of potential energy, including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, mechanical potential energy, and electrical potential energy. Each type of potential energy is associated with different factors and can be converted or transformed into other forms of energy.
Energy Stored When Lifting a Basketball Above the Ground
Let’s consider the example of lifting a basketball above the ground. When you lift the basketball, you are doing work against the force of gravity. As you raise the basketball higher, its potential energy increases.
The potential energy stored in the basketball is a result of its position relative to the ground. The higher you lift the basketball, the greater its potential energy becomes. This is because the basketball has the potential to fall back down to the ground due to the force of gravity.
To better understand this concept, let’s imagine a scenario where you hold the basketball at waist level. At this point, the basketball has a certain amount of potential energy. However, as you lift the basketball above your head, its potential energy increases significantly. This is because the basketball is now at a higher position and has the potential to fall from a greater height.
In this scenario, the potential energy stored in the basketball is converted into kinetic energy when it is released and falls back to the ground. The conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy is a fundamental principle in physics known as the conservation of energy.
In summary, potential energy is a form of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. When you lift a basketball above the ground, the potential energy stored in the basketball increases as its position relative to the ground changes. This potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy when the basketball is released and falls back to the ground.
Potential Energy in ATP
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that plays a crucial role in energy storage and transfer within cells. It is often referred to as the “energy currency” of the cell because it provides the necessary energy for various cellular processes. In this section, we will explore the explanation of ATP and its role in energy storage, as well as where potential energy is stored in ATP molecules.
Explanation of ATP and its role in energy storage
ATP is composed of three main components: a nitrogenous base called adenine, a sugar molecule called ribose, and three phosphate groups. The phosphate groups are the key to ATP’s role in energy storage. When ATP is synthesized, energy from various sources, such as the breakdown of glucose, is used to attach a third phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), forming ATP.
The energy stored in ATP is in the form of chemical potential energy. This means that the energy is stored within the chemical bonds of the molecule. When the cell requires energy for a particular process, such as muscle contraction or active transport, ATP is broken down into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing energy in the process. This energy is then used to drive the cellular processes.
Where potential energy is stored in ATP molecules
The potential energy in ATP is primarily stored in the high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups. These bonds are known as high-energy phosphate bonds. The first and second phosphate groups are relatively easy to break, releasing a moderate amount of energy. However, the third phosphate group, known as the terminal phosphate group, is connected to the rest of the molecule by a high-energy bond.
When this bond is broken, a significant amount of energy is released. This energy is harnessed by the cell to perform work. The breaking of the terminal phosphate bond converts ATP into ADP and Pi, releasing energy that can be used to power cellular processes.
It’s important to note that ATP is a dynamic molecule that is constantly being synthesized and broken down within cells. The energy released during the breakdown of ATP is used to perform work, and then the ADP and Pi can be recombined to form ATP again through processes such as cellular respiration.
In summary, ATP plays a vital role in energy storage and transfer within cells. The potential energy in ATP is stored in the high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups. When these bonds are broken, energy is released and used to power various cellular processes. Understanding the role of ATP and its potential energy is crucial in comprehending the fundamental mechanisms of energy transformation and conversion within living organisms.
Potential Energy in a Car
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in a Car
When we talk about potential energy in the context of a car, we are referring to the energy that is stored within the car’s various systems and components. Potential energy is a form of stored energy that has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy and perform work.
In a car, there are several types of potential energy that are stored and utilized to make the vehicle run efficiently. These include:
-
Gravitational Potential Energy: This type of potential energy is related to the car’s position relative to the Earth’s surface. When a car is parked on an incline or at the top of a hill, it possesses gravitational potential energy. This energy can be converted into kinetic energy when the car starts moving downhill.
-
Elastic Potential Energy: Elastic potential energy is stored in the car’s suspension system and tires. When the car encounters bumps or uneven surfaces, the suspension system compresses and stores energy. This energy is then released, helping the car maintain stability and a smooth ride.
-
Chemical Potential Energy: Cars rely on chemical potential energy stored in the fuel they consume. When fuel is burned in the engine, it undergoes a chemical reaction that releases energy. This energy is then converted into mechanical energy, which powers the car’s movement.
-
Mechanical Potential Energy: Mechanical potential energy is stored in various mechanical components of the car, such as the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. These components store energy in the form of tension, compression, or torsion. When the car is in motion, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, enabling the car to move.
