Instantaneous and average velocity differs in the rate of calculation. In this post, we will know, is instantaneous velocity greater than the average velocity.
The instantaneous velocity can be greater, equal or lesser than average velocity depending on time interval. Average velocity is measured as the total sum of displacement divided by the whole time. In contrast, the instantaneous velocity is the measurement of velocity at any specific period.
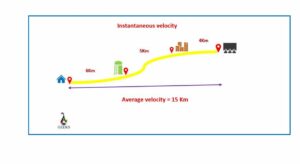
Let us study in-depth the various aspects of instantaneous velocity vs average velocity.
Instantaneous velocity vs average velocity
Both the quantities are different to some extent. Now, let’s study about the expected differences of instantaneous velocity vs average velocity as shown below,
| Parameters | Instantaneous Velocity | Average Velocity |
| Definition | Instantaneous velocity is the measurement of velocity at any value of time when the particle moves. It can also be given as the limit of . | Average velocity is the sum of the total calculation of the rate of change of velocity in the whole motion in consideration of time. |
| Formula | 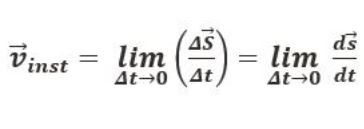 |
 |
| Usage of symbols |  = it refers to the derivative of the position of the particle in consideration with time interval. = it refers to the derivative of the position of the particle in consideration with time interval. = sf – si = sf – si = tf – ti = tf – ti |
Sf = Final position Si = Initial position tf = Final point of time interval ti = Initial point of time interval |
| Nature | Vector quantity | Vector quantity |
| Relation | At a given point of the interval, and is considered as the limit of average velocity. | After the completion of motion in any given time interval, it is measured. |
| Components | Magnitude as well as direction | Magnitude as well as direction |
| Example | If we consider a bicycle race, can calculate the instantaneous velocity at every turning point. | In the same example of instantaneous velocity, one can measure the average velocity after completing the motion. |
These are some of the primary vital points of instantaneous velocity vs average velocity.
Comparison of instantaneous velocity and average velocity
Even though both the quantities are calculated by considering different values of time intervals, there are some similarities.
- The average and instantaneous velocities are obtained through calculating the slope of mathematical quantities secant and tangents.
- They are vector quantities and have a dimension of L/T.
- During constant motion, both the quantities will have the same value.
- Vinst is measured between any two points of a particle in action, while the path of Vavg may be of any form [linear, curved].
These are some similarities between instantaneous velocity and average velocity.
Is instantaneous velocity greater than average velocity
can discuss the relationship between instantaneous and average velocity in time intervals.
Will be able to calculate the Vinst at any point of the total time interval when the body travels, and it is the limit of the average rate. In comparison, can measure average velocity after the completion of motion. Can understand the relationship clearly by knowing the distance-time graph.
The instantaneous velocity is a part of average velocity.
Graphs of instantaneous velocity and average velocity
It is possible to show both Vinst and Vavg in a displacement-time graph.
Instantaneous velocity is the measure of velocity using the slope of tangents.

- Average velocity is the measure of velocity using the slope of secants.
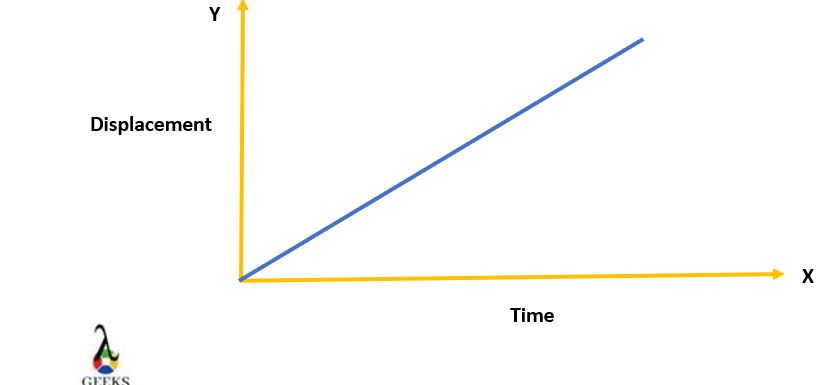
It is the primary comparison of graphs of Vinst and Vavg
Formulas to calculate instantaneous velocity and average velocity
There are two different formulas given according to measure the value of instantaneous velocity and average velocity.
- Instantaneous velocity
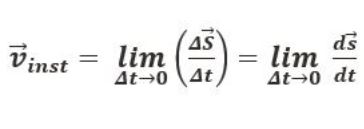
where,
ds/dt = it refers to the derivative of the position of a particle in consideration with time interval.
 = sf – si
= sf – si = tf – ti
= tf – ti
- Average velocity

