A parasite is a creature that lives on or in its host and feeds on or at the expense of that host. There is a detailed description of human parasites examples provided .
Human parasites are classified as endoparasites, which infect the body internally, and ectoparasites, which infect the skin externally.Humans can be infected by a number of parasitic worms. Flatworms, roundworms, and worms with thorny heads are among them (spiny-headed worm.
- Human whipworm
- Taenia saginata
- Threadworm
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Necator americanus
- Schistosoma mansoni
- Dracunculus medinensis
- Human pinworm
- Ancylostoma duodenale
- Fasciola hepatica
- Schistosoma japonicum
- Schistosoma haematobium
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Paragonimus westermani
- Entamoeba coli
- Cryptosporidium parvum
- Malaria parasite P. vivax
- Toxocara canis
- Crab louse
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Trypanosoma brucei
- Plasmodium knowlesi
- Ascaris lumbricoides
Human whipworm
Whipworm is a parasitic roundworm that infects the human large intestine and causes trichuriasis.

It is frequently referred to as the whipworm because of its shape, which resembles a whip with broader “handles” at the back end.
Taenia saginata
Taenia saginata, sometimes known as the beef tapeworm, is a zoonotic tapeworm belongs to the genus Taenia and the order Cyclophyllidea.

In humans, it causes taeniasis and cysticercosis, while in cattle, it causes taeniasis and cysticercosis.
Threadworm
Strongyloides stercoralis is a parasitic roundworm that causes strongyloidiasis in humans.
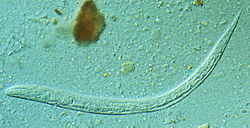
Threadworm is its common name in the United States.
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is a parasitic anaerobic amoebozoan belonging to the Entamoeba genus. E. histolytica, which causes amoebiasis in humans and other primates, is thought to infect about 35-50 million people worldwide.
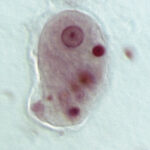
More than 55,000 people are estimated to die each year from E. histolytica infection.
Necator americanus
The New World hookworm, Necator americanus, is a species of hookworm. It belongs to the phylum Nematoda, which also includes other hookworms.
It’s a parasitic nematode that resides in human hosts’ small intestines.
Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma mansoni is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes.
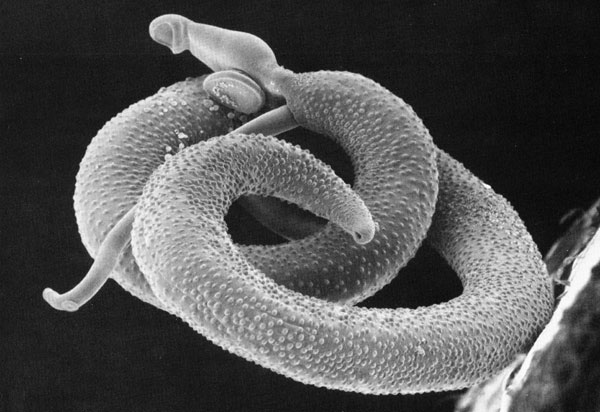
The adult lives in the blood vessels near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis. Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs.
Dracunculus medinensis
Dracunculus medinensis is a parasitic nematode that causes dracunculiasis (guinea worm illness).
The disease is caused by the female, which may grow to be up to 80 cm long and is one of the longest nematodes that can infect humans. The male Guinea worm with the longest recorded length is only 4 cm.
Read more about Archaea Examples
Human pinworm
The parasitic nematode (roundworm) Because of the female’s long, pointed tail, Enterobius vermicularis is commonly referred to as the human pinworm. The popular names “seatworm” and “threadworm” are used in various locations .
Ancylostoma duodenale
Ancylostoma duodenale is a roundworm species belonging to the Ancylostoma genus. It’s a parasitic nematode worm that goes by the name of Old World hookworm. It reproduces and matures in the small intestines of humans, cats, and dogs.
Fasciola hepatica
Fasciola hepatica is a parasitic trematode of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes, popularly known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke. It infects the livers of a variety of mammals, including humans, and is spread over the world by sheep and cattle.
Schistosoma japonicum
Schistosoma japonicum is a significant parasite and one of the main schistosomiasis infecting agents. Because this parasite infects at least 31 species of wild animals, including 9 carnivores, 16 rodents, one primate (human), two insectivores, and three artiodactyls, it is classified as a real zoonosis.
Schistosoma haematobium
