One of the most prevalent forms of human infections is intestinal parasitosis. These creatures affect one-third of the world’s population, including people living in both tropical and temperate regions, and it has been demonstrated that all immigrant groups are confronted to some extent. Here we will see intestinal parasites examples
- Enterobius vermicularis
- Ascaris lumbricoides
- Trichuris trichiura
- Ancylostoma duodenale
- Necator americanus
- Fasciolopsis buski
- Heterophyes heterophyes
- Metagonium yokogawai
- Schistosoma mansoni
- Schistosoma japonicum
- Schistosoma mekongi
- Schistosoma intercalatum
- Clonorchis sinensis
- Opisthorchis viverrini
- Fasciola hepatica
- Encephalitozoon hellem
- Encephalitozoon intestinalis
- Balantidium coli
- Dientamoeba fragilis
- Giardia lamblia
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Blastocystis hominis
- Cryptosporidium parvum
- Cystoisospora belli
- Cyclospora cayetanensis
- Taenia saginata
- Taenia solium
- Diphyllobothrium latum
- Hymenolepis nana
- Strongyloides stercoralis
- Iodamoeba buetschlii
Internal parasites examples
The following are the examples for the the internal parasites:
Enterobius vermicularis
It is perhaps the most common intestinal parasite in the United States. This parasite exclusively lives in humans and is most usually discovered in school-aged youngsters.

Ascaris lumbricoides
Ascaris lumbricoides is the biggest of the roundworms that infect people, reaching up to 35 cm in length and living in the small intestine for up to two years.
Trichuris trichiura
Trichuris trichiura, often known as the whipworm, is a parasitic roundworm (a form of helminth) that infects the human large intestine and causes trichuriasis (a type of helminthiasis that is one of the neglected tropical illnesses).
Ancylostoma duodenale
It is a parasitic nematode worm that goes by the name of old word ‘hookworm’. It reproduces and matures in the small intestines of dogs, cats and humans.
Necator americanus
After ascariasis, they are the second most prevalent source of helminthic infections and a prominent cause of iron deficiency anaemia in the underdeveloped world. Adult worms get their blood from the mucosa’s capillaries.
Fasciolopsis buski
It is a parasite of medicinal significance in humans and veterinary significance in pigs. It’s common throughout South and Southeast Asia.
Heterophyes heterophyes
To fulfil their intricate existence, they require a variety of species. Snails are the first intermediate host, followed by fish. Humans and other mammals are the ultimate hosts.
Metagonium yokogawai
Metagonimiasis is caused by a human parasite. It’s one of a few Metagonimus species that can cause metagonimiasis (others being M. takahashii and M. miyatai).
Schistosoma mansoni
is a human water-borne parasite that belongs to the blood fluke family (Schistosoma). The adult lives in the human gut’s blood vessels (mesenteric veins).
Schistosoma japonicum
Because this parasite infects at least 31 species of wild animals, including 9 carnivores, 16 rodents, one primate (human), two insectivores, and three artiodactyls, it is classified as a real zoonosis.
Schistosoma mekongi
It is one of the five major schistosomes that cause infections in humans. In humans, this trematode causes schistosomiasis.
Schistosoma intercalatum
S. intercalatum is one of the most common causes of schistosomiasis, generally known as bilharzia. It’s a trematode, and because it belongs to the Schistosoma genus, it’s also known as a blood fluke because the adult lives in blood vessels.
Clonorchis sinensis
Fish-eating animals, including humans, are infected. It feeds on bile after infecting the common bile duct and gall bladder in humans.
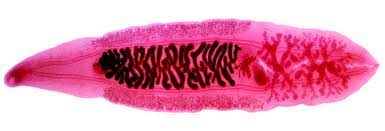
Opisthorchis viverrini
Southeast Asian liver fluke is a bile duct-infecting trematode parasite from the Opisthorchiidae family that is spread by food.
Fasciola hepatica
It affects the livers of different animals, including humans, and is spread over the world by sheep and cattle.
Encephalitozoon hellem
are spore-forming obligate intracellular parasites. Microsporidia is a phylum of fungi that comprises approximately 1200 species, many of which cause infection in humans.
Encephalitozoon intestinalis
The majority of infections are seen in immunocompromised individuals, such as those who have been infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Balantidium coli
The ciliated protozoa B coli causes balantidiasis, an intestinal illness. The main reservoir is thought to be pigs. Those who work with pigs or pig byproducts are more susceptible to illness.
Dientamoeba fragilis
The non-flagellated protozoan D. fragilis infects the large intestine. Human to human fecal oral spread or coinfection with E. vermicularis eggs are considered to be the routes of transmission (human pinworm).
Giardia lamblia
commonly known as Giardia intestinalis, is the most frequent parasite cause of diarrhoea in affluent nations, and it is also quite common in underdeveloped countries.
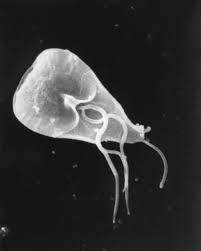
Entamoeba histolytica
E. histolytica, which causes amoebiasis in humans and other primates, is believed to infect roughly 35-50 million individuals globally.
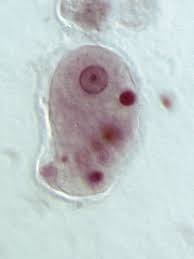
Blastocystis hominis
Blastocystis is one of the most prevalent parasitic infections in humans, with a worldwide distribution. It is the most recurrent parasite infection in the United States.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Cryptosporidiosis is a parasite illness of the mammalian digestive system caused by C. parvum, one of numerous species.
Cystoisospora belli
In immune-compromised humans, this protozoan parasite is opportunistic.
Cyclospora cayetanensis
is a coccidian parasite that causes cyclosporiasis, a diarrheal illness in humans and potentially other primates.
Taenia saginata
The beef tapeworm, T. saginata in humans, it causes taeniasis (a form of helminthiasis), while in cattle, it causes cysticercosis.
Taenia solium
The pork tapeworm, is found all over the world but is more frequent in places where pork is consumed. It’s a tapeworm that has humans as its primary host and pigs as a secondary or intermediate host.
Diphyllobothrium latum
parasite that resides in the intestines of fish is known as the wide or fish tapeworm or broad fish tapeworm. The pseudophyllid cestode D. latum infects both fish and mammals.
Hymenolepis nana
is a worldwide species that is most abundant in temperate zones. It is one of the most frequent cestodes (intestinal worms or helminths) that infect people, particularly youngsters.
Strongyloides stercoralis
Strongyloidiasis is caused by S. stercoralis, a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm.
Iodamoeba buetschlii
is a parasite ameba that lives in the large intestines of humans, pigs, and other animals.
What are the intestinal parasite?
In evolved countries, protozoan parasites cause gastrointestinal disorders more frequently than helminths. In endemic countries, intestinal parasites are a major source of sickness and death.
Conclusion
In the above article, we listed 31 different intestinal parasites and its existence in humans as well as animals and the health effects caused by these intestinal parasites.
Also Read:
- Does lysosome have membrane
- Independent assortment in meiosis 2
- Does mitochondria have double membrane
- Does bacteria have vacuole
- Do prokaryotes have exons
- Trilobite examples
- Do prokaryotes have a nucleus
- Fibrous protein function
- Enzymes in hydrolysis
- Monomer of protein example
Hi….I am Ganeshprasad DN, completed my Ph.D. in Biochemistry from Mangalore University, I intend to use my knowledge and technical skills to further pursue research in my chosen field.