In the realm of geometry, understanding the area of various shapes is a fundamental skill. One such shape that often appears in mathematical problems is the trapezoid. While the basic formula for finding the area of a trapezoid is well-known, there are more advanced techniques and considerations when dealing with specific types of trapezoids. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of finding the area of a trapezoid 2, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to tackle even the most complex scenarios.
Understanding the Trapezoid 2
A trapezoid 2 is a quadrilateral with two parallel sides, but the non-parallel sides are not necessarily equal in length. This distinguishes it from a regular trapezoid, where the non-parallel sides are equal in length. The presence of unequal non-parallel sides adds an additional layer of complexity when calculating the area.
Theorem for the Area of a Trapezoid 2
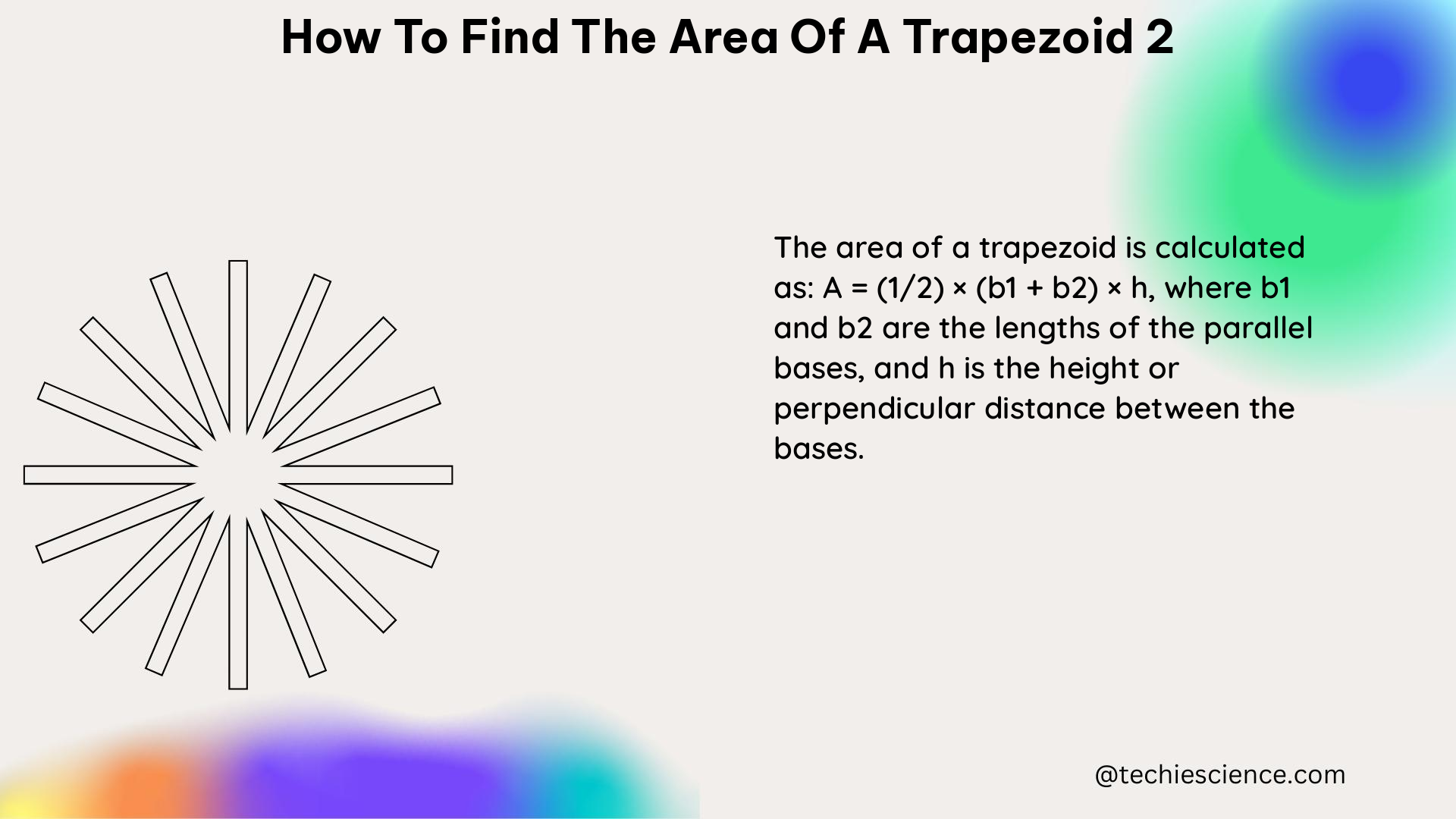
The formula for the area of a trapezoid 2 is:
Area = (1/2) × h × (b1 + b2)
Where:
– h is the height of the trapezoid
– b1 is the length of the top base
– b2 is the length of the bottom base
This formula is derived by dividing the trapezoid 2 into a rectangle and two right triangles, finding the areas of those shapes, and then adding them together.
