In the realm of physics, understanding the relationship between power, velocity, and force is crucial for a wide range of applications, from engineering and transportation to sports and everyday life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating power using the formula P = F * v, where P represents power, F represents force, and v represents velocity.
The Fundamental Equation: P = F * v
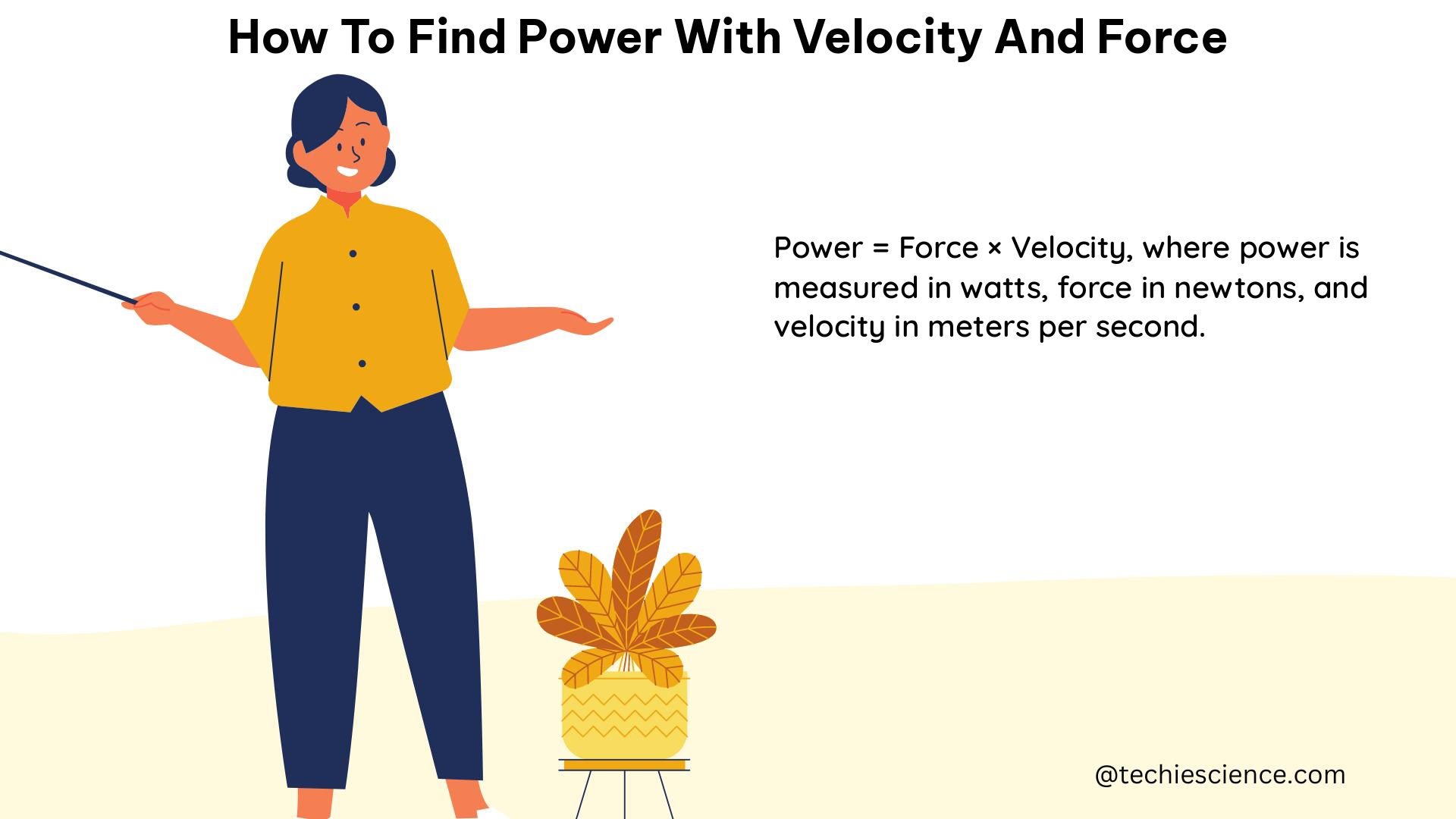
The formula P = F * v is the cornerstone of understanding how to calculate power using velocity and force. This equation states that power is equal to the product of force and velocity, and it is a fundamental principle in the study of mechanics and energy.
Defining the Variables
- Power (P): Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It is measured in watts (W) in the International System of Units (SI).
- Force (F): Force is the interaction that can cause an object to change its velocity, shape, or direction of motion. It is measured in newtons (N) in the SI system.
- Velocity (v): Velocity is the rate of change of an object’s position with respect to time. It is measured in meters per second (m/s) in the SI system.
Understanding the Relationship
The formula P = F * v demonstrates that power is directly proportional to both force and velocity. This means that as the force or velocity increases, the power output also increases proportionally. Conversely, if either the force or velocity decreases, the power output will decrease accordingly.
Practical Examples
Let’s explore some practical examples to illustrate the application of the power formula.
Example 1: Calculating Power for a Moving Object
Suppose we have an object with a mass of 10 kg, and we apply a force of 20 N to it. If the object has a velocity of 5 m/s, we can calculate the power as follows:
P = F * v
P = 20 N * 5 m/s
P = 100 W
In this example, the power output is 100 watts.
Example 2: Calculating Power for a Accelerating Car
Consider a car with a mass of 1500 kg, which accelerates from 0 to 60 mph in 8 seconds. To calculate the power output, we first need to convert the acceleration time and distance to SI units:
t = 8 s
v = 60 mph * 1609.34 m/mile / 3600 s/h = 26.82 m/s
a = v / t = 26.82 m/s / 8 s = 3.35 m/s^2
Next, we can calculate the force using the formula F = m * a:
F = 1500 kg * 3.35 m/s^2 = 5025 N
Finally, we can calculate the power using the formula P = F * v:
P = 5025 N * 26.82 m/s = 135157.5 W or 135.16 kW
In this example, the power output is 135.16 kW.
Example 3: Calculating Power for a Motor
To find the power output of a motor, we can use the formula P = W / t, where W is the work done and t is the time taken.
For instance, if a motor does 500 J of work in 0.5 s, we can calculate the power as follows:
P = W / t
P = 500 J / 0.5 s
P = 1000 W or 1 kW
In this example, the power output is 1 kW.
Importance of Consistent Units
When calculating power using the formula P = F * v, it is crucial to use consistent units. In the SI system, the unit of force is the newton (N), the unit of velocity is the meter per second (m/s), and the unit of power is the watt (W).
If you encounter non-SI units, it is necessary to convert them to their corresponding SI units before performing the calculations. This ensures that the final result is accurate and meaningful.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of calculating power with velocity and force is a fundamental skill in the field of physics. By understanding the formula P = F * v and its underlying principles, you can solve a wide range of problems related to power, energy, and motion.
Remember to always use consistent units, convert non-SI units when necessary, and practice applying the power formula to various scenarios. With a solid grasp of these concepts, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a proficient problem-solver in the realm of physics.
References
- Force & Velocity to Power Calculator – SensorsONE
- Power: Force and Velocity – YouTube
- How to Calculate Power Based on Force and Speed – Dummies
- How to Calculate the Average Power Exerted on an Object from Force and Velocity – Dummies
- Power (video) | Work and energy – Khan Academy

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.