-
Electrical Potential Energy: Modern cars also store electrical potential energy in their batteries. This energy is used to power various electrical systems in the car, such as the lights, radio, and air conditioning. The electrical potential energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as light or heat, to perform specific functions.
Examples of Potential Energy Storage in a Car
To better understand how potential energy is stored in a car, let’s look at a few examples:
-
When a car is parked on top of a hill, it possesses gravitational potential energy. As the car starts moving downhill, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, propelling the car forward.
-
The suspension system of a car stores elastic potential energy. When the car encounters a bump or pothole, the suspension system compresses and absorbs the impact, converting the potential energy into kinetic energy, which helps maintain a smooth ride.
-
The fuel in a car’s gas tank contains chemical potential energy. When the fuel is burned in the engine, it releases energy, which is then converted into mechanical energy to power the car’s movement.
-
The engine of a car stores mechanical potential energy. When the car is turned off, the engine components are in a state of tension or compression. When the car is started, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, allowing the engine to run.
-
The battery in a car stores electrical potential energy. This energy is used to power various electrical systems in the car, such as the lights, radio, and air conditioning. When these systems are turned on, the electrical potential energy is converted into other forms of energy to perform their respective functions.
In conclusion, potential energy is indeed stored energy in a car. The car’s various systems and components store different forms of potential energy, which can be converted into other forms of energy to power the vehicle‘s movement and functionality. Understanding the concept of potential energy in a car helps us appreciate the intricate mechanisms that enable our vehicles to operate efficiently.
Potential Energy in Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a vital source of energy for living organisms, including humans. They play a crucial role in providing fuel for various bodily functions and activities. But have you ever wondered how carbohydrates store potential energy? In this section, we will explore the explanation behind the potential energy storage in carbohydrates and where exactly this energy is stored within the carbohydrate molecules.
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in Carbohydrates
Potential energy is a form of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. In the case of carbohydrates, potential energy is stored in the chemical bonds that hold the molecule together. These bonds are formed between the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms present in the carbohydrate structure.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in specific ratios. The most common type of carbohydrate is glucose, which serves as the primary source of energy for the body. When glucose molecules are broken down during cellular respiration, the potential energy stored in their chemical bonds is released and converted into a usable form of energy called ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Where Potential Energy is Stored in Carbohydrate Molecules
Within a carbohydrate molecule, the potential energy is primarily stored in the bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. These bonds are known as covalent bonds and are formed when electrons are shared between the atoms. The energy required to break these bonds is known as bond dissociation energy.
Carbohydrates can exist in various forms, including monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two sugar units), and polysaccharides (long chains of sugar units). The potential energy stored in carbohydrates increases as the complexity of the molecule increases.
In monosaccharides like glucose, the potential energy is stored in the bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms within the molecule. When glucose is oxidized during cellular respiration, these bonds are broken, releasing the stored energy.
In disaccharides such as sucrose (table sugar), the potential energy is stored in the bonds between the two sugar units. When sucrose is broken down into its individual sugar units (glucose and fructose), the potential energy stored in these bonds is released.
Polysaccharides like starch and glycogen are long chains of sugar units. The potential energy in these molecules is stored in the multiple bonds between the sugar units. When the body needs energy, enzymes break down these polysaccharides into their constituent sugar units, releasing the stored potential energy.
In summary, potential energy in carbohydrates is stored in the chemical bonds between the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms within the molecule. The more complex the carbohydrate structure, the greater the potential energy stored. When these bonds are broken through various metabolic processes, the potential energy is released and converted into usable energy for the body.
| Carbohydrate Type | Potential Energy Storage |
|---|---|
| Monosaccharides | Bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms |
| Disaccharides | Bonds between sugar units |
| Polysaccharides | Multiple bonds between sugar units |
Understanding the concept of potential energy storage in carbohydrates helps us appreciate the vital role these molecules play in providing the energy needed for our bodies to function efficiently.
Potential Energy as Stored Energy

Explanation of Potential Energy as Stored Energy
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that refers to the energy possessed by an object due to its position or state. It is often described as “stored energy” because it has the potential to do work when released or transformed. In other words, potential energy is the energy that an object possesses because of its ability to change its position or shape.
