Summary
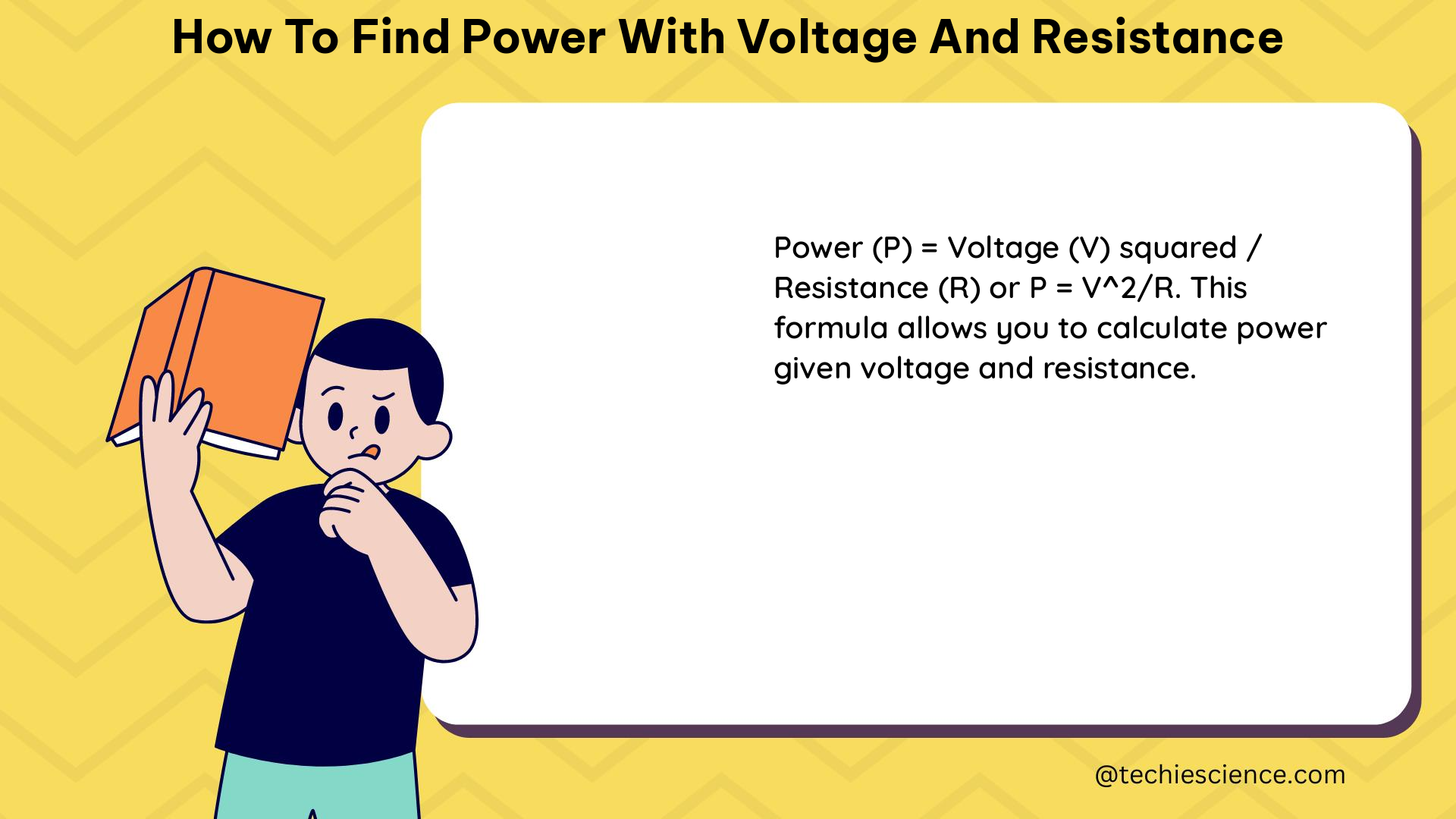
To find power with voltage and resistance, you can use the formulas P = V^2 / R or P = V * I, where P is power, V is voltage, R is resistance, and I is current. These formulas are derived from Ohm’s Law and the power formula, which describe the mathematical relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in an electrical circuit. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a detailed understanding of these concepts, including the variables involved, measurement techniques, and step-by-step calculations, along with relevant examples and numerical problems to help you master the topic.
