In the world of electrical engineering, understanding the relationship between power, voltage, and frequency is crucial for designing and analyzing electrical circuits. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of calculating power using voltage and frequency, providing you with a deep understanding of the underlying principles and practical applications.
Understanding the Impedance of the Circuit
The key to finding power with voltage and frequency lies in the concept of impedance. Impedance is a complex form of resistance that includes both regular resistance and reactive components, such as inductors and capacitors. The relationship between wattage, voltage, and frequency is governed by this impedance.
Step-by-Step Approach to Calculating Power
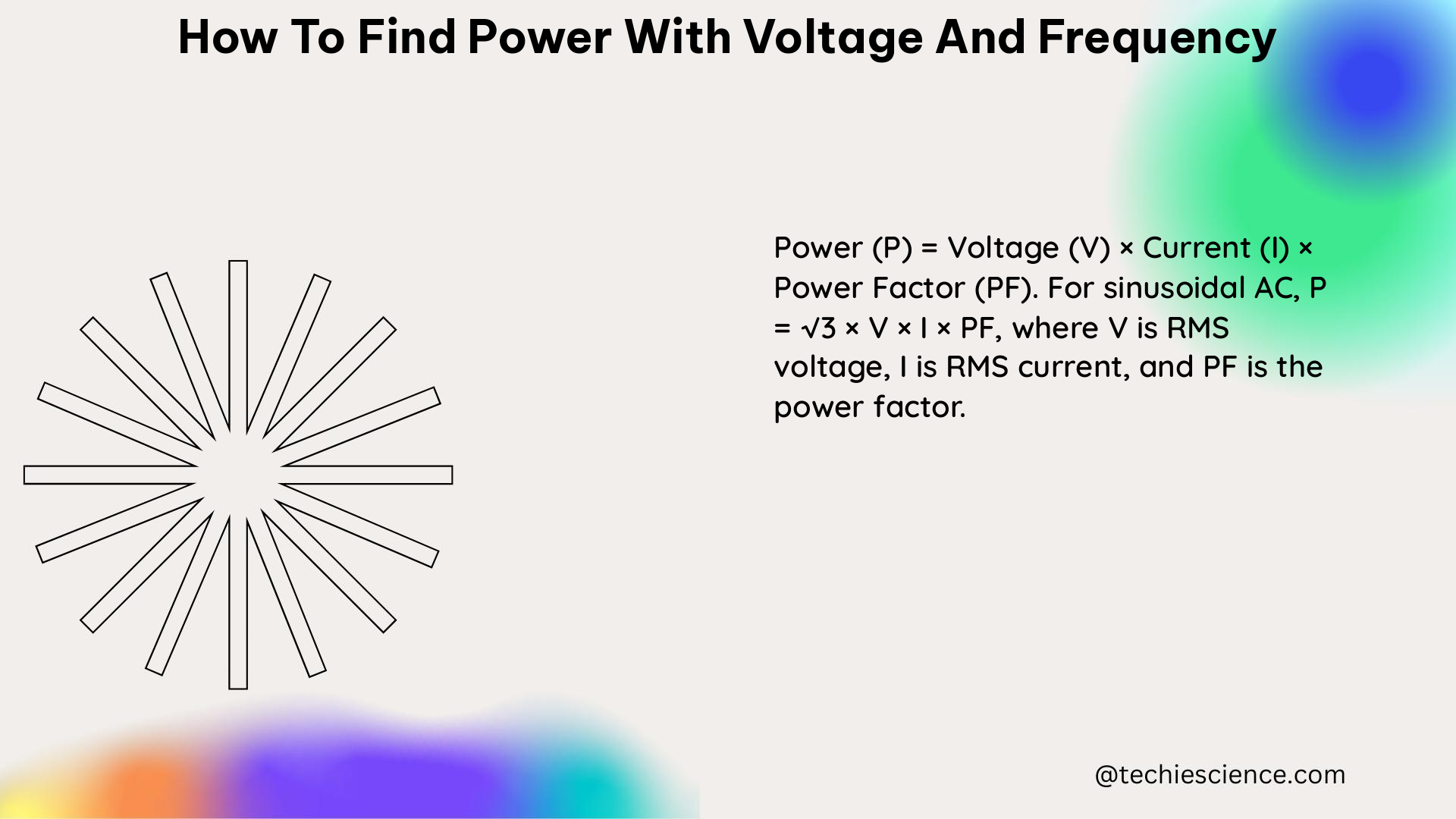
To calculate the power of a circuit using voltage and frequency, follow these steps:
-
Determine the Voltage (V) and Frequency (f) of the Circuit: Start by identifying the voltage and frequency values of the circuit you are working with. Refer to electrical schematics and operational requirements to obtain these values.