There are various forms of potential energy, each associated with different types of systems. Some common examples include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, mechanical potential energy, and electrical potential energy. Let’s explore each of these forms in more detail:
-
Gravitational Potential Energy: This type of potential energy is associated with the position of an object in a gravitational field. The higher an object is lifted, the greater its gravitational potential energy. For example, when you lift a book off the ground, you are increasing its potential energy because it now has the ability to fall and do work.
-
Elastic Potential Energy: Elastic potential energy is stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed, such as a spring or a rubber band. When these objects are deformed from their equilibrium position, they store potential energy. When released, this energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing the object to move.
-
Chemical Potential Energy: Chemical potential energy is stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. When chemical reactions occur, these bonds are broken or formed, releasing or absorbing energy. For example, the potential energy stored in food is converted into kinetic energy when we digest it.
-
Mechanical Potential Energy: Mechanical potential energy is associated with the position or configuration of mechanical systems. For instance, a stretched bowstring or a wound-up clock spring possesses mechanical potential energy. When released, this energy is transformed into other forms, such as kinetic energy or sound energy.
-
Electrical Potential Energy: Electrical potential energy is stored in electric fields. It is the energy that charged particles possess due to their position in an electric field. When a circuit is connected, electrical potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as light or heat.
True or False Statement Regarding Potential Energy as Stored Energy
Now, let’s address a common misconception: potential energy is not the same as stored energy. While potential energy is a form of stored energy, not all stored energy is potential energy. Stored energy refers to any form of energy that is being stored, whether it is potential energy, kinetic energy, or any other type of energy.
Potential energy specifically refers to the energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. It is a type of stored energy that can be converted into other forms, such as kinetic energy, when the object’s position or state changes.
So, the statement “potential energy is stored energy” is true, but it is important to understand that not all stored energy is potential energy. Stored energy can take various forms depending on the system and the type of energy being stored.
In conclusion, potential energy is a type of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. It can be converted into other forms of energy when released or transformed. However, it is crucial to recognize that stored energy encompasses more than just potential energy, as there are other forms of energy that can be stored as well.
Potential Energy in Food
Food is not only a source of nourishment but also a storehouse of potential energy. When we consume food, our bodies convert the stored potential energy into usable forms of energy to power our daily activities. In this section, we will explore the concept of potential energy storage in food and understand where this energy is stored within food molecules.
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in Food
Potential energy is a type of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. In the case of food, potential energy is stored in the chemical bonds of molecules. These molecules contain energy-rich bonds that can be broken down through various metabolic processes to release energy.
When we eat food, our digestive system breaks down complex molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into simpler forms. This process, known as digestion, releases the potential energy stored in these molecules. The energy released is then used by our bodies for essential functions like maintaining body temperature, powering muscle contractions, and supporting organ function.
Where Potential Energy is Stored in Food Molecules
Different types of food molecules store potential energy in distinct ways. Let’s take a closer look at the main types of food molecules and where their potential energy is stored:
-
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches, are a primary source of energy for our bodies. The potential energy in carbohydrates is stored in the chemical bonds between the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms that make up these molecules. When we consume carbohydrates, our bodies break them down into glucose molecules, which can be further metabolized to release energy.
-
Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues in our bodies. The potential energy in proteins is stored in the peptide bonds that link amino acids together. During digestion, proteins are broken down into individual amino acids, which can be used by our bodies to build new proteins or convert into energy when needed.
-
Fats: Fats, also known as lipids, are a concentrated source of energy. The potential energy in fats is stored in the long hydrocarbon chains that make up their structure. When we consume fats, they are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol through digestion. These components can then be metabolized to release energy, making fats an efficient energy storage molecule.
It’s important to note that the amount of potential energy stored in food varies depending on the type and composition of the molecules present. Fats, for example, contain more than twice the amount of energy per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. This is why high-fat foods are often associated with providing more sustained energy.
In conclusion, food serves as a vital source of potential energy for our bodies. Through the process of digestion, the potential energy stored in food molecules is converted into usable forms of energy that power our everyday activities. Understanding where this energy is stored within food molecules helps us appreciate the importance of a balanced diet that provides a variety of nutrients to support our energy needs.
Potential Energy in Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds play a crucial role in storing potential energy. When atoms come together to form molecules, they can store energy in the bonds that hold them together. This potential energy can be released and transformed into other forms of energy when the bonds are broken. Let’s explore the definition and explanation of potential energy storage in chemical bonds.