A urinary blood fluke, Schistosoma haematobium, is a digenetic trematode belonging to the Schistosoma (blood fluke) genus. Africa and the Middle East are home to this species. Schistosomiasis, the most common parasite infection in humans, is caused by it.
Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasitic protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, which is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan. T. gondii can infect almost any warm-blooded animal, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only definitive hosts where the parasite can reproduce sexually.
Paragonimus westermani
Paragonimus westermani is the most common lung fluke that causes paragonimiasis in humans. The most prevalent human infections occur in eastern Asia and South America.
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba coli is a non-pathogenic Entamoeba species that lives in the human gastrointestinal tract as a commensal parasite. E. coli is important in medicine because it can be mistaken for the pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during microscopic examination of stained stool specimens.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Cryptosporidiosis is a parasite disease of the mammalian digestive tract caused by Cryptosporidium parvum, one of several species. Parvum Cryptosporidium C. parvum oocysts in immunofluorescence. Classification in science.
Malaria parasite P. vivax
Plasmodium vivax is a human disease and protozoal parasite. The parasite that causes recurrent malaria is the most common and widespread.
Toxocara canis
Toxocara canis is a parasitic helminth parasite that affects dogs and other canids all over the world. The term comes from the Greek words “toxon,” which means “bow or quiver,” and “caro,” which means “flesh.” They dwell in the final host’s small intestine.
Plasmodium malariae
The parasitic protozoan Plasmodium malariae causes malaria in humans. It’s one of numerous Plasmodium parasite species that infect other creatures as pathogens, including Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, which are responsible for the majority of malaria infections.
Crab louse
The crab louse, sometimes known as the pubic louse, is a parasitic insect that feeds solely on human blood. The crab louse lives in the pubic hair of most people.
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum is a human unicellular protozoan parasite and the deadliest Plasmodium species that causes malaria. The parasite is spread by a female Anopheles mosquito bite and produces falciparum malaria, the most deadly form of malaria.
Trypanosoma brucei
The parasitic kinetoplastid Trypanosoma brucei belongs to the genus Trypanosoma. Tsetse fly species in Sub-Saharan Africa carry this parasite, which causes vector-borne illnesses in vertebrate animals, including humans. T. brucei causes African trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness, in humans.
Plasmodium knowlesi
The parasite Plasmodium knowlesi causes malaria in humans and other primates. It can be found all over Southeast Asia, and in Malaysia, it is the most common cause of human malaria. P. knowlesi, like other Plasmodium species, has a life cycle that necessitates the infection of a mosquito and a warm-blooded host.
Ascaris lumbricoides
Ascaris lumbricoides is a human “big roundworm” that can grow up to 35 cm in length. It is one of several Ascaris species. It is the most prevalent parasitic worm in humans and is an ascarid nematode of the phylum Nematoda.
Also Read:
- Hypertonic vs hypotonic
- Do animal have enzymes
- Fungi parasites examples
- Dental anatomy
- Enzymes and substrates
- Protoctista examples
- Do animal cells have flagella
- Is fatty acid a lipid
- Are bacteria pathogens
- Cellular respiration process

Hi…I am Sadiqua Noor, done Postgraduation in Biotechnology, my area of interest is molecular biology and genetics, apart from these I have a keen interest in scientific article writing in simpler words so that the people from non-science backgrounds can also understand the beauty and gifts of science. I have 5 years of experience as a tutor.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-