Understanding the Variables
- Power (P): Power is the rate at which energy is transferred or the amount of work done per unit of time. It is measured in watts (W).
- Voltage (V): Voltage is the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit. It is measured in volts (V).
- Resistance (R): Resistance is the measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is measured in ohms (Ω).
- Current (I): Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is measured in amperes (A).
Measuring Voltage and Resistance
- Measuring Voltage:
- Use a digital multimeter to measure the voltage across the two points in the circuit where you want to calculate the power.
- Set the multimeter to the appropriate direct current (DC) voltage range.
-
Ensure that the multimeter is connected in parallel with the circuit or component you are measuring.
-
Measuring Resistance:
- Use a digital multimeter to measure the resistance of the circuit or component where you want to calculate the power.
- If you are using a resistor, you can use a Vernier Resistor Board to include a known resistance in your circuit.
- Ensure that the circuit or component is disconnected from the power source before measuring the resistance.
Calculating Current
- Using Ohm’s Law:
- If you have measured the voltage and resistance, you can calculate the current using the formula I = V / R.
-
Ohm’s Law states that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
-
Measuring Current:
- If you have already measured the current, you can use the value you measured.
- Use a digital multimeter to measure the current in the circuit or component where you want to calculate the power.
- Ensure that the multimeter is connected in series with the circuit or component you are measuring.
Calculating Power
- Using the Power Formula:
-
Once you have measured or calculated the voltage, resistance, and current, you can calculate the power using one of the following formulas:
- P = V^2 / R
- P = V * I
-
Examples:
- Example 1: Find the power of a circuit with a voltage of 120 V and a resistance of 60 Ω.
- Solution: Use the formula P = V^2 / R.
- P = 120^2 / 60
- P = 2400 / 60
- P = 40 W
- Example 2: Find the power of a circuit with a voltage of 120 V, a resistance of 60 Ω, and a current of 2 A.
- Solution: Use the formula P = V * I.
- P = 120 * 2
- P = 240 W
Factors Affecting Power Calculations
- Temperature Changes: The resistance of a circuit or component can change with temperature, which can affect the power calculations.
- Manufacturing Tolerances: The actual values of voltage, resistance, and current may differ from the theoretical or measured values due to manufacturing variations.
- External Factors: Other external factors, such as electromagnetic interference, can also influence the performance of a circuit and the accuracy of power calculations.
Numerical Problems
- Problem 1: A circuit has a voltage of 220 V and a resistance of 100 Ω. Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit.
-
Solution:
- P = V^2 / R
- P = 220^2 / 100
- P = 48,400 / 100
- P = 484 W
-
Problem 2: A resistor with a resistance of 1 kΩ is connected to a 12 V power supply. Calculate the power dissipated in the resistor.
-
Solution:
- P = V^2 / R
- P = 12^2 / 1000
- P = 144 / 1000
- P = 0.144 W
-
Problem 3: A circuit has a voltage of 120 V and a current of 5 A. Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit.
- Solution:
- P = V * I
- P = 120 * 5
- P = 600 W
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the fundamental concepts and formulas for finding power with voltage and resistance. By understanding the variables involved, measuring voltage and resistance, calculating current, and applying the power formulas, you can accurately determine the power dissipated in electrical circuits. Remember to consider the factors that can affect the accuracy of your calculations, and always verify the results before applying them in your projects or calculations.
References
- Ohm’s Law Calculating
- Current in Electrical Circuits
- Ohm’s Law
- Multimeter Lab Sheet
- Ohm’s Law Calculator

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.