Definition and Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are formed when atoms share or transfer electrons to achieve a stable configuration. These bonds can be strong or weak, depending on the types of atoms involved and the way they interact. The potential energy stored in chemical bonds is a result of the arrangement of atoms and the strength of the bonds holding them together.
When atoms bond, they rearrange their electrons to achieve a lower energy state. This rearrangement allows the atoms to become more stable and reduces their overall potential energy. The energy required to break these bonds and separate the atoms is equal to the potential energy stored in the bonds.
Specific Term for Potential Energy Stored in Chemical Bonds
The specific term used to describe the potential energy stored in chemical bonds is “chemical potential energy.” Chemical potential energy refers to the energy stored within the chemical bonds of a substance. It is a form of potential energy that can be released or transformed during chemical reactions.
Chemical potential energy can be released when bonds are broken, resulting in the formation of new substances with lower potential energy. This energy release can occur in the form of heat, light, or other forms of energy. For example, when fuel burns, the chemical potential energy stored in the bonds of the fuel molecules is converted into heat and light energy.
Chemical potential energy is an essential concept in understanding the behavior of substances and their reactions. It allows scientists to predict and explain the energy transformations that occur during chemical processes.
In summary, potential energy can be stored in chemical bonds. When atoms come together to form molecules, they rearrange their electrons, resulting in the formation of bonds and the storage of potential energy. This potential energy can be released or transformed during chemical reactions, leading to the formation of new substances and the release of energy in various forms. Chemical potential energy is the specific term used to describe the potential energy stored in chemical bonds.
Potential Energy in Systems
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that refers to the energy stored within a system due to its position or configuration. It is a form of stored energy that has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy or to do work. In this section, we will explore the definition and explanation of potential energy storage in systems, as well as the dependence of potential energy on the relative position of system parts.
Definition and Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in Systems
Potential energy is a type of stored energy that an object possesses by virtue of its position or condition. It is not directly observable but can be calculated based on the characteristics of the system. The concept of potential energy is closely related to the idea of work, which is the transfer of energy from one object to another.
There are various types of potential energy, including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, mechanical potential energy, and electrical potential energy. Each type of potential energy is associated with specific systems and conditions.
Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its height above the ground. For example, when a book is lifted onto a shelf, it gains gravitational potential energy because it is now higher above the ground.
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object when it is deformed or stretched. A common example is a compressed spring. When a spring is compressed, it stores potential energy that can be released when the spring is allowed to return to its original shape.
Chemical potential energy is the energy stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. It is released during chemical reactions. For instance, when fuel is burned, the chemical potential energy stored in the fuel is converted into heat and light energy.
Mechanical potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its position or shape. For example, a stretched rubber band has mechanical potential energy because it can snap back to its original shape when released.
Electrical potential energy is the energy stored in an electric field. It is associated with the position of charged particles within the field. When a charged object is placed in an electric field, it gains electrical potential energy.
Dependence of Potential Energy on the Relative Position of System Parts
The amount of potential energy stored in a system depends on the relative positions of its parts. In other words, potential energy is a function of the configuration of the system.
For gravitational potential energy, the amount of energy stored depends on the height of the object above a reference point, such as the ground. The higher the object is, the greater its gravitational potential energy. Similarly, the lower the object is, the lower its gravitational potential energy.
Elastic potential energy is determined by the amount of deformation or stretching of an object. The more the object is deformed or stretched, the greater its elastic potential energy. When the object returns to its original shape, the potential energy is released.
Chemical potential energy is influenced by the types and arrangements of atoms and molecules within a substance. Different substances have different chemical potential energies. For example, a battery stores chemical potential energy that can be converted into electrical energy.
Mechanical potential energy is dependent on the position or shape of an object. A compressed or stretched object has more mechanical potential energy than an object in its relaxed state.
Electrical potential energy is determined by the position of charged particles within an electric field. The closer the particles are to each other, the higher their electrical potential energy.
In conclusion, potential energy is a form of stored energy that exists within a system. It can be converted into other forms of energy or used to do work. The amount of potential energy stored in a system depends on the relative positions of its parts and the characteristics of the system itself. Understanding potential energy is crucial in comprehending the behavior and transformations of energy in various systems.
Potential Energy in Batteries
Explanation of potential energy storage in batteries
Batteries are an essential part of our everyday lives. They power our smartphones, laptops, and even electric vehicles. But have you ever wondered how batteries store energy? It all comes down to potential energy.
