Kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the energy an object possesses due to its motion. Determining the kinetic energy of an object is crucial in various fields, from engineering and transportation to sports and everyday life. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of calculating kinetic energy using the object’s speed and mass, providing you with a thorough understanding of the topic.
Understanding the Kinetic Energy Formula
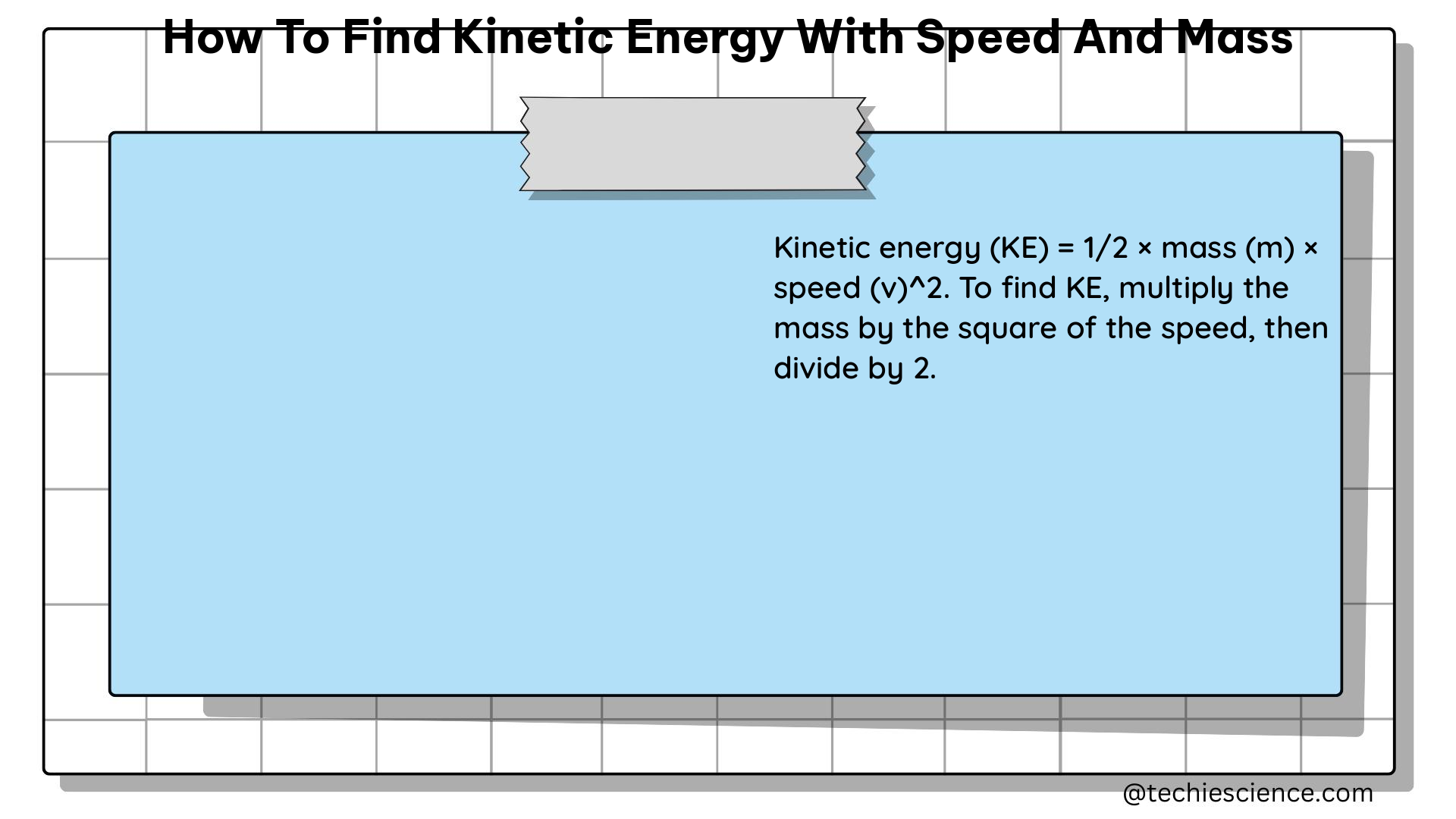
The formula to calculate kinetic energy (KE) is:
[ KE = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2 ]
Where:
– KE is the kinetic energy (measured in Joules, J)
– m is the mass of the object (measured in kilograms, kg)
– v is the velocity of the object (measured in meters per second, m/s)
This formula is derived from the principles of classical mechanics and is a fundamental relationship in physics. Let’s explore the implications and applications of this formula in detail.
Calculating Kinetic Energy Given Mass and Velocity
To find the kinetic energy of an object when you know its mass and velocity, simply plug the values into the formula:
[ KE = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2 ]
For example, if an object has a mass of 10 kg and a velocity of 5 m/s, the calculation would be:
[ KE = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times (5)^2 = 125 \text{ J} ]
This means the object has a kinetic energy of 125 Joules.