-
Calculate the Total Resistance (Rt) of the Circuit: Determine the total resistance of the circuit based on the number of resistors and how they are connected. If there is only one resistor, Rt is the value of that resistor. If there are multiple resistors, you need to determine if they are connected in series or parallel and use the appropriate formula to calculate the total resistance.
-
Calculate the Total Inductance (Lt) of the Circuit: Determine the total inductance of the circuit based on the number of inductors and how they are connected. If there is only one inductor, Lt is the value of that inductor. If there are multiple inductors, you need to determine if they are connected in series or parallel and use the appropriate formula to calculate the total inductance.
-
Calculate the Total Capacitance (Ct) of the Circuit: Determine the total capacitance of the circuit based on the number of capacitors and how they are connected. If there is only one capacitor, Ct is the value of that capacitor. If there are multiple capacitors, you need to determine if they are connected in series or parallel and use the appropriate formula to calculate the total capacitance.
-
Calculate the Reactance from the Inductor (XL): Use the formula XL = 2 * π * f * Lt to calculate the reactance from the inductor.
-
Calculate the Reactance Associated with the Capacitor (XC): Use the formula XC = 1/[2 * π * f * Ct] to calculate the reactance associated with the capacitor.
-
Calculate the Total Reactance (XT): Use the formula XT = XL – XC to calculate the total reactance.
-
Calculate the Impedance (Z): Use the formula Z = sqrt [Rt^2 + XT^2] to calculate the impedance of the circuit.
-
Calculate the Circuit Current Flow (I): Use the formula I = V/Z to calculate the current flow in the circuit.
-
Calculate the Power (P): Finally, use the formula P = V * I to calculate the power of the circuit.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the process:
Assume the following values:
– Voltage (V) = 120 volts
– Frequency (f) = 8 megahertz or 8 x 10^6 hertz
– Total Resistance (Rt) = 300 ohms
– Total Inductance (Lt) = 5 microhenries
– Total Capacitance (Ct) = 3 microfarads
Using these values, we can calculate the power as follows:
- XL = 2 * π * 8 x 10^6 * 5 x 10^-6 = 251.32 ohms
- XC = 1/(2 * π * 8 x 10^6 * 3 x 10^-6) = 1/150.79 = 0.0066 ohms
- XT = 251.32 – 0.0066 = 251.31 ohms
- Z = sqrt [300^2 + 251.31^2] = sqrt [90,000 + 63,156.7] = sqrt[153,156] = 391.35 ohms
- I = 120/391.35 = 0.3 amps
- P = 120 * 0.3 = 36 watts
Therefore, the power of the circuit is 36 watts.
Practical Applications and Considerations
The ability to calculate power using voltage and frequency has numerous practical applications in the field of electrical engineering. Some of the key applications include:
-
Power System Design: Accurately determining the power requirements of electrical systems is crucial for designing efficient and reliable power distribution networks.
-
Motor and Generator Efficiency: Analyzing the relationship between voltage, frequency, and power can help optimize the performance and efficiency of electric motors and generators.
-
Electronic Circuit Analysis: Understanding the power dynamics in electronic circuits is essential for designing and troubleshooting various electronic devices and systems.
-
Energy Efficiency Optimization: Calculating power using voltage and frequency can assist in identifying opportunities for improving energy efficiency in electrical systems and devices.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Analyzing the power output of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, requires a thorough understanding of the relationship between voltage, frequency, and power.
It’s important to note that the calculations presented in this guide assume a purely resistive load. In real-world scenarios, the presence of reactive components, such as inductors and capacitors, can introduce additional complexities. In such cases, you may need to consider the phase angle between voltage and current, as well as the power factor, to accurately determine the power.
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to calculate power using voltage and frequency is a crucial skill for electrical engineers and anyone working with electrical systems. By following the step-by-step approach outlined in this guide, you can confidently determine the power of a circuit, enabling you to design, analyze, and optimize electrical systems with greater precision and efficiency.
References
- Sciencing. (n.d.). How to Find Wattage with Voltage & Frequency. Retrieved from https://sciencing.com/how-to-find-wattage-with-voltage-frequency-13372439.html
- NCBI. (2021). Electrical Power and Energy Calculations. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8036391/
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Measured Voltage. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/measured-voltage

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.