Potential energy is a form of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition. In the case of batteries, potential energy is stored in the chemical compounds within them. When a battery is fully charged, it contains a high amount of potential energy ready to be converted into other forms of energy, such as electrical energy.
To understand how potential energy is stored in batteries, let’s take a closer look at their composition. Batteries consist of two electrodes, an electrolyte, and a separator. The electrodes are typically made of different materials, such as lithium and cobalt. The electrolyte is a substance that allows ions to move between the electrodes, and the separator prevents direct contact between the electrodes.
When a battery is charged, a chemical reaction occurs within it. This reaction causes ions to move from one electrode to the other through the electrolyte. As the ions move, potential energy is stored in the chemical bonds of the electrode materials. This potential energy is released when the battery is connected to a device, allowing the stored energy to be converted into electrical energy.
How potential energy is stored in batteries
The storage of potential energy in batteries involves a series of energy transformations and conversions. Let’s break it down step by step:
-
Chemical potential energy: When a battery is fully charged, it contains a high amount of chemical potential energy. This energy is stored in the chemical compounds of the electrode materials. For example, in a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions are stored in the anode material, which is typically made of graphite.
-
Electrochemical reactions: When a battery is connected to a device, a series of electrochemical reactions occur. These reactions involve the movement of ions between the electrodes through the electrolyte. As the ions move, the chemical potential energy stored in the electrode materials is converted into electrical energy.
-
Electrical potential energy: As the electrochemical reactions take place, the potential energy is transformed into electrical potential energy. This electrical potential energy is the energy that can be used to power devices connected to the battery.
-
Energy transformation and conversion: The electrical potential energy stored in the battery is then transformed and converted into other forms of energy, such as mechanical energy to turn a motor or heat energy to generate warmth. This transformation and conversion of energy allow batteries to power various devices and systems.
In summary, potential energy is indeed stored energy, and batteries are a prime example of how potential energy can be stored and converted into other useful forms of energy. Understanding the concept of potential energy in batteries helps us appreciate the technology that powers our modern world. So the next time you use a battery-powered device, remember the hidden potential energy that lies within it.
Potential Energy as Actual Energy
Explanation of potential energy as a form of energy
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding how energy is stored and transformed. It is important to note that potential energy is not the same as stored energy, but rather a type of energy that has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy and perform work.
Potential energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position or condition. It is essentially the energy that is stored within an object or a system, waiting to be released and transformed into another form. When this stored energy is converted into another form, it becomes actual energy, which is the energy that is actively doing work.
There are several types of potential energy, each associated with different factors. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common forms of potential energy:
-
Gravitational Potential Energy: This type of potential energy is associated with the height of an object above the ground. The higher an object is positioned, the greater its gravitational potential energy. For example, a book placed on a shelf has gravitational potential energy because it has the potential to fall and release that stored energy.
-
Elastic Potential Energy: Elastic potential energy is stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed, such as a spring or a rubber band. When these objects are deformed from their equilibrium position, they store potential energy that can be released when they return to their original shape.
-
Chemical Potential Energy: Chemical potential energy is stored within the chemical bonds of substances. When chemical reactions occur, these bonds are broken or formed, releasing or absorbing energy. For example, the potential energy stored in food is converted into kinetic energy when we digest and metabolize it.
-
Mechanical Potential Energy: Mechanical potential energy is associated with the position or configuration of mechanical systems. For instance, a stretched bow possesses mechanical potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy when the arrow is released.
-
Electrical Potential Energy: Electrical potential energy is stored in electrically charged objects or systems. It is the energy that can be released when charges move through a conductor, such as a wire, and create an electric current.
Clarification of potential energy as stored energy
While potential energy is often referred to as stored energy, it is important to understand that potential energy is not stored in the traditional sense. Instead, it is a measure of the energy an object or system possesses due to its position or condition.
When an object or system has potential energy, it means that work has been done on it to change its position or configuration. This work transfers energy to the object or system, allowing it to store that energy until it is released and transformed into another form.
Think of potential energy as a form of “stored potential” rather than “stored energy.” It represents the capacity for an object or system to do work and release the stored energy when the conditions are right.
To better understand this concept, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine a ball sitting on a hill. The ball has gravitational potential energy because it is at a higher position relative to the ground. If the ball is allowed to roll down the hill, its potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy, the energy of motion.