Calculating Mass Given Kinetic Energy and Velocity
Rearranging the kinetic energy formula, we can solve for the mass of an object if we know its kinetic energy and velocity:
[ m = \frac{2 \times KE}{v^2} ]
For example, if the kinetic energy of an object is 125 J and its velocity is 5 m/s, the calculation would be:
[ m = \frac{2 \times 125}{(5)^2} = 10 \text{ kg} ]
This means the object has a mass of 10 kilograms.
Calculating Velocity Given Kinetic Energy and Mass
Similarly, we can rearrange the kinetic energy formula to solve for the velocity of an object if we know its kinetic energy and mass:
[ v = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times KE}{m}} ]
For instance, if the kinetic energy of an object is 125 J and its mass is 10 kg, the calculation would be:
[ v = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 125}{\frac{1}{2} \times 10}} = 5 \text{ m/s} ]
This means the object has a velocity of 5 meters per second.
Graphical Representation of Kinetic Energy
Visualizing the relationships between kinetic energy, mass, and velocity can provide valuable insights. By plotting these variables on graphs, you can better understand the underlying principles and patterns.
Kinetic Energy vs. Mass
When plotting kinetic energy against mass for a constant velocity, you will observe a linear relationship. As the mass of the object increases, the kinetic energy increases proportionally.

Kinetic Energy vs. Velocity
On the other hand, when plotting kinetic energy against velocity for a constant mass, you will notice a quadratic relationship. As the velocity of the object increases, the kinetic energy increases exponentially.
These graphical representations can help you better understand the behavior of kinetic energy and its dependence on mass and velocity.
Online Kinetic Energy Calculators
To simplify the calculations and make them more accessible, various online kinetic energy calculators are available. These tools use the same formulas discussed in this guide and can be helpful for quick computations or verifying your own calculations.
Some popular online kinetic energy calculators include:
- Calculator Soup Kinetic Energy Calculator
- Omni Calculator Kinetic Energy Calculator
- Physics Classroom Kinetic Energy Calculator
These calculators can be particularly useful when you need to quickly determine the kinetic energy, mass, or velocity of an object without having to perform the calculations manually.
Practical Applications and Examples
Kinetic energy is a crucial concept in various fields, and understanding how to calculate it can be beneficial in many real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples of how kinetic energy calculations can be applied:
-
Transportation: Calculating the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle can help determine the force required to stop or accelerate the vehicle, which is essential for designing braking systems and safety features.
-
Sports and Athletics: Kinetic energy calculations are used in sports like archery, baseball, and golf to analyze the performance of athletes and equipment, such as the power of a bow or the speed of a baseball.
-
Engineering and Design: Kinetic energy considerations are crucial in the design of machinery, structures, and systems that involve moving parts, such as turbines, cranes, and roller coasters.
-
Collision Analysis: Understanding kinetic energy is essential in the analysis of collisions, as it helps determine the forces involved and the potential for damage or injury.
-
Energy Conversion: Kinetic energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as electrical energy in wind turbines or thermal energy in braking systems. Calculating the kinetic energy is crucial for designing and optimizing these energy conversion systems.
By mastering the concepts and calculations presented in this guide, you will be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of problems and applications involving kinetic energy.
Conclusion
Kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the energy an object possesses due to its motion. By understanding the kinetic energy formula and the relationships between mass, velocity, and kinetic energy, you can effectively calculate and analyze the kinetic energy of various objects.
This comprehensive guide has provided you with the necessary tools and knowledge to master the calculation of kinetic energy using speed and mass. Whether you’re a physics student, an engineer, or simply someone interested in understanding the physical world, the insights and examples presented here will empower you to confidently tackle kinetic energy-related problems and applications.
Remember, the key to success in understanding and applying kinetic energy principles lies in practice and a deep understanding of the underlying concepts. Utilize the formulas, graphs, and online calculators provided in this guide to reinforce your knowledge and develop your problem-solving skills.
Happy learning and exploring the fascinating world of kinetic energy!
References
- The Wonder of Science. (n.d.). MS-PS3-1: Kinetic Energy of an Object. Retrieved from https://thewonderofscience.com/msps31
- YouTube. (2022). F21g How to graph mass v kinetic energy and speed v kinetic energy data. Open SciEd 8.1. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SnntFBD12Wo
- Arbor Scientific. (n.d.). Kinetic Energy and Velocity Lab. Retrieved from https://www.arborsci.com/blogs/cool/kinetic-energy-and-velocity
- Calculator Soup. (2023). Kinetic Energy Calculator. Retrieved from https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/physics/kinetic.php
- ArcheryTalk. (2019). Kinetic energy, mass, velocity, momentum, online calculators—let’s get it right. Retrieved from https://www.archerytalk.com/threads/kinetic-energy-mass-velocity-momentum-online-calculators%E2%80%94lets-get-it-right.5720701/

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.