Summary
Velocity is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the rate of change in an object’s position over time. To find the velocity at a specific point in time, known as velocity 3, we need to use the formula v = d/t, where v is the velocity, d is the displacement (distance), and t is the time. This guide will provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how to calculate velocity 3, including the necessary formulas, examples, and practical applications.
Understanding Velocity
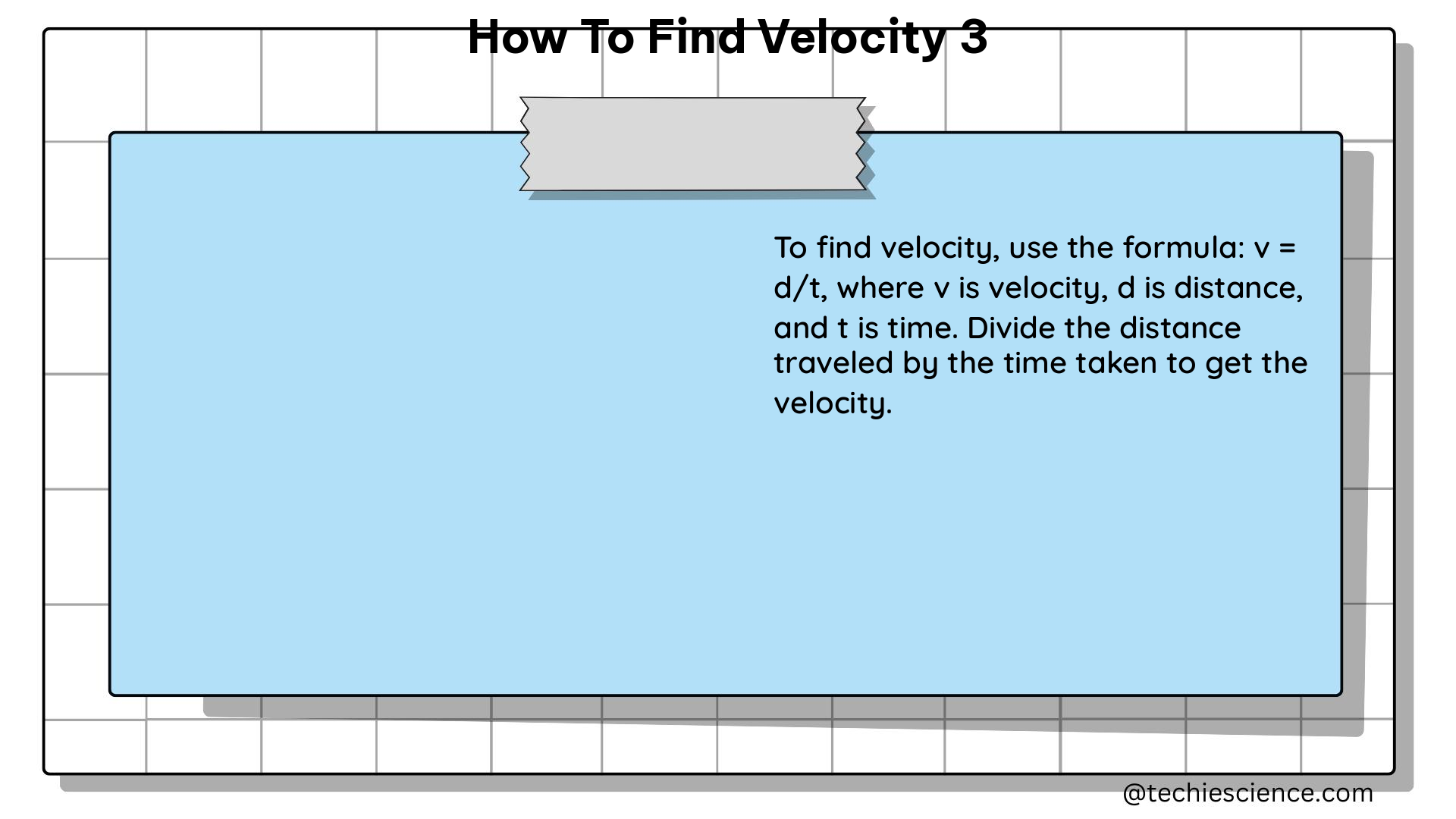
Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. The formula for velocity is:
v = d/t
Where:
– v is the velocity (in units of distance per time, such as m/s, ft/s, or mph)
– d is the displacement (distance traveled, in units of distance)
– t is the time (in units of time, such as seconds or minutes)
Velocity can be positive or negative, depending on the direction of motion. For example, an object moving east at 5 m/s has a velocity of +5 m/s, while an object moving west at 5 m/s has a velocity of -5 m/s.
Calculating Velocity 3
To find the velocity 3, we need to know the displacement and time at that specific point in time. Here’s the step-by-step process:
-
Identify the time point: Determine the time at which you want to find the velocity, which in this case is “velocity 3”.
-
Measure the displacement: Measure the distance the object has traveled up to the time point you identified in step 1.
-
Calculate the velocity: Plug the displacement and time values into the velocity formula:
v = d/t
Where:
– v is the velocity at the time point (velocity 3)
– d is the displacement up to the time point
– t is the time at the time point
Let’s look at an example:
Suppose an object travels a distance of 60 meters in 12 seconds. To find the velocity at the 3-second mark (velocity 3), we would:
- Identify the time point: 3 seconds
- Measure the displacement: Let’s say the object has traveled 15 meters in 3 seconds
- Calculate the velocity:
v = d/t
v = 15 meters / 3 seconds
v = 5 m/s
Therefore, the velocity of the object at the 3-second mark (velocity 3) is 5 m/s.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Velocity is a crucial concept in various fields, including physics, engineering, and transportation. Understanding how to calculate velocity 3 can be useful in the following scenarios:
-
Motion Analysis: Calculating velocity 3 can help analyze the motion of an object, such as a moving vehicle, a projectile, or a falling object. This information can be used to study the object’s behavior, predict its future position, or optimize its performance.
-
Kinematics Equations: Velocity is a key variable in the kinematic equations, which describe the relationship between position, velocity, acceleration, and time. Knowing the velocity at a specific time point can help solve these equations and understand the object’s motion.
-
Velocity-Time Graphs: Plotting the velocity of an object over time can provide valuable insights into its motion. The slope of the velocity-time graph represents the acceleration, and the area under the curve represents the displacement.
-
Velocity Measurements: Velocity can be measured using various instruments, such as speedometers, radar guns, or laser-based systems. Knowing how to interpret and analyze these measurements is essential in fields like transportation, sports, and scientific research.
-
Relative Velocity: When dealing with multiple objects in motion, it is often necessary to calculate their relative velocity, which is the velocity of one object with respect to another. This concept is crucial in areas like air traffic control, spacecraft navigation, and sports analytics.
Conclusion
In summary, finding velocity 3 involves using the formula v = d/t, where v is the velocity, d is the displacement, and t is the time. By understanding the principles of velocity and applying the appropriate calculations, you can determine the velocity of an object at a specific point in time, which can be valuable in a wide range of applications.
References
- Study.com, Velocity, Distance & Time Word Problems | Overview & Examples
- wikiHow, Calculate Velocity
- GymAware, Velocity Based Training: theory and application

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.