In this example, the potential energy of the ball is not stored within the ball itself. Instead, it is a result of the ball’s position relative to the ground. Once the ball starts rolling, the potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which is the actual energy that is actively doing work.
In summary, potential energy is a form of energy that is not directly usable but has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy and perform work. It is not stored energy in the traditional sense, but rather a measure of the energy an object or system possesses due to its position or condition.
Potential Energy in Objects
Potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that refers to the energy an object possesses due to its position or state. In simpler terms, it is the stored energy an object has, waiting to be released and transformed into other forms of energy. Understanding potential energy is crucial in comprehending the various ways energy can be stored and converted.
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in Objects
Potential energy is a result of the forces acting on an object and the object’s position within a system. When an object is in a stable position, it possesses potential energy that can be converted into other forms of energy when the object is subjected to external forces. The concept of potential energy allows us to understand how energy is stored within objects and how it can be harnessed for various purposes.
There are different types of potential energy, each associated with specific types of objects and their characteristics. These include gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, mechanical potential energy, and electrical potential energy. Let’s explore each of these in more detail.
Where Potential Energy is Stored in Objects
-
Gravitational Potential Energy: This type of potential energy is associated with the position of an object in a gravitational field. When an object is lifted to a higher position, it gains gravitational potential energy. The amount of potential energy depends on the mass of the object and the height it is lifted to. For example, when a book is placed on a shelf, it possesses gravitational potential energy that can be released if it falls.
-
Elastic Potential Energy: Elastic potential energy is stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed, such as springs or rubber bands. When these objects are deformed from their equilibrium position, they store potential energy. The amount of potential energy stored depends on the stiffness of the object and the amount of deformation. When the object returns to its original shape, the potential energy is released. This is commonly observed in activities like launching a slingshot or compressing a spring.
-
Chemical Potential Energy: Chemical potential energy is stored in chemical bonds within molecules. When chemical reactions occur, these bonds are broken or formed, releasing or absorbing energy. This energy can be stored and later released when needed. For example, the potential energy stored in food is converted into kinetic energy when we consume it and use it for bodily functions.
-
Mechanical Potential Energy: Mechanical potential energy is associated with the position or configuration of mechanical systems. For instance, a stretched bowstring possesses mechanical potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy when the arrow is released. Similarly, a raised weight on a pulley system possesses mechanical potential energy that can be converted into other forms of energy when the weight is allowed to fall.
-
Electrical Potential Energy: Electrical potential energy is stored in electrical systems, such as charged particles or capacitors. When charges are separated or brought closer together, electrical potential energy is stored. This energy can be released when the charges are allowed to move or when a circuit is completed. Electrical potential energy is the basis for the functioning of batteries and electrical power systems.
In conclusion, potential energy is indeed stored energy. It is the energy an object possesses due to its position or state within a system. Understanding potential energy and its various forms allows us to comprehend how energy is stored, transformed, and utilized in different objects and systems. By harnessing potential energy, we can power our world and make use of the energy that surrounds us.
Potential Energy in the Human Body
The human body is a remarkable machine that constantly converts and stores energy to perform various functions. One form of energy that plays a crucial role in our bodies is potential energy. Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position or condition. In the case of the human body, potential energy is stored in different forms and locations, allowing us to carry out essential activities and movements.
Explanation of Potential Energy Storage in the Human Body
Potential energy in the human body can be understood as the energy that is waiting to be released or transformed into another form. It is like a coiled spring, ready to unleash its power when needed. This stored energy is essential for our survival and enables us to perform physical tasks, such as walking, running, and even breathing.
Where Potential Energy is Stored in the Human Body
Potential energy is stored in various parts of the human body, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some examples of where potential energy is stored:
-
Gravitational Potential Energy: Our bodies store gravitational potential energy, which is the energy associated with an object’s height or position relative to the Earth’s surface. When we climb stairs or raise our arms, our muscles work against gravity, storing potential energy that can be released when we descend or lower our arms.
-
Elastic Potential Energy: Elastic potential energy is stored in our muscles, tendons, and ligaments. When we stretch these tissues, they store potential energy that can be released to generate movement. For example, when we bend our knees before jumping, the potential energy stored in our leg muscles is converted into kinetic energy as we propel ourselves off the ground.