where,
Sf = Final position
Si = Initial position
tf = Final point of time interval
ti = Initial point of time interval
The above formulas can even be obtained in different forms according to necessity.
Problems on instantaneous velocity and average velocity
Let us understand the concept of instantaneous velocity vs average velocity by solving some primary problems.
Problem 1
Find instantaneous velocity at t = 5, given the displacement equation as S = 4t3 – 2t2 + t + 9.
Solution:
The given equation of motion is
S(t) = 4t3 – 2t2 + t + 9.
Vinst = 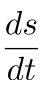 =
= 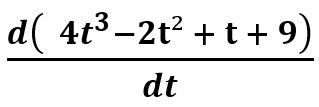 = [ (3 x 4 t2) – (2 x 2t) + 1]
= [ (3 x 4 t2) – (2 x 2t) + 1]
Vinst = 12t2 – 4t + 1
Instantaneous velocity at t = 5s
Vinst = 12(5)2 – 4(5) + 1
Vinst = 300 – 20 + 1
Vinst = 281 meters/second
The instantaneous velocity is 281 meters/second
Problem 2
A toy is thrown from a height to fall under the influence of gravity. The equation of motion is given by s(t) = 7.2 t2. Find the instantaneous velocity of the body at the eight-second after release?

Pixabay free images
Solution:
The equation of motion is
s(t) = 7.2 t2
To find Instantaneous velocity at t = 8s
Vinst = 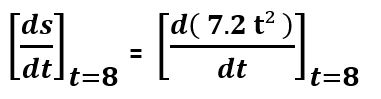
Vinst = [7.2 x 2 x t]t=8
Vinst = [7.2 x 2 x 8]
Vinst = 115.2 m/s
The instantaneous velocity is 115.2 meters/second
Problem 3
The motion of the truck is given by the function s = 5t2 + 11t + 6. and it moves at 30 km off the street in 6 minutes and again comes back and moves 13km back the street in 4reverses and drives 12 km back down the road in 4 minutes. Calculate instantaneous at t=2s and average velocity?

Pixabay free images
Solution:
To calculate Instantaneous velocity
Given function is s = 5t2 + 11t + 6.
Differentiating the given function with respect to t, we get
Vinst = ds/dt = 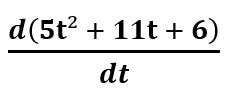
Vinst = v(t)= 10t + 11
For time t = 2s, the Instantaneous Velocity is articulated as,
V(2) = 10(2) + 11
V(2) = 31 m/s.
To find the Average velocity, the formula is
V = Displacement/time
V = (30 – 13)/ (6+4)
V = 17/10
V = 1.7 kilometre / minute
The instantaneous velocity is 31m/s, and the average velocity is 1.7 Km/min.
In this way, we got to know the various problem of instantaneous velocity vs average velocity.
Frequently asked Questions | FAQs
Mention the fundamental difference between instantaneous velocity and average velocity?
The primary difference between average velocity and instantaneous velocity lies in the calculation of position.
In general, we know that average velocity is the total change in the position of an object in consideration of time during the motion. In comparison, the instantaneous velocity is the calculation of instant change in the displacement related to time within the movement.
How can we find instantaneous velocity from average velocity?
There is some meaningful connection between average and instantaneous velocity.
When we try to measure Vinst of a particle during this, If we notice carefully, Vinst will be taken as the limit of Vavg as time tends towards zero. It can be even written in the form of derivative of x as given below,
v ( t ) = d d t x ( t )
Why do we use instantaneous velocity?
Instantaneous velocity acts according to its definition, and it helps in measuring tiny values of velocity.
Instantaneous velocity helps in calculating very tiny values of velocity at any point of motion of a body. It sometimes helps to note down the velocity of an object in any race at a particular time.
Can variation in instantaneous velocity affect the value of average velocity?
The variation in instantaneous velocity may or may not lead to any change in the average velocity.
We know from the definitions of both instantaneous and average velocity that they are used to measure the velocity of a body in any motion according to specific time intervals. Since the average is the total calculation and instantaneous is the calculation at a point, there may or may not be any changes.
Which scale of quantity is more critical among average velocity and instantaneous velocity?
Both the quantities have equal importance when it comes to the measurement of velocity.
If we consider an example of a race, then with the help of average velocity, we can calculate the total value of the velocity of motion of the car. Similarly, with the help of instantaneous velocity, we can know the velocity at any particular time.
On what condition do instantaneous velocity and average velocity become equal?
At some specific conditions, instantaneous velocity becomes equal to average velocity, and it is given below.
We know that the derivative of velocity with time leads to acceleration, and it plays a vital role in measuring both types of velocities. When the acceleration of the body is equal to zero, automatically, both the velocities will become equal since there is no chance of change in velocity.
Also Read:
- How to find velocity in superfluids
- Orbital velocity of moon
- How to find velocity from electric field
- How to determine velocity in multiverse theories
- How to calculate negative velocity
- What is constant in velocity time graph
- Velocity of sound in air 2
- Negative velocity graph
- How to find velocity using derivatives
- How to calculate velocity in molecular physics

I am Raghavi Acharya, I have completed my post-graduation in physics with a specialization in the field of condensed matter physics. I have always considered Physics to be a captivating area of study and I enjoy exploring the various fields of this subject. In my free time, I engage myself in digital art. My articles are aimed towards delivering the concepts of physics in a very simplified manner to the readers.