Proof of the Formula
To prove the formula for the area of a trapezoid 2, we can use the following steps:
- Divide the trapezoid 2 into a rectangle and two right triangles.
- Find the area of the rectangle using the formula: A = b × h, where b is the base and h is the height.
- Find the area of each right triangle using the formula: A = (1/2) × b × h, where b is the base and h is the height.
- Add the area of the rectangle and the two right triangles to get the total area of the trapezoid 2.
By following this process, we can arrive at the formula: Area = (1/2) × h × (b1 + b2).
Practical Applications and Examples
To better understand the application of the formula for the area of a trapezoid 2, let’s explore some real-world examples.
Example 1: Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid 2 in Engineering
In the field of engineering, trapezoids are often used in the design of structures, such as roofs or support beams. Consider a trapezoid 2 with the following dimensions:
– Height (h) = 8 meters
– Top base (b1) = 6 meters
– Bottom base (b2) = 10 meters
To find the area of this trapezoid 2, we can use the formula:
Area = (1/2) × h × (b1 + b2)
Area = (1/2) × 8 × (6 + 10)
Area = (1/2) × 8 × 16
Area = 64 square meters
This information can be crucial in determining the material requirements and structural integrity of the engineering project.
Example 2: Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid 2 in Architecture
In the field of architecture, trapezoids are often used in the design of roofs, windows, and other architectural elements. Consider a trapezoid 2 with the following dimensions:
– Height (h) = 4 feet
– Top base (b1) = 3 feet
– Bottom base (b2) = 7 feet
To find the area of this trapezoid 2, we can use the formula:
Area = (1/2) × h × (b1 + b2)
Area = (1/2) × 4 × (3 + 7)
Area = (1/2) × 4 × 10
Area = 20 square feet
This information can be used to determine the material requirements, energy efficiency, and overall design of the architectural structure.
Example 3: Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid 2 in Art and Design
In the realm of art and design, trapezoids are often used in the creation of various visual elements, such as frames, logos, or patterns. Consider a trapezoid 2 with the following dimensions:
– Height (h) = 6 inches
– Top base (b1) = 4 inches
– Bottom base (b2) = 8 inches
To find the area of this trapezoid 2, we can use the formula:
Area = (1/2) × h × (b1 + b2)
Area = (1/2) × 6 × (4 + 8)
Area = (1/2) × 6 × 12
Area = 36 square inches
This information can be used to determine the size and proportions of the design elements, ensuring a visually appealing and balanced composition.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the basic formula for the area of a trapezoid 2 is straightforward, there are some advanced techniques and considerations that can be helpful in more complex scenarios.
Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid 2 without the Height
In some cases, you may not have the height of the trapezoid 2 available, but you do have the lengths of the non-parallel sides (the legs). In such situations, you can use the following formula to calculate the area:
Area = (1/2) × a × (a + b)
Where:
– a and b are the lengths of the non-parallel sides (the legs) of the trapezoid 2
This formula is derived by dividing the trapezoid 2 into a rectangle and two right triangles, finding the areas of those shapes, and then adding them together.
Dealing with Irregular Trapezoids 2
If the trapezoid 2 has non-parallel sides that are not straight lines, the area calculation becomes more complex. In such cases, you may need to divide the shape into smaller, more manageable segments and calculate the area of each segment individually, then add them together to find the total area.
Incorporating Angles and Trigonometry
In some advanced scenarios, you may need to consider the angles of the trapezoid 2 in addition to the lengths of the sides. In these cases, you can use trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, to calculate the area more precisely.
Numerical Problems and Exercises
To further solidify your understanding of finding the area of a trapezoid 2, it’s recommended to practice solving numerical problems and exercises. This will help you develop a deeper intuition for the concepts and improve your problem-solving skills.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of finding the area of a trapezoid 2 is a valuable skill that can be applied in various fields, from engineering and architecture to art and design. By understanding the underlying theorem, the proof of the formula, and the practical applications, you can confidently tackle even the most complex scenarios involving trapezoids 2.
Remember, the key to success in this domain is to practice, experiment, and continuously expand your knowledge. With the guidance provided in this comprehensive guide, you are well on your way to becoming a true expert in the area of trapezoid 2 geometry.
References:
- Varsity Tutors – How to Find the Area of a Trapezoid
- Omni Calculator – Area of a Trapezoid
- Khan Academy – Area of a Trapezoid
- CueMath – Area of a Trapezoid
- YouTube – How to Find the Area of a Trapezoid

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.