-
Chemical Potential Energy: The food we consume contains chemical potential energy. Through the process of digestion, our bodies convert this energy into a form that can be utilized for various bodily functions. This stored energy is released when our cells break down glucose molecules through cellular respiration, providing the fuel needed for our muscles to contract and perform work.
-
Mechanical Potential Energy: Mechanical potential energy is stored in our joints and connective tissues. When we flex or extend our limbs, potential energy is stored in the stretched muscles and tendons. This stored energy is then converted into kinetic energy when we release the tension and move our limbs.
-
Electrical Potential Energy: Our nervous system relies on electrical potential energy to transmit signals throughout the body. Nerve cells, known as neurons, store electrical potential energy in the form of charged ions. When a nerve impulse is triggered, this potential energy is converted into electrical signals that travel along the neurons, allowing communication between different parts of the body.
In summary, potential energy is indeed stored energy in the human body. It is stored in various forms and locations, enabling us to perform essential functions and movements. Understanding how potential energy is stored and converted within our bodies helps us appreciate the incredible energy transformations that occur to sustain our everyday activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, potential energy is a form of stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition. It is the energy that can be converted into other forms, such as kinetic energy, when the object is in motion. Potential energy can exist in various forms, including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is associated with an object’s height and mass, while elastic potential energy is stored in stretched or compressed objects like springs. Chemical potential energy is stored in the bonds of molecules and can be released during chemical reactions. Understanding potential energy is crucial in many fields, including physics, engineering, and everyday life. By harnessing and utilizing potential energy, we can power our homes, transport goods, and even explore the vastness of space. So, the next time you see an object at rest, remember that it may be storing a significant amount of potential energy, just waiting to be unleashed.
Is potential energy a form of stored energy related to the understanding of gravitational force as a central force?
Understanding the concept of gravitational force as a central force is crucial in comprehending the relationship between potential energy and stored energy. The gravitational force is considered a central force as it acts towards the center of mass of an object, such as the pull of Earth’s gravity towards its center. When an object is lifted above the ground, it gains potential energy because of its position with respect to the center of mass of the Earth. This potential energy is a form of stored energy that can be converted into other forms, such as kinetic energy, when the object falls or is released. To delve deeper into the understanding of gravitational force as a central force, refer to the article on Understanding Gravitational Force as Central Force.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is potential energy stored in an object?

Yes, potential energy is stored in an object. It is the energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition.
2. Where is potential energy stored in the human body?
Potential energy can be stored in various forms in the human body, such as chemical potential energy stored in food or mechanical potential energy stored in muscles.
3. How is potential energy stored in a battery?
In a battery, potential energy is stored in the form of chemical potential energy. It is the energy stored in the chemical bonds of the battery’s components.
4. Is potential energy actually energy?
Yes, potential energy is a form of stored energy. It represents the potential for an object or system to do work or undergo a transformation.
5. Why is potential energy stored in an object?
Potential energy is stored in an object because of its position, composition, or condition. It allows the object to have the potential to do work or undergo a transformation.
6. What is potential energy stored in chemical bonds called?
Potential energy stored in chemical bonds is called chemical potential energy. It is the energy stored in a substance due to its composition.
7. Is kinetic energy stored energy?
No, kinetic energy is not stored energy. It is the energy of motion possessed by an object. In contrast, potential energy is the stored energy in an object or system.
8. Where is potential energy stored when lifting a basketball above the ground?
When lifting a basketball above the ground, the potential energy is stored in the gravitational potential energy of the basketball. It is due to its position in the Earth’s gravitational field.
9. How is potential energy stored in a rubber band?
In a rubber band, potential energy is stored in the form of elastic potential energy. It is the energy stored in the stretched or compressed state of the rubber band.
10. Where is potential energy stored in a molecule?
Potential energy can be stored in a molecule in various forms, such as chemical potential energy stored in the bonds between atoms or electrical potential energy stored in the distribution of charges within the molecule.
Also Read:
- How to calculate gravitational energy in satellite orbits
- How to calculate the magnetic energy in an mri for improved imaging
- Example of kinetic to thermal energy
- How to calculate renewable energy sources
- How to measure the potential energy of a ski jumper at the jump s start point
- How to find energy in a fluctuating vacuum
- How to estimate energy in a holographic display
- How to measure radiant energy in lasers
- How to enhance sound energy clarity in hearing aids for better audio quality
- How to determine energy in holographic technology

The lambdageeksScience Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.